UMTS Interface Protocol
Content:
Network Architecture
Iu Interface
Iur Interface
Iub Interface
Uu Interface
Service Data Processing Flow
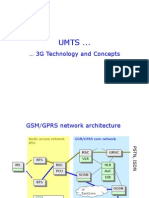
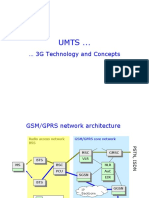
�Terminology of UMTS RNS Network
UTRAN: UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network
RNS: Radio Network Subsystem
RNC: Radio Network Controller
UE: User Equipment
Uu: Radio Interface
Iub: The interface between NodeB and RNC
Iur: The interface between RNCs
Iu_CS: between RNC and CS domain
Iu_PS:between RNC and PS domain
Iu_BC:for BroadCast domain
�Universal model of the UTRAN
interfaces
Horizontal: UTRAN falls into 2 layers
Radio Network Layer (RNL)
Transport Network Layer (TNL)
Vertical: UTRAN falls into 4 planes
Control plane
User plane
TNL control plane
TNL user plane
In R99 and R4, the ATM technology is adopted at the transport network layer, while R5, IP transmission is
introduced.
����Iu interface Functions
RAB management
RAB setup, modification and release
mapping of RAB characteristics to the Uu bearer
mapping of RAB characteristics to the Iu transmission bearer
RAB queuing, preemption and priority
Iu radio resource management
radio resource acceptance control
Iu connection management
Iu signaling connection management
Iu-UP (RNL) management
Iu-UP frame protocol mode selection and protocol initialization
Mobility management
Security management
Service and network access
�Paging coordination
Stream Control Transmission
Protocol(SCTP)
SCTP is a reliable datagram transfer protocol based on an unreliable transfer protocol such as UDP.
SCTP End Point is a logical entity, logical datagram sender and receiver. Each SCTP End Point is only
identified by IP address and port number, similar to TCP.
SCTP Association is a logical association or channel established between two SCTP End Points.
Client/Server mode is adopted.
MTP3-User Adaptation Layer
Protocol(M3UA)
M3UA (MTP3-User Adaptation Layer) protocol conducts conversion between SPCs and IP addresses. It is
used for the SS7 signaling to transfer between the Softswitch and the Signaling Gateway(SG). It supports
to transfer the MTP3 user messages over the IP network, including ISUP, TUP, and SCCP messages.
Signaling connection control protocol
SCCP
RNC, SCCP protocol is mainly used to transport signaling message by Iu/Iur interface. The client
is RANAP and RNSAP.
It offers the connectionless or connection-oriented services for its client. The SCCP also offers the
segmentation and reassembly functions
����Iur interface Functions
Iur interface has the following functions:
Inter-RNC mobility management
SRNC relocation, inter-RNC cell and UTRAN registration area update, inter-RNC paging, and protocol error
report.
Dedicated channel data transmission
used to transmit dedicated channel data between two RNCs.
Common channel data transmission
setup and release of the transmission connection needed in common channel data stream transmission of
the Iurinterface,
Global resource management
transmission of inter-RNC cell measurement information.
transmission of inter-RNC Node B timing information.
�Iur Flow Overview
Radio Link Management
Physical Channel Reconfiguration
Radio Link Supervision
Compressed Mode Control
Measurements on Dedicated Resources
DL Power Drifting Correction
CCCH Signaling Transfer
Paging
Common Transport Channel Resources Management
Relocation Execution
Iub Interface Stack Structure
�Iub interface Functions
Management of the Iub interface transmission resources.
Logic operation maintenance of Node B, including:
the cell configuration management
radio network performance measurement
common transmission channel management
radio resource management
Transmission of application-related operation & maintenance data.
System information management.
Channel traffic management.
Timing and synchronization management, including:
node synchronization
transmission channel synchronization between the RNC and Node B
�Iub Flow Overview
Click to edit master text style
System Information Management
Configuration Alignment
Measurements
Radio Link Management
Radio Link Supervision
Compressed Mode Control
DL Power Drifting Correction
Uu Interface Stack Structure
�Uu Interface Stack Structure
Physical Layer Protocol
provides the MAC sublayer with transmission channel services.
MAC Protocol (Media Access Control)
provides the RLC sublayer with logic channel services.
RLC Protocol (Radio Link Control)
on the control plane, provides the RRC sublayer with signaling radio bearer services.
on the user plane, provides service radio bearer services together with the PDCP sublayer.
PDCP (Packet data convergence protocol)
adapt different types of network layer protocols to the radio interface.
only exists in the packet domain
BMC (Broadcast main control)
transfer broadcast and multicast information over the radio interface.
RRC (Radio resource control)
Provide services for the non-access layer, for example, transmitting messages like call control, session
management and mobility management at the control interface.
Setup, maintenance and release of an RRC connection between UE and UTRAN.
Setup, reconfiguration and release of radio bearer.
Distribution, reconfiguration and release of radio resources used in the RRC connection.
RRC connections mobility function management.
Request for QoS control.
�UE measurement report and report control.
Outer loop power control, ciphering control, paging.
Initial cell selection and reselection in the idle mode.
�PDCP Function
User Data Transport: Transmit NAS data to RLC layer or reverse.
IP Head Compression: Compress or decompress the IP data in the Transport entities and receive entities.
Different network layer has different compression algorithm.
Sequence Number Maintenance: If RB supports lossless SRNS Reselection, the Sequence Number can be
kept synchronized between UE and RNC.
PDCP is only used in PS services
�BMC Services and Function
BMC services adopt TM or UM to provide Broadcast/Multicast services for the public users
The functions of BMC include cell broadcast message depository, service flow monitor, radio resource
request for cell broadcast, BMC message scheduling, sending and receiving cell broadcast message and
so on.
BMC Sub-layer Structure
�RLC Layer Work Modes
RLC provides the services for the upper layer: RLC connection setup/release, TM data Transport, UM data
Transport, AM data Transport, unrecoverable error notify and so on.
The functions for RLC include Segment, Reassemble, Concatenation, Padding added, Data Transport, Error
Detect, PDU delivery in order, Detection Repeat, Flow Control, Sequence Number Detection, Protocol
Error Detection/ Retrieval/ Encryption/ Suspend function.
RLC work modes: TM, UM,AM. Different work mode is adopted according to the QoS requirement of
different services; for the signaling, the work mode also depends on the significance.
�����MAC-Some Transport Channel
Principles
Transport Block
The basic switching unit between L1 and MAC layer
Transport Block Set
A Set of Transport Blocks which are Transmitted in a Transport channel on a certain moment.
Transport Block Size
The bit number of a Transport Block.
Transport Block Set Size
The bit number of a Transport Block Set.
Transport Time Interval
Transport Time Interval is defined as a time interval for a Transport Block arrived,
and it equals to the time for transporting a Transport Block on the Physical Layer of
Radio Interface. It is always the gemination of MIN. interleaving cycle (10ms, Size of
Radio Frame). MAC layer transports a Transport Block Set to the physical layer
in each TTI.
Transport Format
Transport Format is defined as the format of a Transport Block Set which is
transported on a Transport channel. The format is provided for MAC layer by L1 (or
�MAC layer provides for L1). The Transport Format is consisted of two parts:
dynamical part and static part.
MAC-Some Transport Channel
Principles
Transport Format Set
Transport Format Set is defined as a set of Transport Format on a Transport
Channel. In side of a Transport Format Set the static part of transport format is the
same. The previous two features of the dynamic part determine the instantaneous bit
rate of the Transport channel.
Transport Format Combination
When one or more transport channels map in L1, for each transport channel, there
should be a sets of Transport Format (Transport Format Set) available. For a certain
time, not all the Format Combination is appropriate for L1, but only a sub-set, which
is Transport Format Combination.
Transport Format Combination Set
Transport Format Combination Set is defined as a set of Transport Format
Combination of Coded Composite Transport Channel (CCTrCH) .
Transport Format Indicator
TFI is the specific indicator for a certain Transport Format among the Transport
Format Set. It is used between L1 and MAC layer, when they exchange a transport
block set.
Transport Format Combination Indicator
TFCI is a indicator of the current Transport Format Combination.
The Services Provided by L1 and Timing Operation
The Physical Layer provides Data Transport Services for the upper layer, which are implemented by MAC
sub-layer through Transport Channel.
�Transport Format (or Transport Format Set) defines the feature of the transport channel, meanwhile, it also
indicates the processing on the transport channel by physical layer, such as convolutional encoding and
interleaving, rate match required by the services and so on.
The operation on the physical layer is strictly according to the timing of L1 Radio frame. And for every 10ms
(or multiple times of 10ms) to generate a transport block.
Physical Layer Function
FEC encoding/decoding of transport channel
To provide measurement and indicator for the upper layer (such as FER, SIR,
Interference Power, Transport Power and so on)
Macro Diversity distribution/ Combination and soft handover implementation
Error Detection of transport channel
Transport Channel multiplexing, Coding Combination Transport Channel demultiplexing
Rate Matching
To map Coding Combination Transport Channel to physical channel
Physical channel modulation/Frequency Spreading and Demodulation/Frequency De-spreading
Frequency and Timing (Chip, Bit, Slot, Frame) synchronization
Close loop power control
Physical channel power weight and combination
RF Processing
Radio Network Control-Plane protocol