CHAPTER 5 : THE AIR AROUND US
The Composition of Air
Air is a mixture consist of
Nitrogen
78%
Oxygen
21%
Carbon dioxide
0.03%
Inert gases
0.97%
Water vapour
Microorganism
Dust
The percentage of the constituents of air are different from one place to another.
To show the percentage of oxygen in the air
Inert Gases
Argon Helium
Krypto
n
Xenon
Observation :
The burning candle goes out.
The water level in the gas jar rises one fifth up the gas jar (20% of
air in the air)
Neon
Conclusion :
The percentage of oxygen in the air is approximately 20%.
Radon
��Review 1
Complete the chart below to show the composition of air and the percentage of each of
its components.
Tick ( ) the correct statements.
Air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and inert gases.
The average percentage of oxygen in air is the same everywhere. I
Air contains dust, microorganisms and water vapour.
The composition of air in a jungle is not the same as that in the city centre.
The air in a crowded hall has the same content of oxygen as the air in an empty hall.
Air is a mixture because its composition is not always the same.
The content of water vapour in the air changes at different times of the day.
�Changes the colour of
hydrogen carbonate from red to
yellow
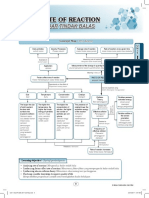
The Properties of Gas
Does not support combustion
Acidic
Colourless
Odourless
Slightly soluble in water
Colourless
Odourless
More soluble in water
Very soluble in sodium
hydroxide
Turns damp blue litmus paper
to red
Turns lime water milky
Not soluble in sodium
hydroxide
No effect on damp litmus
paper
No effect on lime water
Relights a glowing splinter
No effect on hydrogen carbonate
solution
Support combustion
Neutral
Extinguishes a burning splinter
CARBON DIOXIDE
OXYGEN
Relights glowing splinter
�Lime water turns cloudy, chalky
and milky
�Review 2
1. Choose the correct answers in the brackets.
Oxygen is (slightly soluble,
not soluble) in water.
of Oxygen
Oxygen is (slightly soluble,
Oxygen (reacts, does
not
not soluble) in
sodium
react) with lime water.
hydroxide solution.
Properties
Oxygen is a (neutral.
acidic) gas. It has no
effect on blue and red
�litmus papers.
Oxygen makes a burning
wooden splinter burn
(more, less) brightly.
Oxygen (ignites, extinguishes)
glowing wooden splinter
goes out) in
the
presence of
carbon
Carbon
Dioxide
The colour of bicarbonate indicator
(changes, does not change) in the
presence of oxygen.
Carbon dioxide is (slightly soluble,
not soluble) in water.
Carbon dioxide is (more soluble,
not soluble) in sodium hydroxide
solution.
Carbon dioxide is a (neutral.
acidic) gas. It changes the colour
of (blue, red) litmus paper to
(blue, red).
Carbon dioxide reacts with
(lime water, bicarbonate
indicator) to form a cloudy
precipitation.
A burning wooden splinter (goes
out, burns more brightly) in the
presence of carbon dioxide.
Propertie
s
A g lowing wooden splinter (ignites, of
Carbon dioxide changes the
colour of bicarbonate indicator
from (yellow, red) to (yellow, red).
�OXYGEN IS NEEDED FOR RESPIRATION
Oxygen is needed by all living organisms for the respiration process.
Respiration involves the oxidation of glucose (food) and the production of carbon
dioxide, water vapour and energy.
The body gets oxygen that is needed for respiration when inhaled air enters the
lungs. Inhaled air the air that is breathed in during respiration.
Exhaled air the air is breathed out during respiration.
Composition of Inhaled Air and Exhaled Air
Gas
Inhaled Air
Exhaled Air
Nitrogen
78%
78%
Oxygen
21%
16%
Carbon dioxide
0.03%
4%
Inert gases
1.0%
1%
Water vapour
Varies
Saturated
Temperature
25C
�37C
Heat
Less
More
Glucose + Oxygen
Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
�To show living things use oxygen during respiration
Observation :
The drop of coloured water in tubes A and B move towards the tube.
Discussion :
Cockroaches and germinating seeds (living things) take in oxygen and give out carbon
dioxide during respiration.
Carbon dioxide is absorbed by sodium hydroxide.
Pressure inside tube A and B decrease.
Higher pressure outside pushes the drop of coloured water towards the tubes.
Conclusion:
Living things used oxygen during respiration.
To show that living things give out carbon dioxide during respiration
Observation :
The colour of hydrogen carbonate indicator in tubes P and Q change from red to
yellow.
Discussion :
Cockroaches and germinating seeds (living things) give out carbon dioxide during
respiration.
Hydrogen carbonate indicator absorbs the carbon dioxide and changes colour from red
to yellow.
Conclusion:
Living things give out carbon dioxide during respiration.
�Review 3
Tick ( ) the correct statements.
The cells in our body carry out respiration to obtain energy from food.
Oxygen is needed for respiration.
Carbon dioxide is a by- product of respiration.
Inhaled air has more carbon dioxide than exhaled air.
exhaled air contains about 16% of oxygen.
Inhaled air contains more water vapour than exhaled air.
Nitrogen is not used in respiration.
Living things use oxygen during respiration.
Living things give out carbon dioxide during respiration.
Inhaled air contains more nitrogen than exhaled air.
Complete the following table.
Gas
Inhaled Air
Exhaled Air
Nitrogen
78%
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
0.03%
Inert gases
1.0%
1%
Water vapour
�Varies
Temperature
25C
37C
Heat
Less
�OXYGEN IS NEEDED FOR COMBUSTION
in engines to move the vehicles.
Burning the kerosene in aircraft engine
to produce energy to fly.
Others
Combustion is a
process of burning
substances that gives
of heat and light.
Condition for
combustion are :
Oxygen
Heat
Fuel
Burning of candles as source of light.
Burning of natural gas for cooking.
Combustion of carbon
Produces carbon dioxide,
heat and light.
Example:
Charcoal + Oxygen
Carbon dioxide + Heat + Light
Product of
Combustion
Combustion of hydrocarbon
Produces carbon dioxide,
water, heat and light.
IMPORTANCE
Industry
Burning of fuel to generate
electricity in power station.
Boiling water to produce
steam to turn the turbines.
Example:
Kerosene + Oxygen
Carbon dioxide + Water +
Heat + Light
The water formed by combustion of
hydrocarbon can be tested with :
Transportation
Dry cobalt chloride paper ( blue to
pink)
Burning of petrol or diesel
Anhydrous copper sulphate ( white
�to blue)
Methods To Put Out A
Fire
Remove fuel
Take away fuel from fire
source.
Remove oxygen
Using fire blanket, sand,
supply
cloth.
Remove heat
Using water
�To show that oxygen is needed for combustion
Observation :
The candle inside the gas jar goes out after a short while.
The candle outside the gas jar continues to burn
Conclusion:
Oxygen is needed for combustion.
To investigate the effect of the size of a container on the length of
time a candle burns.
Observation :
The candle in the 500 ml beaker goes out first.
The candle in the 1000 ml beaker continues to burn for some time
before it goes out.
Conclusion:
The bigger the size of container, the longer the time for candle to burn.
��Review 4
1. Fill in the blanks in the sentences below by using the word give.
water vapour
hydrocarbon
oxygen
heat energy
fuel
carbon
carbon dioxide
Combustion is a chemical reaction between a substance and
_________________ which produces heat and light.
Oxygen, __________________ and enough amount of heat must be available for
combustion to take place.
During combustion, the chemical energy stored in a fuel is changed into
____________________ and light energy.
Charcoal and coal are examples of _________________.
Petrol, natural gas, kerosene and diesel are examples of
_________________.
The combustion of charcoal gives out heat energy, light energy and
___________________.
(g) The combustion of
kerosene produces carbon dioxide,
_______________ , light energy and heat energy.
2. Complete the following table.
Situation
Material or apparatus for
Variable that
�the investigation
Is kept
Is
Responds
constant
manipulated
1