AM Syllabus: (2013): Physics
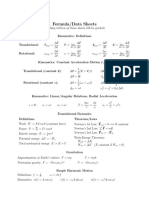
Data and Formulae Booklet The following equations and formulae may be useful in answering some of the questions in the examination. Uniformly accelerated motion: Useful formulae:
v = u + at 1 s = ut + at 2 2 v 2 = u 2 + 2as u+v s= t 2
Ray optics: Refractive index: n1 sin 1 = n 2 sin 2
1
n2 =
sin 1 v1 = sin 2 v 2
1 n3
= 1 n2 . 2 n3
Thin lenses:
Mechanics: Newtons second law: Power: Momentum:
F= d (mv) dt
1 1 1 = + (real is positive) f u v 1 1 1 = (Cartesian) f v u
P = Fv p = mv
Magnification:
m=
v hi = (real is positive) u ho h v = i (Cartesian) u ho
m=
Current electricity: Circular motion and rotational dynamics: Angular speed: Angular acceleration: Centripetal force: Torque: Work done in rotation:
d = dt d = = dt mv 2 F= r = I
Current: Resistors in series: Resistors in parallel: Power: Resistivity:
I = nAve RTOTAL = R1 + R2 +
1
RTOTAL =
v r a r
1 1 + + ... R1 R 2
P = IV
1 2
I2
RA l
R R 0 R 0
Temperature coefficient: = Alternating current:
Simple harmonic motion: Displacement: Velocity:
x = xo sin(t + ) v = xo cos(t + )
v = xo 2 x 2
For sinusoidal alternating current:
I = Io sin2ft
Root mean square for sinusoidal alternating I V I rms = 0 ; V rms = 0 current and voltage: 2 2 Reactance: X L = 2fL ; X C = 1 (2fC )
Acceleration: Period:
a = 2 x 1 2 T = = f
m k
Mass on a light spring: T = 2
�AM Syllabus: (2013): Physics
Stationary waves: Speed of waves on strings: Wave motion: Two slit interference: Diffraction grating: Single slit diffraction: Diffraction of circular aperture:
s= v= T
Capacitance: Capacitance of parallel plates: C = Capacitors in parallel:
0 r A
Capacitors in series: Energy stored: Charging:
d d sin = n
d C = C1 + C2 + 1 1 1 = + + ... C C1 C 2 1 W = CV 2 2
sin = 1.22
t Q = Q0 1 e RC
Discharging:
Q = Q0 e
RC
Fields: Electric field strength: Uniform field: Force between point charges:
E= F dV = dr +q F V E= = +q d
Inductance: Mutual inductance: Self inductance: Energy stored:
E dI dt E L= dI dt 1 2 W = LI 2 M =
4 0 r 2 Electric field strength of a point charge: Q E= 4 0 r 2 M 1M 2 r2 Q V= 4 0 r GM VG = r F =G
W = QV
F=
Q1Q 2
Electromagnetism:
Force between point masses: Electric potential: Gravitational potential: Work:
Force on wire:
F = BIl
F = BQv
Torque on a rectangular coil: = BANI Force on moving charge: Magnetic flux: Field inside a solenoid:
= BA
B = 0 r nI I
Field near a long straight wire: B = 0 Induced emf:
2 r
d dt
E = N
Emf induced in a moving conductor:
E = Blv
Simple alternator emf:
V = V0 sin( t + ) BI nQt
Hall voltage:
VH =
�AM Syllabus: (2013): Physics
Temperature:
Materials:
P K Ptr
Temperature (K): T = 273.16 Celsius scale:
Hooke's law: Stress: Strain: Young's modulus: Energy stored in a stretched wire:
(C) = T (K) 273.15 K
F = kx F = A l = l Y=
E=1 k l ) 2 (
2
First and second laws of thermodynamics:
Heat transfer:
First law of thermodynamics: Ideal heat engine:
U = Q + W
Thermal conduction:
= 1
Tc Th
dQ d = kA dt dx
Gases: Ideal gas equation:
PV = nRT
Quantum phenomena:
Quantum energy: Mass-energy
E = hf E = mc2
1 hf = + mv2 2 max hf = E2 E1
Kinetic theory of an ideal gas:
PV =
Boltzmann's constant: k =
1 Nm < c 2 > 3
Photoelectric effect: Energy levels: De Broglie wavelength:
Radioactivity:
R NA
Principal molar heat capacities of an ideal gas:
h mv
=
Adiabatic process:
CP ; CP CV = R CV
Decay rate:
PV = Constant
Half-life:
dN = N ; A = N dt
N = No et T1 =
2
ln 2
Absorption law for gamma radiation:
I = Io ed
�AM Syllabus: (2013): Physics
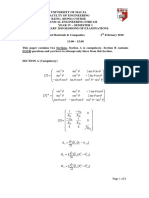
Mathematical Formulae:
Surface area of a sphere: Volume of a sphere: Surface area of a cylinder: Volume of a cylinder: Logarithms:
S = 4 r 2 V=
4 3 r 3
S = 2 rh + 2 r 2 V = r 2h
ln x n = n ln x ln e kx = kx
( )
( )
Equation of a straight line:
y = mx + c
Relationship between cosine and sine: sin ( 90 ) = cos Small angles:
sin tan (in radians) cos 1
The following constants may be useful in answering some of the questions in the examination. Acceleration of free fall on and near the Earths surface g = 9.81 m s2 Gravitational field strength on and near the Earths surface g = 9.81 N kg1 Boltzmann constant k = 1.38 1023 J K1 Molar gas constant R = 8.31 J K1 mol1 Avogadros constant NA = 6.02 1023 mol1 Coulombs law constant k = 1/(4o) = 8.99 109 N m2 C2 Charge of an electron e = 1.60 1019 C Mass of an electron me = 9.11 1031 kg Electronvolt 1 eV = 1.60 1019 J Gravitational constant G = 6.67 1011 N m2 kg2 Permittivity of free space o = 8.85 1012 F m1 Permeability of free space o = 4 107 H m1 Planck constant h = 6.63 1034 J s Speed of light in a vacuum c = 3.00 108 m s1 Unified atomic mass unit u = 1.66 1027 kg