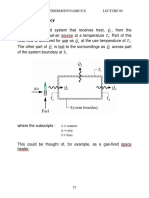
Synthesis of linkages Graphical Method
�Mechanism Synthesis
Design or creation of a mechanism to obtain a specified motion or force. Type Synthesis Given the required performance, what type of mechanism is suitable? Linkages, gears, cam and follower, belt and pulley and chain and sprocket. Number Synthesis How many links should the mechanism have? How many degrees of freedom are desired? Dimensional Synthesis Deals with determining the length of all links, gear diameter, cam profile.
2
�Mechanism Synthesis
Function Generation, Path Generation, Body Guidance Function Generation- Design requirement is that of causing
out put member to rotate, oscillate, or reciprocate according to a specified function of time or function of the input motion.
Path Generation- Refers to a problem in which a coupler
point is to generate a path having prescribed shape. i.e. circular arc, elliptical, or straight line
Body Guidance- Deals with moving an object from one
position to another. May be simple translation or combination of translation and rotation. i.e. Moving Bulldozer blades.
3
�Mechanism Synthesis
Dimensional and position Synthesis
Graphical Methods provide the designer with
a quick straightforward method but parameters cannot easily be manipulated to create new solutions.
Analytical Methods this approach is suitable
for automatic computation. Once a mechanism is modeled and coded for computer, parameters are easily manipulated to create new designs.
4
�Mechanism Synthesis
Graphical position Synthesis
�Two position synthesis of slider crank mechanism
Stroke B1B2 = 2* r2 Limiting positions B1 and B2 =
r3+r2 and r3- r2
For centered slider crank mechanism r3> r2 When r3= r2 Called as Isosceles slider crank mechanism
(a) Centered slider-crank mechanism.
6
�Two position synthesis of slider crank mechanism
Stroke B1B2 is always > 2* r2 Limiting positions B1 and B2 =
r3+r2 and r3- r2
Crank angle required to executive the forward stroke is different from that for the return stroke. This feature can be used in quick return mechanisms
General or offset slider-crank mechanism
7
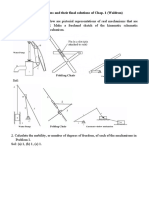
�Limiting Conditions 4 Bar Mechanism
Toggle positions of a crank-rocker mechanism. Links 2 and 3 become collinear.
�Two position synthesis of crank and rocker mechanism
Limiting positions B1 and B2 =
r3+r2 and r3- r2
Crank and coupler form a single straight line at each extreme position. Forward stroke- Crank executive the angle y , Rocker executive the angle Return stroke - Crank executive the angle 360 - y , Rocker executive the same angle
The extreme positions of the crank-and-rocker mechanism
9
�Mechanism Synthesis
Graphical Dimension Synthesis
10
�Graphical Synthesis; Quick Return Mechanism
4-Bar crank-Rocker mechanism Advance stroke mechanism operates under the load. Return stroke mechanism operates under no load. Q = time of advance stroke / time of return stroke Q>1 quick-return mechanism
11
�Graphical Synthesis; Quick Return Mechanism, Crank and rocker
Equation for timer ratio of the forward and backward motions of the rocker is
1800 + Q= 1800
12
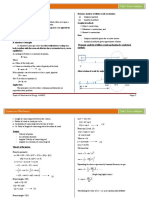
�Quick Return Mechanism
Consider the two toggle positions of a crank-rocker mechanism.
C
B2
3 2 4
B1
A1 O4
A2
O2
Locate point C to satisfy the following two conditions; 1) C is on extension of line A2B2. 2) O2C = O2B1 = r2 + r3
B2C = r2 +r3 - (r3 r2) = 2r2
13
�Quick Return Mechanism
B2
B1
A1 O4
A2
O2 180 , Return stroke
Q = advance / Return = (180 + ) / (180 ), Time Ratio
14
�Synthesis of a Quick Return Mechanism
Known or selected;
Rocker angle, Rocker length, r4 Time ratio, Q
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Select the location for the fixed pivot point, O4. Draw the two toggle positions, knowing r4 and . Calculate the angle from known time ratio Q = (180 + ) / (180 ) Construct an arbitrary line XX through point B1. Construct the line YY through point B2 making an angle with XX. The intersection of XX and YY is the other fixed pivot, O2 Y B2
Determine; r1, r2, r3
B1 X
O2 X
O4
6.
15
�Synthesis of a Quick Return Mechanism
C 7. 8. 9. Locate point C on YY so O2C = O2 B1. Measure length B2 C, Link 2 = r2 = (B2 C) /2 Calculate the length of link 3, AB = r3 = O2 B1 r2 B2 2r2 B1 X Y
B O2 X A A2 O2 O4 Y r2 A1 O4
10. Verify the motion of the mechanism and check the minimum transmission angle.
16
�Two- Position synthesis of crank-and-rocker mechanisms
The extreme positions of the crank-and rocker-mechanism
17
�Crank rocker mechanism Hall and Soni method
Layout showing all possible locations of B1 and B2.
Determination of the link lengths for one of the possible crankrocker mechanisms 18
�Draw O2O4
1. Locate point C defined by angle (f/2 a)and f/2 2. Locate point C symmetrical about O2O4 3. Then using C as centre and CO2 as radius draw circular arc from O2 showing locus of B2 4. Using C as centre and CO2 as radius draw circular arc from O2 showing locus of B1
Layout showing all possible locations of B1 and B2.
19
�Determination of the link lengths for one of the possible crankrocker mechanisms
1. Choose any point B1 on the locus of B1 2. Draw an arc about O4 to locate B2 on the locus of the B2 3. Once points B1 and B2 are defined methods of the preceding section are used to locate A1 and A2 together with r2 and r3
20
�Graphical Synthesis Motion Generation Mechanism
Two positions, coupler as the output
1. 2. 3. Draw the link AB in its two desired positions, A1B1 and A2B2 Connect A1 to A2 and B1 to B2. Draw two lines perpendicular to A1 A2 and B1B2 at the midpoint (midnormals). Select two fixed pivot points, O2 and O4, anywhere on the two midnormals. Measure the length of all links, O2A = link 2, AB = link 3, O4B = link 4 and O2 O4 = link 1 B1 A1 A2 B2 O2 O4
4.
5.
21
�Graphical Synthesis Motion Generation Mechanism
Three positions, coupler as the output
Same procedure as for two positions. 1. 2. Draw the link AB in three desired positions. Draw the midnormals to A1A2 and A2A3, the intersection locates the fixed pivot point O2. Same for point B to obtain second pivot point O4. Check the accuracy of the mechanism, Grashof condition and the transmission angle. B3 4. Change the second position of link AB to vary the locations of the fixed points
22
A2 A1 B1 A3
O2 B2
O4
3.