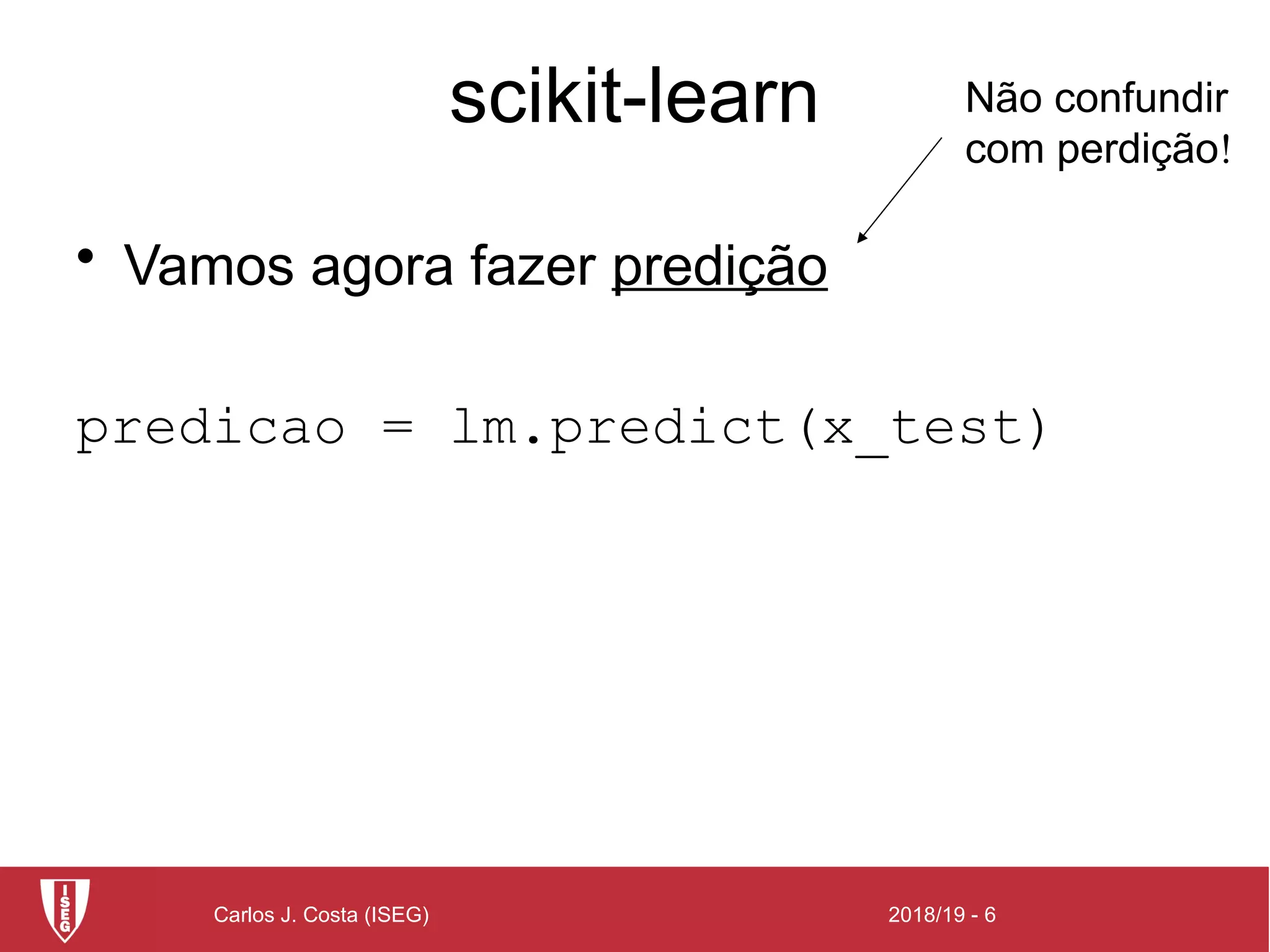
O documento apresenta a biblioteca scikit-learn para machine learning, destacando suas funcionalidades como algoritmos de classificação, regressão e clustering. Também descreve um exemplo prático de como dividir dados em conjuntos de treino e teste, criar um modelo de regressão e realizar previsões. Além disso, menciona a utilização do matplotlib para visualização de dados.