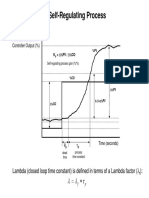
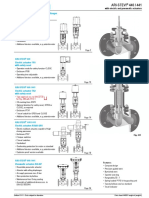
FIDEC Training Center
Control Valves
�Category of Valves
Valves Manual valves Automated valves
These valves are operated automatically.
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Modulating valves Self Operated valves On-Off valves
On-Off valves just put the flow on or off . On the other word, let the flow medium run or stop. There types of valves are mainly used for sequential control or rough control like air conditioning. Self-operated valves operate receiving energy from fluid pressure of fluid temperature. It has high responsibility but generally is not good at accuracy.
Modulating valves are moreover categorized into 2 types.
Control valves
Control valves operate receiving energy from compressed air, electric power, etc. used with controllers and sensors. Control valves and related equipment realizes most accurate control.
Control Valves
�Introduction
What Is A Control Valve? The control valve manipulates a flowing fluid, such as gas, steam, water, or chemical compounds, to compensate for the load disturbance and keep the regulated process variable as close as possible to the desired set point. The control valve assembly typically consists of the: * Valve body * The internal trim parts * An actuator to provide the motive power to operate the valve * A variety of additional valve accessories, which can include positioners, transducers, supply pressure regulators, manual operators, snubbers, or limit switches.
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Roles of control valves
Process parameters Flow Pressure Level Temp. Sensor Orifice, Flow meter Press. Transmitter Level Transmitter Temperature Transmitter
Orifice
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valve
Controller
4-20mA 4-20mA D.P. Transmitter
Control Valves
�Example of process control
Flow control FC PC Boiler Boiler feed pomp Minimum flow control valve Level control Reactor LC Heat exchanger T bi b Turbine bypass valve l Temperature control TC Pressure control Boiler
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Turbine
Control Valves
�Introduction
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Typical Valve Assembly
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Component parts
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Actuator Positioner Convert electrical signal to pneumatic signal so that valve can operate using pneumatic energy. Control valve travel so that correct amount of fluid runs inside valve.
Yamatake Standard Single Seated Valve Control Valves
Body
�Structure of actuator and valve body
Diaphragm Convert pneumatic energy to force Spring Convert force to displacement
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Valve Body
Gasket Seal the space between valve body and bonnet Valve Plug Seat Ring Trim modulates flow passage to control flow rate.
Control Valves
�Introduction
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Major Component of Typical Control Valve Body
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Introduction
Rain cap Eye bolt Diaphragm Spring Actuator stem Diaphragm case Scale plate Stem connector Yoke Packing flange Packing g follower Yoke claming nut Gland packing Valve stem Bonnet Stud bolt and nut Gasket Guide ring Guide bushing Valve plug Seat ring Valve body
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Actuator
Body
Trim
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Combination of body and actuator
Control valves Actuator
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Pneumatic
Motorized
Hydraulic
Body
Glove
Control Valves
Angle
Butterfly
�Features of each actuator types
Pneumatic type Hydraulic type Motorized type Response time Dead time is rather long. Action speed is fast. Possible by using integrated spring or connecting volume tank easily and certainly. Middle for spring diaphragm type. Big for piston cylinder t type. Simple Dead time is short. Action speed is fast Difficult to maintain
FIDEC
(Training Center)
No dead time. Action speed is slow Can stop and maintain only the position at an emergency time. Bigger than pneumatic type and oil pressure type Complicated
Maintaining safety position at supply fail time Output power
Small for oil integrated type. Big for oil separated i t ll ti t installation type Complicated
Structure
Weather proof and Exprosion proof Air piping or electric wiring
Not necessary Simple
Should be considered Simple for oil integrated type. Complicated for oil separated installation Complicated Expensive
Should be considered Simple
Maintenance work Cost
Easy Reasonable
Complicated Expensive
Control Valves
�Features of each body types
Linear motion Glove valve 3-1. Single seated valve 3-2. Top & Bottom guided valve 3-3. Cage valve 3-4. Angle valve Control Valves 3-5. Tree-way valve 3-6. Diaphragm valve Gate valve Rotary motion 3-7. Rotary valve 3-8. Butterfly valve Ball valve
Control Valves
FIDEC
(Training Center)
�Cv calculation
When you decide port size of control valve, you need to calculate required Cv value with fluid condition given on control valve data sheet. Then, you can specify appropriate Rated Cv value and port size. At this chapter, most popular Cv calculation formula that is established by FCI (Fluid Controls Institute, Inc.) is introduced. What is Cv value ? One of the popular coefficients that express flow capacity. Cv value us defined as follows. Fl Flow rate of f 60 degF d F (15 (15.6 6 degC) d C) clean l water with i h the h unit i of f US gal/ l/ min at differential pressure of 1 psi and specific travel of valve. -Rated Cv value: Cv value at a valve is fully opened. -Required Cv value: Cv value calculated with fluid condition
FIDEC
(Training Center)
water 60degF
1 psi
Control Valves
US gal/min
�Introduction
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Flow Control Characteristics As the actuator moves the valve plug through its travel range, the unobstructed flow area changes in size and shape depending on the contour of the valve plug. When a constant pressure differential is maintained across the valve, the changing relationship between percentage of maximum flow capacity and percentage of total travel range can be portrayed , and is designated as the inherent flow characteristic of f the th valve. l Commonly specified inherent flow characteristics include: * Linear Flow Characteristic * Equal-Percentage Flow Characteristics * Quick-Opening Flow Characteristic
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Introduction
Linear Flow Characteristic Cv = K . L (K: Constant, L: Valve plug travel)
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Equal-Percentage Flow Characteristics
Inherent Flow Characteristics Curves
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Introduction
Quick-Opening Flow Characteristic
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Typical Construction to Provide Quick-Opening Flow Characteristic
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Introduction
Selection of Flow Characteristic
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Liquid Level Systems
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Introduction
Rangeability
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Rangeability denotes the ratio between the maximum flow rate and the minimum flow rate which can be controlled by a control valve.
Inherent rangeability =
Cv � max imum Cv � min imum
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Control Valves
Valve and Actuator Types Control Valves
FIDEC
(Training Center)
The control valve regulates the rate of fluid flow as the position of the valve plug or disk is changed by force from the actuator. To do this, the valve must: * Contain the fluid without external leakage; q capacity p y for the intended service; ; * Have adequate * Be capable of withstanding the erosive, corrosive, and temperature influences of the process; and * Incorporate appropriate end connections to mate with adjacent pipelines and actuator attachment means to permit transmission of actuator thrust to the valve plug stem or rotary shaft.
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Valve Bodies
Globe Valves Single-Port Valve Bodies
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Single-Ported Globe-Style Valve Body
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Valve Bodies
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Most Popular type Valve plug has only one seat to shut-of fluid Seat leakage is low even though it has metal seat Unbalancing fluid force is higher than pressure balancing p g type yp When required valve size is lower than 2 inch, This type is most advantageous because small sized actuator can be mounted. That means price is reasonable. When required size is larger than 2 inch, generally, price is not reasonable because the larger the valve size is, the bigger the actuators size is comparing single seated type to pressure balancing type.
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Valve Bodies
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Gasket Valve Plug
Valve Body Seat Ring
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Top and Bottom Guided valve
FIDEC
(Training Center)
The valve plug is guided at top and bottom. Pressure balanced type. This type is used mainly for oil refinery industry. Generally, seat leakage is larger than single seated valves.
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Cage valve
FIDEC
(Training Center)
This type comes after single seated type in market. Valve plug is guided by cage (shaped like pipe and set in valve body. It has window that consists of flow characteristics.) Pressure balanced type is more popular than unbalanced type. For pressure balanced cage type, actuator size is smaller than single seated type when body size is same. Therefore price is more competitive than single seated type when valve size larger than 3 inch or used with highhigh pressure rating. This type can reduce cavitation erosion and aerodynamic noise that are typical control valve claim. Generally, seat leakage is larger than single seated valve.
Seat ring
Valve plug
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Valve Bodies
High Capacity, Cage-Guided Valve Bodies
FIDEC
(Training Center)
High Capacity Valve Body with Cage-Style Noise Abatement Trim
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Angle valve
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Center of inlet and outlet of valves are right angle. This type is advantageous for erosive or abrasive fluid. Also used because of piping design advantage. Wetted parts design is simpler than general 2 way valves. So this type is also advantageous for viscous fluid fluid. Erosion: Destruction of valve bodies or trims due to high fluid velocity Abrasion: Erosion due to slurry that contains solids or particles.
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Tree-way valve Three-Way Valve Bodies
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Diverting type is used to separate flow to 2 way. Mixing type is used to mix 2 flow. Mainly used for temperature control.
Mixing type
Control Valves
Diverting type
training@fidec.ir
�Diaphragm Valve
Elastic diaphragm made with rubber and PTFE the flow passage. modulate Wetted parts can be lined with several materials (PTFE, Glass, and rubbers). So this type is advantageous for slurry or corrosive fluid. This type is cost effective.
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Full open
Control
Full close
Control Valves
�Valve Bodies
Rotary Valves Butterfly Valve Bodies
FIDEC
(Training Center)
A disk that is almost same diameter as pipe size rotate so as to modulates flow. Valve capacity is highest for all types of valves. Generally this type is used at pressure Generally, rating 300# or lower. For higher-pressure rating, this type cannot be applied.
High-Performance Butterfly Control Valve
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Valve Bodies
V-Notch Ball Control Valve Bodies
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Rotary-Shaft Control Valve with V-Notch Ball
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Eccentric-Disk Control Valve Bodies
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Center of the plug rotating point is eccentric from the center of valve body. CV capacity is bigger than that of other globe valves. Fluid can be passed easily because of straight trough construction.
Eccentric-Disk Rotary-Shaft Control Valve
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�PTFE Valve
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Plug: PTFE with 304ss core Bellows: PTFE Casing: SUS304 Body: PTFE
A branch of single seated control valve. Especially used for corrosive fluid. All wetted parts are made with PTFE, which resist most of acids and alkalis. Body has rigid stainless casing to avoid warp with piping stress. Applicable pressure and temperature is limited. Max Operating Temperature: 140 deg C
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�PVC / Polypropylene Valve
FIDEC
(Training Center)
A branch of single seated control valve. Especially used for corrosive fluid. All wetted parts are made with PVC or Polypropylene, which resist most of acids and alkalis Applicable pressure and temperature is limited. Cheaper than PTFE valve
Max Operating Temperature: PVC: 50 deg C, Polypropylene: 80 deg C Model VNP
Control Valves
�Ceramic Valve
Wetted part materials are all ceramics All wetted parts are made with ceramics that resists most of acids and alkalis. 3.Highest abrasion resistance.
FIDEC
(Training Center)
4. There are application limitations for temperature, pressure and seat leakage class. Ceramic
99% aluminum ceramic or Silicon carbide ceramic
Model HMC CV < 4.0 Model HIC 13<CV<120
Control Valves
Aluminum ceramic: 70 deg C
�Valve Plugs
Types of Valve Plugs
Cage
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Plug for cage valve
Contoured plug EQ%
Control Valves
Linear
training@fidec.ir
�Valve Plugs
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Cage-Guided
Characterization of Cage-Guided Valve Bodies
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Characterized Cages for Globe-Style Valve Bodies
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�End Connections
Control Valve End Connections
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�End Connections
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Bonnets
Valve Body Bonnets
The bonnet of a control valve is that part of the body assembly through which the valve plug stem or rotary shaft moves.
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Typical Bonnet, Flange, and Stud Bolts
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Bonnets
Extension Bonnets
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Extension Bonnet
Control Valves
Valve Body with Fabricated Extension Bonnet
training@fidec.ir
�Packing
Control Valve Packing
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Single PTFE V-Ring Packing
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Packing
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Comprehensive Packing Material Arrangements for Globe-Style Valve Bodies
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Packing
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Typical Valve Stem Packing Assemblies
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Packing
PTFE V-Ring Laminated and Filament Graphite Single PTFE V-Ring Packing ENVIRO-SEAL_ PTFE Packing
FIDEC
(Training Center)
ENVIRO-SEAL PTFE Packing System
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Packing
FIDEC
(Training Center)
V-PTFE
V7132Y
#4519 y yarn
Graphite (T2200)
Control Valves
SM636
TK2006
training@fidec.ir
�Packing
Graphite Ribbon for Rotary Valves
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Packing
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Gaskets
Gaskets
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Gaskets
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Gaskets
Examples on Uses of Gaskets
Serrated metal gasket
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Spiral gasket
Model HTS
M d l ACP Model
V543
V543 PTFE coated
V8590 Spiral gasket
training@fidec.ir
Serrated metal gasket
Control Valves
�Gaskets
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Grease
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Lubricator
PS6
Control Valves
#800
#400
#650
training@fidec.ir
�Valve Plug Guiding
Valve Plug Guiding 1. Cage Guiding
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Valve Plug Guiding
2. Top Guiding
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Valve Plug Guiding
3. Stem Guiding
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Left view
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Valve Plug Guiding
4. Top-and-Bottom Guiding
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Valve Plug Guiding
5. Port Guiding
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Right view
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Valve Plug Guiding
Restricted-Capacity Control Valve Trim
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Adapter Method for Providing Reduced Flow Capacity
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Actuators
Actuators
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Pneumatically operated control valve actuators are the most popular type in use, but electric, hydraulic, and manual actuators are also widely used. The spring-and-diaphragm pneumatic actuator is most commonly specified due to its dependability and simplicity of design. Pneumatically operated piston actuators provide high stem force output for demanding service conditions.
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Actuators
1. Diaphragm Actuators
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Actuators
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Field-Reversible Multi-Spring Actuator
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Actuators
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Diaphragm Actuator for Rotary Shaft Valves
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Actuators
2. Piston Actuators
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valve with Double-Acting Piston Actuator
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Actuators
3. Electrohydraulic Actuators
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valve with Double-Acting Electrohydraulic Actuator and Handwheel
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Actuators
4. Manual Actuators
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Typical Manual Actuators
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Actuators
5. Rack and Pinion Actuators
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Typical Rack and Pinion Actuator
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Actuators
6. Electric Actuators
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Traditional electric actuator designs use an electric motor and some form of gear reduction to move the valve. Through adaptation, these mechanisms have been used for continuous control with varying degrees of success.
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Actuators
7. Types (Directions) of Valve and Actuator Actions
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Types of valve and actuator actions should be correctly selected for fail-safe plant operation when the driving power (air supply) has failed. The type (direct and reverse) are defined as follows: (a) Direct action: Valve opens when driving power has failed. (b) Reverse action: Valve closes when driving power has failed.
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Actuators
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Actuators
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Actuators
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Positioners
Control Valve Accessories Positioners
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Pneumatically operated valves depend on a positioner to take an input signal from a process controller and convert it to valve travel. These instruments are available in three configurations: 1. Pneumatic Positioners 2. Analog I/P Positioner 3. Digital Controller
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Positioners
FIDEC
(Training Center)
1. Pneumatic Positioners: A pneumatic signal (usually 3-15 psig) is supplied to the
positioner.
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Positioners
2. Analog I/P Positioner
FIDEC
(Training Center)
This positioner performs the same function as the one above, but uses electrical current(usually 4-20 mA) instead of air as the input signal. 3. Digital Controller Although this instrument functions very much as the Analog I/P described above, it differs in that the electronic signal conversion is digital rather than analog. The di it l products digital d t cover th three categories. t i * Digital Non-Communicating * HART * Fieldbus
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Positioners
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Modern Control Valves Utilizing Digital Valve Controllers
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Positioners
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Positioner Schematic for Piston Actuator
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Volume Booster
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Volume Booster
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Other Accessories
Other Control Valve Accessories
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Top-Mounted Handwheel for Direct-Acting Diaphragm Actuator
Control Valves
Top-Mounted Handwheel for Reverse-Acting Diaphragm Actuator
training@fidec.ir
�Other Accessories
Limit Switches
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Cam-Operated Limit Switches
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Other Accessories
Solenoid Valve Manifold
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Other Accessories
Supply Pressure Regulator
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Supply Pressure Regulator with Filter and Moisture Trap
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Other Accessories
Pneumatic Lock-Up Systems
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Other Accessories
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Other Accessories
Fail-Safe Systems for Piston Actuators
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Other Accessories
Electro-Pneumatic Transducers
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Electro-Pneumatic Transducer Mounted on a DiaphragmActuated Control Valve
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Other Accessories
Electro-Pneumatic Valve Positioners
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Other Accessories
Diagnostics
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Digital valve controllers incorporate predefined instrument and valve diagnostics within firmware to provide alerts if there are problems with instrument mounting, electronics, hardware or valve performance.
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Seat Leakage Classifications
Standards and Approvals Control Valve Seat Leakage Classifications
(In accordance with ANSI/FCI 702 and IEC 60534-4)
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Seat Leakage Classifications
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Seat Leakage Classifications
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Cavitation and Flashing
Cavitation and Flashing Choked Flow Causes Flashing and Cavitation
FIDEC
(Training Center)
The IEC liquid sizing standard calculates an allowable sizing pressure drop, 3PD[� ,I WKH DFWXDO SUHVVXUH GURS DFURVV WKH YDOYH� DV GHILQHG E\ WKH V\VWHP conditions of P1 and P2� LV JUHDWHU WKDQ 3PD[ WKHQ HLWKHU IODVKLQJ RU FDYLWDWLRQ may occur. The change is from the liquid state to the vapor state and results from the increase in fluid velocity at or just downstream of the greatest flow restriction, normally the valve port.
Vena Contracta Illustration
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Cavitation and Flashing
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Comparison of Pressure Profiles for High and Low Recovery Valves
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Cavitation and Flashing
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Typical Appearance of Flashing Damage
Typical Appearance of Cavitation Damage
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Noise Prediction
Noise Prediction 1. Aerodynamic The method defines five basic steps to a noise prediction: 1. Calculate the total stream power in the process at the vena contracta. 2. Determine the fraction of total power that is acoustic power 3. Convert acoustic power to sound pressure.
FIDEC
(Training Center)
4. Account for the transmission loss of the pipewall and restate the sound pressure at the outside surface of the pipe 5. Account for distance and calculate the sound pressure level at the observers location 2. Hydrodynamic
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Noise Prediction
Noise Control
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Valve Trim Design for Reducing Aerodynamic Noise
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Noise Prediction
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Valve and Inline Diffuser Combination
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Noise Prediction
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Valve and Vent Diffuser Combination
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Noise Prediction
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Special Valve Design to Eliminate Cavitation
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Noise Prediction
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Typical In-Line Silencer
Control Valves
training@fidec.ir
�Noise Prediction
Noise Summary
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Globe Style Valve with Noise Abatement Cage for Aerodynamic Flow
Control Valves training@fidec.ir
�Noise Prediction
FIDEC
(Training Center)
Ball Style Valve with Attenuator to Reduce Hydrodynamic Noise
Control Valves training@fidec.ir