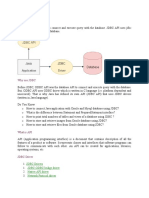
04/04/11 6:03 PM Questions
on
Data
Structure
1. What is a Data Structure? a. A data structure is a way of organizing data that considers not only the items stored, but also their relationship to each other. Advance knowledge about the relationship between data items allows designing of efficient algorithms for the manipulation of data. 2. In RDBMS, what is the efficient data structure used in the internal storage representation? a. B+ tree. 3. Minimum number of queues needed to implement the priority queue? a. Two. One queue is used for actual storing of data and another for storing priorities. 4. What is the data structures used to perform recursion? a. Stack. Because of its LIFO (Last In First Out) property it remembers its 'caller' so knows whom to return when the function has to return. 5. How to find the number of possible tree in the given tree. a. The number of possible tree = (2 power of n) - n.
�04/04/11 6:03 PM Questions on Algorithms
1. What is hashing? Hashing is a way retrieving records from memory in faster way. Record is inserted into memory by using hash function(division, midsqure,folding,digit analysis)and also records are retrieved using same hash function. 2. List out the areas in which data structures are applied extensively? 1. Compiler Design, Operating System, Database Management System, Statistical analysis package, Numerical Analysis, Graphics, Artificial Intelligence, Simulation
2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
3. In tree construction which is the suitable efficient data structure? Linked list is the efficient data structure. 4. Whether Linked List is linear or Non-linear data structure? According to Access strategies Linked list is a linear one. According to Storage Linked List is a Non-linear one. 5. Is it possible to implement trees using arrays ? If yes, how?
Yes, it is possible. Here is an example of implementing a binary tree: Consider an attay : a[n]; Place the root in first position. and let the current position to be i = 0; place left node at the position: 2i+1 place right node at the position: 2i+2.
�Repeat these steps.
�04/04/11 6:03 PM Questions on Java Basics 1. What are the new features introduced in Java 5? Generics, Enhanced for Loop, Autoboxing/Unboxing, TypesafeEnums, Variable Arguments, Static Import, Annotations. 2. Relationship between JRE& JVM. They both are the same. 3. What is the difference between an Interface and an Abstract class? An abstract class can have instance methods that implement a default behavior. An Interface can only declare constants and instance methods, but cannot implement default behavior and all methods are implicitly abstract. 4. What is the purpose of garbage collection in Java, and when is it used? The purpose of garbage collection is to identify and discard objects that are no longer needed by a program so that their resources can be reclaimed and reused. 5. What is the difference between StringBuffer and StringBuilder class? StringBuilder is a feature of Java 5. Methods in StringBuffer are Synchronized& thread safe. Methods in StringBuilder are not Synchronized& not thread safe. If you want faster access use StringBulder. 6. What is ClassDefNotFoundException and NoClassDefFoundError and explain differences between these two? Given a class A. A ClassNotFoundException means that the classloader cannot load class A. A ClassDefNotFoundError means that the classloader can load class A but cannot instantiate it because it cannot load the other classes that class A depend on.
�7. Tell me the differences between enumeration and iteration?Which can use where in realtime? Enumeration acts as Read-only interface because it has the methods only to travels and fetch the objects where as using Iterator we can manipulate the objects also like adding and removing the objects. So Enumeration is used when ever we want to make Collection objects as Read-only.
8. What is the order of initialization of variables in Java 9. Static block variables initialize at first Static method of variables initialize second Static variables initialize third Constructor variables initialize at fourth and then Instance Variables initialize at last.
What is static in java?
Static means one per class, not one for each object no matter how many instance of a class might exist. This means that you can use them without creating an instance of a class. Static methods are attached to a class, not an object. 10. What is final? A final class can't be extended i.e., final class may not be sub classed. A final method can't be overridden when its class is inherited. You can't change value of a final variable (is a constant).
�11. State the significance of public, private, protected, default modifiers both singly and in combination and state the effect of package relationships on declared items qualified by these modifiers. public : Public class is visible in other packages, field is visible everywhere (class must be public too) private : Private variables or methods may be used only by an instance of the same class that declares the variable or method, A private feature may only be accessed by the class that owns the feature. protected : Is available to all classes in the same package and also available to all subclasses of the class that owns the protected feature. This access is provided even to subclasses that reside in a different package from the class that owns the protected feature. default :What you get by default i.e., without any access modifier (i.e., public private or protected).It means that it is visible to all within a particular package.
12.
What are transient variables in java? Transient variables are variable that cannot be serialized.
13.
What is synchronization? Synchronization is the ability to control the access of multiple threads to shared resources. Synchronization stops multithreading. With synchronization, at a time only one thread will be able to access a shared resource. 14.
What
is
a
daemon
thread?
These
are
the
threads
which
can
run
without
user
intervention.
The
JVM
can
exit
when
there
are
daemon
thread
by
killing
them
abruptly.
�15.
What
is
mutable
object
and
immutable
object?
If
a
object
value
is
changeable
then
we
can
call
it
as
Mutable
object.
(Ex.,
StringBuffer,
)
If
you
are
not
allowed
to
change
the
value
of
an
object,
it
is
immutable
object.
(Ex.,
String,
Integer,
Float,
)
16.
What
are
the
approaches
that
you
will
follow
for
making
a
program
very
efficient?
By
avoiding
too
much
of
static
methods
avoiding
the
excessive
and
unnecessary
use
of
synchronized
methods
Selection
of
related
classes
based
on
the
application
(meaning
synchronized
classes
for
multiuser
and
non-synchronized
classes
for
single
user)
Usage
of
appropriate
design
patterns
Using
cache
methodologies
for
remote
invocations
Avoiding
creation
of
variables
within
a
loop
and
lot
more.
17. What is singleton? It is one of the design pattern. This falls in the creational pattern of the design pattern. There will be only one instance for that entire JVM. You can achieve this by having the private constructor in the class. For eg., public class Singleton { private static final Singleton s = new Singleton(); private Singleton() { } public static Singleton getInstance() { return s; } // all non static methods } 18. Is
null
a
keyword?
The
null
value
is
not
a
keyword.
19.
Is
sizeof
a
keyword?
The
sizeof
operator
is
not
a
keyword.
20.
Does
garbage
collection
guarantee
that
a
program
will
not
run
out
of
memory?
Garbage
collection
does
not
guarantee
that
a
program
will
not
run
out
of
memory.
It
is
possible
for
programs
to
use
up
memory
resources
faster
than
they
are
�garbage
collected.
It
is
also
possible
for
programs
to
create
objects
that
are
not
subject
to
garbage
collection.
21.
What
is
the
purpose
of
the
Runtime
class?
The
purpose
of
the
Runtime
class
is
to
provide
access
to
the
Java
runtime
system.
22.
Which
class
is
extended
by
all
other
classes?
The
Object
class
is
extended
by
all
other
classes.
23.
What
is
the
difference
between
the
Reader/Writer
class
hierarchy
and
the
InputStream/OutputStream
class
hierarchy?
The
Reader/Writer
class
hierarchy
is
character-oriented,
and
the
InputStream/OutputStream
class
hierarchy
is
byte-oriented.
24.
What
is
casting?
There
are
two
types
of
casting,
casting
between
primitive
numeric
types
and
casting
between
object
references.
Casting
between
numeric
types
is
used
to
convert
larger
values,
such
as
double
values,
to
smaller
values,
such
as
byte
values.
Casting
between
object
references
is
used
to
refer
to
an
object
by
a
compatible
class,
interface,
or
array
type
reference.
25.
What
restrictions
are
placed
on
method
overriding?
Overridden
methods
must
have
the
same
name,
argument
list,
and
return
type.
The
overriding
method
may
not
limit
the
access
of
the
method
it
overrides.
The
overriding
method
may
not
throw
any
exceptions
that
may
not
be
thrown
by
the
overridden
method.
26.
What
are
the
disadvantages
of
using
threads?
DeadLock.
27.
What
is
the
difference
between
instanceof
and
isInstance?
�
instanceof
is
used
to
check
to
see
if
an
object
can
be
cast
into
a
specified
type
without
throwing
a
cast
class
exception.
isInstance()
determines
if
the
specified
object
is
assignment-compatible
with
the
object
represented
by
this
Class.
This
method
is
the
dynamic
equivalent
of
the
Java
language
instanceof
operator.
The
method
returns
true
if
the
specified
Object
argument
is
nonnull
and
can
be
cast
to
the
reference
type
represented
by
this
Class
object
without
raising
a
ClassCastException.
It
returns
false
otherwise.