PICAXE Powered CW Beacons
CW (Continuous Wave) is an electromagnetic (radio) wave of constant amplitude and frequency and also the name given to an early form of radio transmission where a radio frequency carrier wave is switched on/off (in a specific pattern) to communicate information. It is the successor to Spark Gap (Damped Wave) radio communications and the precursor to AM (Amplitude Modulation) radio. The two most well-known and still in use forms of CW are the Morse code and [Feld] Hellschreiber or just Feld Hell. Over the past few months, Ive made contact with many Hams who have written various radio programs for MCUs (Micro Controller Units) such as the PICAXE, BASIC Stamp and Arduino. They have all graciously allowed others to use their original source code (with credit given where credit is due) and modify it. After some searching, a Morse code PICAXE BASIC and standard Feld Hell Arduino C programs were found; each could key a CW transmitter and send a repeating beacon. As a former C programmer, it wasnt hard to translate the C to BASIC; my low-power (QRP) CW transmitter could send both types of CW transmissions!
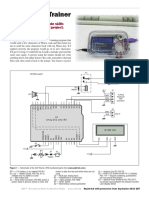
Pictured (above) is the Revolution Education Schools Experimenter Kit (right), optional Morse code speed control 10K pot (center) with simple NPN transistor switch (upper center) to key the CW transmitter (I use Pixie II type minimalist QRP transceivers but you can use any CW rig). The added female SIP header (top of Schools Kit) makes it easy to connect off-board components.
�CW Keying Interface (with optional Morse code speed control) Both the Morse code and Feld Hell CW beacons use the same hardware except that the speed control potentiometer that isnt used for Feld Hell; the only thing that changes is the PICAXE BASIC program loaded into the PICAXE 08M2 (or older 08M) MCU. The circuit that connects any MCU platform to my QRP transmitter is just a simple NPN transistor (2N2222 type) and a 1K resistor switched on and off by an output port from the MCU. For Morse code CW, you plug into the normal hand key jack; a 2N7000 MOSFET (N-channel) can be used instead or you can parallel two and increase the current handling capability of the switching circuit. Standard Feld Hell CW requires bypassing the transmit/receive offsets and keying/shaping filters by directly keying of the PA (Power Amplifier) or the buffer stage before it (depends on the complexity of the CW transmitter) as we require an OOK (On-Off Keying) rate of 8.125ms. This produces hard keying and harmonics that the PAs low pass or band pass filter will reduce to an acceptable level.
�Pictorial/schematic of the Schools Kit board (previous page) and added circuitry for the CW transmitter interface. Vdd is connected to 4.5 to 5.0V DC and Vss connected 0V or ground. A 10socket SIP header (H1) was added to make it easier to connect off board circuits. The optional Morse code speed control can be omitted for Feld Hell (its transmitted at a fixed speed equivalent to 25 WPM). The potentiometer is as an example of using 8-bt ADC (Analogue to Digital Conversion) to control MCUs or other devices attached to it. The included PICAXE BASIC CW programs (Morse code and Feld Hell) are well-documented and easy to modify design for use with Revolution Educations Schools Experimenter (PICAXE 08M/08M2) Kit and a solderless breadboard. This should help you to get started in using MCUs for simple Amateur Radio applications. The program is easy to convert other MCU platforms and they are all very similar and except for the programming language (Assembler, C or BASIC, etc.). Below is the Lil Squall II minimalist QRPp (< 1 watt) transceiver based on the famous Pixie II design by Rex, W1REX. Its a DCR (Direction Conversion Receiver) using a Colpitts crystal controlled RF (Radio Frequency) oscillator with a single PA transistor stage that acts as both as transmitter and receiver mixer. The oscillator provides the RF carrier thats keyed on/off by the PA. Received RF is mixed with the oscillators signal (by the PA) to produce a 600 Hz tone thats fed to an LM386 op amp audio amplifier. Its a fun kit to build and just great for experimentation (add side tone, variable frequency, audio filter, etc.)!
�Feld Hell Hello World! CW Beacon Since Morse code CW is understand and known, Ill just mention Feld Hell CW. Below is a photo of Flidigi copying my Lil Squalls transmission of HELLO WORLD! using a dummy load antenna, for testing purposes. My Schools Experiment Kit 08M2 was programmed (download the software from my website) to send a repeating Fell Hell CW beacon. Note: Contrary to popular misconception, CW doesnt mean Morse code; the Morse code is not a form of transmission but a method of encoding/decoding data. For Feld Hell (unlike Morse code) the PA is directly keyed or through the preceding buffer stage, but you must bypass any RIT/XIT and keying/shaping circuits! The RF carrier must be rapidly keyed on/off at a rate of 8.125ms to transmit a sequentially pattern of 1s and 0s (mark/space, high/low, etc.). In the picture below, an HF radio is receiving the signal and feeding a laptop/decoding software via an audio patch cord. The printed text is wavy as theres no way to fine tune (to hundredths of a Hertz) with an MCU as you with a microcomputer, however receiving stations have to deal with other issues like fading/atmospheric noise that can mangle the signal far more. Feld Hell has no synchronization between transmitting/receiving stations and is called a fuzzy logic data mode as is the Morse code. Both are pseudo-digital data modes that rely solely on the human eye/brain or ear/brain to recognize and understand patterns that we call language! Even if some of the patterns are missing, we can usually fill in the blanks using our fuzzy logic and approximation (guessing) abilities. You can create a Feld Hell character set any language (real or artificial): English, Chinese or even Klingon! Thats the beauty and power of fuzzy logic digital modes that machines will never be able to master!
�My MCU Prototyping Platform Converted 300-in-1 Electronic Project Lab made by removing the radio and other less used parts to mount PICAXE, Parallax and Arduino MCU development boards (and extra solderless breadboard); 3M mounting tape (great stuff!) securely holds the boards. A netbook (for portable programming) completes the entire package and everything runs off of battery power! Better yet, all the MCU development software is FREE!
This type of electronics kit is still widely available and relatively inexpensive. The speaker slots (upper right) just happen to be excellent holders for small pc boards! The larger breadboard has a header that provides various DC voltages from 1.5 to 9V DC (using 6 internally stored AA cells); 5V DC is required for the MCU prototyping boards. The Parallax BASIC Stamp Homework Board is unique in using a 9V battery (it lays flat on the board) that feeds on onboard 5V regulator and it also has a built-in mini-breadboard. Everything is easily interconnected using DuPont cable connectors (male-female, male-male and female-female).
�Using the Software Note: All hardware references are made specific to Revolution Educations Schools Experimenter Kit. PICAXE Morse code CW Program The variable WPM can be used to set a fixed Morse code transmission speed if you dont want to use the variable speed control potentiometer. The default speed is set to 20 (wpm). To use the speed control, uncomment the block of code starting with readADC 4 WPM. The other variable that you can optional change is the CW_Tone (0 to 128). The new 08M2 chips have a very square wave and raspy sounding tone as compared to the old 08M that had a more sine wave sounding tone. A simple RC filter (series resistor, shunt capacitor) inserted into the Piezo speaker line could be used to smooth out the tone. Use the Schools Kit DIP switch 2 to turn the Piezo speaker on and off for monitoring your beacon (the green LED is wired in parallel and will flash in sync). Lastly, you need to add your beacon encoded text to the eeprom memory and set the Beacon_Length variable. The red LED (port 0) flashes in sync with the Morse code transmission and the transistor switch circuitry also shares port 0 and will turn your transmitter on and off. Thats it! PICAXE Feld Hell CW Program Preferably, you want to use the simplest CW transmitter to make interfacing easier. As noted in this article, you must bypass the receive/transmit offset, keying and shaping circuits and key the PA directly, or the buffer stage before it. Feld Hell requires 8.125ms OOK of the transmitter and this will cause hard keying. The transmitters low pass or band pass filter is used to remove the harmonics produce. With this program you just setup your eeprom beacon text string and Beacon_Length variable. Feld Hell is transmitted at a fixed rate and the speed control potentiometer is ignored and not required. The Schools Kit red LED (port 0) flashes in sync with the Feld Hell transmission and the transistor switch circuitry also shares port 0 and will turn your transmitter on and off. Thats it! You cant decipher Feld Hell by ear so theres no speaker output available but you can use the same monitoring setup previously described. Thats it! Obviously, a transistor/MOSFET switch circuit can be used to control other on/off devices (hint: switch a relay on/off connected to a 120V device), so feel free to modify the programs and experiment. You can connect wireless devices to the PICAXE and remotely control devices because if you can transmit a signal to a device you certainly can receive one!
73, Robert, VA3ROM http://my.tbaytel.net/va3rom November 2012
�References and Resources
Revolution Education Schools Experimenter Kit
<www.pixace.com> <www.picaxe.com/docs/axe092.pdf>
Programming and Customizing the PICAXE Microcontroller, David Lincoln <http://lincsoft.com/Lincsoft/Code_download.html> Getting Started with the Schools Experiment Kits <www.microzed.com.au/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=78&products_id=276> PICAXE Microcontroller Projects for the Evil Genius, Ron Hackett <http://jrhackett.net> Arduino Parallax BASIC Stamp Lil Squall II Transceiver Pixie II (more info) <www.arduino.cc> <www.parallax.com/Home/tabid/36/Default.aspx> <www.qrpme.com> http://www.kenneke.com/jon/pixie/ www.al7fs.us/AL7FS2.html http://homepage.ntlworld.com/g4kki.william/pixie_ii_is.htm Canadian MCU & Electronic Kits Companies Aztec MCU Prototyping <www.aztecmcu.com>
Cana Kits (300-in-1 Electronic Project Lab) <www.canakit.com/electronic-kits> HVW Technologies Robot Shop SOLARBOTICS <www.hvwtech.com> <www.robotshop.com/ca> <www.solarbotics.com>