0% found this document useful (0 votes)
148 views1 pagePointers and Operators
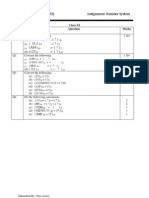
This document discusses pointers to classes in C++. It provides an example of a base class A with data members and methods, including an initialize method and display method. An object of class A is created, and a pointer variable is used to point to the object. The -> operator is used to access members of the object being pointed to, and the . operator is used to access members when dereferencing the pointer with *. It also provides a summary of common pointer operators like *, &, ., and -> and notes that pointers to structures work the same way as pointers to classes.
Uploaded by
nita23arora2321Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
148 views1 pagePointers and Operators
This document discusses pointers to classes in C++. It provides an example of a base class A with data members and methods, including an initialize method and display method. An object of class A is created, and a pointer variable is used to point to the object. The -> operator is used to access members of the object being pointed to, and the . operator is used to access members when dereferencing the pointer with *. It also provides a summary of common pointer operators like *, &, ., and -> and notes that pointers to structures work the same way as pointers to classes.
Uploaded by
nita23arora2321Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 1