100% found this document useful (1 vote)
550 views19 pagesChem Eng Process Control Intro
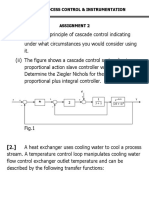
This document provides an outline for the CHE334 Instrumentation and Process Control unit. It introduces the topics that will be covered, which include fundamentals of instrumentation, basic control theory, and common measurement techniques. Assessment will include two sessional tests, quizzes, assignments, and a final exam. Chapter 1 will introduce process control, instrumentation, basic concepts like systems and control loops, and components of measurement and control systems. The goal of process control is to safely and satisfactorily operate chemical processes through automation. Controllers are used to suppress external disturbances and ensure safety while optimizing performance and reducing variability.
Uploaded by
Tamoor TariqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
550 views19 pagesChem Eng Process Control Intro
This document provides an outline for the CHE334 Instrumentation and Process Control unit. It introduces the topics that will be covered, which include fundamentals of instrumentation, basic control theory, and common measurement techniques. Assessment will include two sessional tests, quizzes, assignments, and a final exam. Chapter 1 will introduce process control, instrumentation, basic concepts like systems and control loops, and components of measurement and control systems. The goal of process control is to safely and satisfactorily operate chemical processes through automation. Controllers are used to suppress external disturbances and ensure safety while optimizing performance and reducing variability.
Uploaded by
Tamoor TariqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 19