VERILOG FOR VERIFICATION
An Pham-Duc
�Contents
Modules
Data types
Procedural blocks
Operators
Tasks & functions
System tasks
Compiler directivities
�Modules
Basic unit of hierarchy in
Verilog
A module in Verilog is
somewhat like a function in C
Modules are static instances
// module declaration
module module_name #(
parameter_declaration,
parameter_declaration,
...
)(
port_declaration port_name,
port_declaration port_name,
...
);
endmodule
// module instance
module_name #(
.parameter_name(value),
.parameter_name(value),
...
) instance_name (
signal,
...
);
�Modules
�Data types: net
Net Declaration Examples
Notes
wire a, b, c;
3 scalar (1-bit) nets
tri1 [7:0] data_bus;
8-bit net, pulls-up when tri-stated
wire signed [1:8] result;
an 8-bit signed net
wire [7:0] Q [0:15][0:256];
a 2-dimensional array of 8-bit wires
wire #(2.4,1.8) carry;
a net with rise, fall delays
wire [0:15] (strong1,pull0)
sum = a + b;
a 16-bit net with drive strength and a continuous assignment
trireg (small)
#(0,0,35) ram_bit;
net with small capacitance and 35 time unit decay time
�Data types: variable
Data types
Description
reg
a variable of any bit size; unsigned unless explicitly declared as signed
integer
a signed 32-bit variable
time
an unsigned 64-bit variable
real
a double-precision floating point variable
realtime
same as real
�Data types: variable
Variable Declaration Examples
Notes
reg a, b, c;
three scalar (1-bit) variables
reg signed [7:0] d1, d2;
two 8-bit signed variables
reg [7:0] Q [0:3][0:15];
a 2-dimensional array of 8-bit variables
integer i, j;
two signed integer variables
real r1, r2;
two double-precision variables
reg clock = 0, reset = 1;
two reg variables with initial values
�Data types: others
Data types
Description
parameter
a run-time constant for storing integers, real numbers, time, delays, or ASCII
strings; may be redefined for each instance of a module (see section 7.0)
localparam
a local constant for storing integers, real numbers, time, delays, or ASCII
strings; may not be directly redefined, but may be indirectly redefined by
assigning the localparam the value of a parameter
specparam
a specify block constant for storing integers, real numbers, time, delays or
ASCII strings; may be declared in the module scope or the specify block
scope; may be redefined through SDF files or the PLI
genvar
a temporary variable used only within a generate loop; cannot be used
anywhere else, and cannot be read during simulation
event
a momentary flag with no logic value or data storage; can be used for
synchronizing concurrent activities within a module
�Data types: others
Data Type Examples
Notes
parameter [2:0] s1 = 3b001,
s2 = 3b010,
s3 = 3b100;
three 3-bit constants
parameter integer period = 10;
an integer constant
localparam signed offset = -5;
unsized signed constant defaults to width of initial value
event data_ready, data_sent;
two event data types
�Data types: bit/array select
Types
Syntax
Bit Select
vector_name[bit_number]
Constant Part Select
vector_name[bit_number : bit_number]
Variable Part Select
vector_name[starting_bit_number +: part_select_width]
vector_name[starting_bit_number -: part_select_width]
Array Selects
array_name[index][index]
array_name[index][index]...[bit_number]
array_name[index][index]...[part_select]
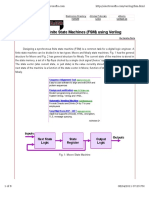
�Procedural blocks
// syntax
type_of_block @(sensitivity_list)
statement_group: group_name
local_variable_declarations
time_control procedural_statement
end_of_statement_group
Type of block: initial & always
Sensitivity list: signals, posedge, negedge, * (wildcard)
Statement group: begin-end & fork-join
Group name (optional): optional
Local variables (optional): data types
Time control: #delay, @, wait
Procedural statement: assignment statement & programming
statement
�Procedural blocks
Assignment statements
blocking ( = )
non-blocking ( <= )
assign
deassign
force
release
�Procedural blocks
Programming statements
if-else
case/casez/casex-endcase
for
while
repeat
forever
disable
�Operators
Bitwise Operators: ~, &, |, ^, ~^, ^~, <<, >>
Unary reduction Operators: &, ~&, |, ~|, ^, ~^, ^~
Logical Operators: !, &&, ||
Equality and Relational Operators: ==, !=, <, >, <=,
>=
Identity Operators: ===, !==
Miscellaneous Operators: ?:, {}, {{}}, ->
Arithmetic Operators: +, -, -, *, /, %, **, <<<, >>>
�Tasks & functions
// task declaration
task automatic task_name (
port_declaration port_name,port_name,... ,
port_declaration port_name,port_name,...
);
local variable declarations
procedural_statement or statement_group
endtask
// function declaration
function automatic range_or_type function_name (
input range_or_type port_name,port_name,... ,
input range_or_type port_name,port_name,...
);
local variable declarations
procedural_statement or statement_group
endfunction
�System tasks: STDIO
Syntax: $system_task(text_with_format_specifiers,
list_of_arguments);
$display: print the message and add a newline
$write: print the message
$strobe: like $display, except that the printing is
delayed until the end of simulation time slot
$monitor: create background process, print the
message whenever one of the arguments changes
�System tasks: STDIO
Text Formatting Codes
%b
%o
%d
%h
%e
%f
%t
%s
binary values
octal values
decimal values
hex values
real valuesexponential
real valuesdecimal
formatted time values
character strings
%m
%l
\t
\n
\
\\
%%
hierarchical name of scope
configuration library binding
print a tab
print a newline
print a quote
print a backslash
print a percent sign
%0b, %0o, %0dand %0h truncates any leading zeros in the value.
%e and %f may specify field widths (e.g. %5.2f).
%m and %l do not take an argument; they have an implied argument value.
The format letters are not case sensitive (i.e. %band %Bare equivalent).
�System tasks: file I/O
mcd = $fopen(file_name);
fd = $fopen(file_name,type);
$fclose(mcd_or_fd);
$fmonitor(mcd_or_fd, text with format specifiers, signal, signal,...);
$fdisplay(mcd_or_fd, text with format specifiers, signal, signal,...);
$fwrite(mcd_or_fd, text with format specifiers, signal, signal,...);
$fstrobe(mcd_or_fd, text with format specifiers, signal, signal,...);
�System tasks: file I/O
c= $fgetc(fd);
code= $ungetc(c, fd);
code= $fgets(str, fd);
code= $fscanf(fd, format, arguments);
code= $fread(reg_variable, fd);
code= $fread(memory_array, fd, start, count);
position= $ftell(fd);
code= $fseek(fd, offset, operation);
code= $rewind(fd);
errno= $ferror(fd, str);
$fflush(mcd_or_fd);
�System tasks: others
$finish/$stop
$time
$timeformat(unit, precision, suffix, min_field_width);
$swrite(reg_variable, format, arguments, format, arguments,...);
$sformat(reg_variable, format, arguments);
code= $sscanf(str, format, arguments);
$readmemb(file_name, variable_array, start_address, end_address);
$readmemh(file_name, variable_array, start_address, end_address);
64-bit_reg_variable= $realtobits(real_variable);
real_variable= $bitstoreal(64-bit_reg_variable);
integer= $test$plusargs(invocation_option)
integer= $value$plusargs(invocation_option=format, variable)
�Compiler directivities
`timescale
`define
`undef
`ifdef
`ifndef
`else
`elsif
`endif
`include
�References
[1] Stuart Sutherland, Verilog-HDL Quick Reference
Guide, Sutherland HDL Inc, Sep 2007
�Assignments
1.
Write a simple program in Verilog that:
1.
2.
3.
4.
2.
Read video data from a binary file, invoke an error if failed
Print video information to monitor (get form SPC file)
Invert video data
Write it back to another binary file
Write a clock/reset module