10/26/2014
Hemoglobin Estimation
physiology Lab.
Midwifery
October 2014
by: Mehdi Mafakheri
Procedures
Hemoglobin
estimation method
a) Sample:
Both capillary and venous blood may be used for this test.
Automated
Manual
b. Method:
1. Cyanmethemoglobin method:
o Accurate. Because:
Cyanmethemoglobin
method
Acid Hematin
method
Coulter counter
1- depend on spectrophotometer (O.D) of Cyanmethemoglobin
2- stable for long time (about 6 month in 4C)
3- possibility of formation Cyanmethemoglobin from all hemoglobin type
except Sulfahemoglobin.
o Commonly used.
o Recommended by ICSH (international committee for standardization in
hematology).
alkali hematin not suitable for estimation infant hemoglobin Because NaOH not
react with Hb F.
�10/26/2014
a) Principle of Cyanmethemoglobin method:
Blood + diluent (Drabkins solution)
Reagent and equipment for Cyanmethemoglobin method:
b)
potassium ferricyanide + potassium cyanide
Converts: Hemoglobin (Hb) and Methemoglobin (Hi)
Cyanmethemoglobin (HiCN)
Measure the absorbance of the solution by using a calorimeter at a
wavelength = 540nm. Then compare it with the standard solution of
HiCN.
Diluent (Drabkins solution)
5 ml pipette.
Cuvettes.
Test tube.
20 micro liter pipettes.
Spectrophotometer
c)
2. Acid hematin method:
Procedure of Cyanmethemoglobin method:
a)
20micl blood + 4ml diluent
Principle:
HiCN.
mix, 5-10min
Blood + 0.1 N HCL
Acid Hematin.
(then match the color of solution with reference solution colorimeter or colored strip)
sample
i.e. SAHLIS hemoglobinometer
Measured by spectrophotometer at 540nm
standard
However this method is inaccurate. Because:
1- interference of some compound such as plasma protein and lipid with RBCs cell
membrane
2- HCl have no effected on some hemoglobin derivatives such as Sulfahemoglobin .
3- read by naked eye
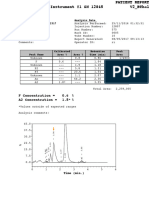
Use the calculator:
Absorbance of test
X Conc. of standard
Hb (g/dl)=
Absorbance of standard
7
�10/26/2014
b)
c) Procedure of Acid Hematin method :
100ul HCL + 20micl blood mix in a graduated Tube (keep for 3min) to make
Reagent and equipment for Acid Hematin method:
Acid Hematin
A black counting chamber, round Hb Tube, 20ul Pipette, Rubber
tube with mouth piece, Cleaning brush, Glass dropper with rubber
teat, Glass rod, Amber bottle.
How can we read Hb value?
Compare the color of solution in the graduated tube with that of reference strip
on either side of hemoglobinometer.
Graduated tube has two scales: % and g/100 ml of whole blood.
If the color of graduated tube is Darker add D.W -drop by drop- with pipette; mix
with glass rod until the color matches with reference strip.
The reading in graduated tube refers to Hb level in g/dl
(some tubes give reading in %; to convert into g/dl X 0.146
e.g. : 10% X 0.146 = (14.6 g/dl).
Q. What is the unite of measurement for Hb? Whole blood Hb concentration is in g/dl
10
Reference Values
Precaution
Before the sample is read the solution should be clear.
If high WBC in specimen centrifuge the specimen then use the
supernatant.
Adult male:
13 - 18 g/dl
Adult female:
12 - 16 g/dl
In case of Hb S or C dilute the mixture in 1:1 ratio with DW then
read in colorimeter.
In case of abnormal globins add 0.1g of potassium carbonate to
the solution.
11
10y old child
11 - 15 g/dl
6 m old child
11 - 14 g/dl
New born
14 - 22 g/dl
12
�10/26/2014
Stage formation of RBCs
Interpretation:
Reference values for Hb are variable.
Clinical significance:
1.
Proerythroblast.
2.
Basophilic normoblast (early stage).
1.
Polychromatic normoblast (intermediate stage ).
2.
Orthochromatic erythroblast or Nucleated RBC (late stage ).
5.
Reticulocyte.
6.
Normal erythrocytes
Hb value
Anemia
+
RBC count and indices (upcoming labs)
13
Stage formation of RBC:
14
2.
Basophilic Normoblast (early stage)
1. Proerythroblast
The earliest precursors of erythropoiesis and do not contain
hemoglobin.
Nucleus: The nucleus has a dense, finely honeycombed chromatin
structure with pale blue nucleoli, which disappear as the cell matures.
Cytoplasm : darkly basophilic.
Seen in BM
These cells tend to be smaller than proerythroblasts.
Like proerythroblast in general character.
The nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio is shifted in favor of the cytoplasm.
Seen in Bone morrow.
15
16
�10/26/2014
3.
Polychromatic normoblast (intermediate stage)
Nucleus :
appears coarse and smudgy, and there is partial clumping of the nuclear
chromatin.
Cytoplasm:
loses more of its basophilic with a greater abundance of hemoglobin.
4.
Orthochromatic erythroblast or Nucleated RBC (late stage )
Red blood cell with nucleus
The nuclear- cytoplasmic ratio is shifted in favor of the cytoplasm,
which acquires an increasingly red tinge ultimate
Seen in bone marrow and blood
Seen in sickle cell disease ,AIHA ,and beta-thalassaemia
Seen in bone marrow
17
5.
Reticulocyte
18
6.
Normal erythrocytes (Normochromic)
Immature RBCs that contain cytoplasmic RNA and organelles such as
mitochondria and ribosomes in various stages of maturity.
The more filamentous reticula are characteristic of younger cells (brilliant
cresyl blue stain)
Seen in bone marrow and blood
Seen in hemolytic anemia
Cells are uniform size & shape
Normal hemoglobin conc.
19
small, central pallor which is
Less than one-third of the total cell volume.
20
�10/26/2014
Hypochromic erythrocytes
Sever Hemorrhage
Systemic diseases e.g. leukemia,
lymphoma, uremia, cirrhosis,
hyperthyroidism, carcinomatosis and
systemic lupus erythematosis.
Haemolysis due to transfusion
of incompatible blood,
reactions to chemicals and
drugs, bacteremia, and artificial
heart valves
IDA, Thalassemia & Sideroblastic anemia
21
22
Anaemia
Hypochromic
Polycythaemia
High altitudes
Congestive heart failure
(CHF)
Hemoconcentration states of blood
e.g. sever burns
23
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
(COPD)
24
�10/26/2014
Polychromasia and Normoblasts
Polychromasia
Mature RBCs with increased staining with basic stain and Hb staining.
Occurs in red cells have high RNA content with Hb synthesis is not yet
complete.
25
Quality Control
1.
If the patients specimen running in automated machine
there are 3 levels controls should be run.
2.
While if its running by manual method; send patients
specimen to the reference laboratory; and perform duplicate
testing in your own lab.
1.
All personnel performing Hb should be checked for color
blindness (Sahlis Method).
27
Increased erythrocyte production &
Hemolytic anemia
26