World Wide Web: HTTP
Objectives
Upon completion you will be able to: Understand the components of a browser and a server Understand the function of the URL and cookies Understand how HTML is related to static documents Understand how CGI is related to dynamic documents Understand how Java is related to active documents Know how HTTP accesses data on the WWW
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
�1 ARCHITECTURE
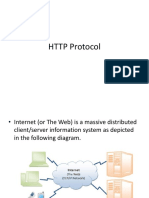
The WWW is a distributed client-server service, in which a client using a browser can access a service using a server. The service provided is distributed over many locations called sites.
The topics discussed in this section include: Client (Browser) Server Uniform Resource Locator (URL) Cookies
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
�Figure 1
Architecture of WWW
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
�Figure 2
Browser
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
�Figure 3
URL
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
�2 WEB DOCUMENTS
The documents in the WWW can be grouped into three broad categories: static, dynamic, and active. The category is based on the time the contents of the document are determined.
The topics discussed in this section include: Static Documents Dynamic Documents Active Documents
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
�Figure 4
Static document
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
�Figure 5
Boldface tags
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
�Figure 6
Effect of boldface tags
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
�Figure 7
Beginning and ending tags
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
10
�Figure 8
Dynamic document using CGI
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
11
�Figure 9
Dynamic document using server-site script
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
12
�Note: Dynamic documents are sometimes referred to as server-site dynamic documents.
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
13
�Figure 10
Active document using Java applet
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
14
�Figure 11
Active document using client-site script
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
15
�Note: Active documents are sometimes referred to as client-site dynamic documents.
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
16
�3 HTTP
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is a protocol used mainly to access data on the World Wide Web. HTTP functions like a combination of FTP and SMTP.
The topics discussed in this section include: HTTP Transaction Persistent versus Nonpersistent Connection Proxy Server
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
17
�Note: HTTP uses the services of TCP on well-known port 80.
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
18
�Figure 12
HTTP transaction
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
19
�Figure 13
Request and response messages
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
20
�Figure 14
Request and status lines
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
21
�Table 1 Methods
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
22
�Table 2 Status codes
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
23
�Table 2 Status codes (continued)
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
24
�Figure 15
Header format
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
25
�Table 3 General headers
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
26
�Table 4 Request headers
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
27
�Table 5 Response headers
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
28
�Table 6 Entity headers
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
29