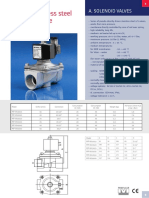
02-12-14
Introduction to Vibration Analysis
Programs as Part of a Predictive
Maintenance Strategy
Emad Bitar,
Leader, Bently Supporting Services & Portables,
MEA, Turkey & Pakistan
Emad.Bitar@ge.com
Imagination at work
�02-12-14
About me
Emad Bitar Emad.Bitar@ge.com
More than 26 years of experience in Condition Monitoring
Programs: Application Engineer / Application Manager
Expertise in services, support, implementation and Training
with more than 19 years in the Middle East
Expertise in machinery troubleshooting using advanced
vibration techniques
Certified Trainer for advanced vibration , and Certification of
Vibration Analyst I & II from the Vibration Institute (1994).
Certified ISO Vibration Analysis CAT III.
Wrote many technical papers for the Vibration Institute, PdM,
Rotate, Uptime, Maintenance Management
BS and MS in Mechanical Engineering from The University of
Tennessee USA
�02-12-14
Few things to start with
Unplanned Downtime:
What does it do to your operation?
How often does it happen?
How much does it cost?
Old Plant:
Are you trying to extend the life of your plant?
Are you trying to increase production with the same equipment?
Maintenance:
What equipment needs maintenance next?
Can we skip this outage and run for few more months?
�02-12-14
Many Technologies One Answer
Vibration measurement contains information
from the machine and its surrounding
Every problem on a machine has a distinct
vibration behavior
Any changes in the vibration signature
indicate there are changes in the dynamic
condition of the machine
�02-12-14
Many Problems One Technology
Imbalance, Misalignment and Resonance can
be detected and corrected
Bearing defects can be tracked through its
various stages
The severity of gear problems can be identified
without stopping the machine
Wears in mechanical and structural parts
can be distinctly identified and corrected
Electrical problems in motors shows up in the
vibration waveform and spectrum
Lubrication problems produce friction and
impacting with distinctive vibration behaviors
Other problems like cavitations in pump, soft
foot, and belt problems and others can be
trended and diagnosed
�02-12-14
Elements of a Vibration Analysis Program
System:
Hardware Data Collector / Analyzer
Software
People:
Personnel
Training
Process:
Workflow
Reports
Management:
Commitment
Funding
Monitoring
�02-12-14
Steps of a Successful Vibration Analysis Program
1. Gather machine information
2. Create database
3. Collect data
4. Detect problems
5. Analyze the nature and the severity of
problems
6. Generate reports on equipment status
7. Follow up on findings
�02-12-14
Machine Information
Shaft speed
Bearing types
Gearbox design and number of
teeth
Belt lengths and pulleys
diameters
Motor load and number of bars
Coupling type
Number of vanes or blades
Measurement locations and
directions
Sensors type and sensitivity
8
�02-12-14
Steps of a Successful Vibration Analysis Program
1. Gather machine information
2. Create database
3. Collect data
4. Detect problems
5. Analyze the nature and the severity of
problems
6. Generate reports on equipment status
7. Follow up on findings
�02-12-14
Machine Setup Made Easy: RPM
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
10
10
�02-12-14
Library of more than 1 Million Bearings
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
11
11
�02-12-14
Criticality, Orientation and Support
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
12
12
�02-12-14
Multiple Bearings Option
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
13
13
�02-12-14
ISO or TA
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
14
14
�02-12-14
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
15
15
�02-12-14
Transducer Setup
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
16
16
�02-12-14
Spectra and Waveforms
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
17
17
�02-12-14
Measured Variables
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
18
18
�02-12-14
Setpoints / Alarms
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
19
19
�02-12-14
Automated Setup
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
20
20
�02-12-14
Copy / Paste
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
21
21
�02-12-14
Database Setup Results
Without any vibration knowledge, the
machine has been setup quickly with the use
of normal machine information readily
available in the maintenance library
All the alarm limits, analysis parameter sets
and fault frequencies are easily setup with
the machine
After just few steps, you are ready to collect
data and do analysis
22
�02-12-14
Create Routes
Locate machines to be monitored in plant
List of machines and measurement points
Choose logical order for data collection of
machines and points
Do a cold walkthrough to locate the
machines and modify the order to suite the
actual locations
A different route may be created for each
section of the plant
A machine may be on multiple routes
23
�02-12-14
Route Setup
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
24
24
�02-12-14
3. Data Collection
Routes that contain
Machines and
measurement points
are transferred to
portable or online
analyzers
25
�02-12-14
Sensor Selection
The sensor converts
the vibration into an
electronic signal
The most common
sensor is an
accelerometer
The sensor is
commonly attached
using a magnet
Other vibration
sensors:
Velocity Pickup
Displacement
26
�02-12-14
Mounting the Sensor
Proper mounting is
very important
Repeatability is
essential
Good mechanical
transmission path
from the bearing
27
�02-12-14
Repeatability
Vibration changes when the
speed and load change
The machine must operate in
the same state during every
test
Check the speed and load
with each measurement
Collect data in the same
location, direction and
methodology every time
Best Option - collecting data
from permanently installed
sensors
28
�02-12-14
Periodicity
Vibration is directional,
so data must be taken in
3 directions:
Horizontal
Vertical
Axial
On every bearing
Typically once a month
C anne ry M oto r - O E (left ) - H orizonta l - Ac c F req 120 000 C PM
18 /02 /200 0 8 :43: 18
O /A ll 3. 169 m /s /s rm s
1.2
0.8
m/s/s rms
Some machines require
vbOnline system
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0
2 0,0 00
40 ,00 0
6 0,00 0
C PM
80 ,0 0 0
1 00 ,00 0
12 0,0 00
29
�02-12-14
Transfer Data to the Database
Captured data on every
point is stamped with
time and date
All data on the route and
off-route is transferred
to the database
USB
Data can be transferred
using:
High speed USB cables
Network connections
Ethernet
Wireless
LAN
USB Memory Sticks
30
�02-12-14
4. Problem Detection
Vibration levels on every Analysis Parameter on
every point are automatically checked against
its corresponding alarm Limits
Exception Report generates a list of machines
and measurement points that only exceed the
pre-set alarm levels
31
�02-12-14
Alarms in Database Structure
Color Coded Structure
to indicate the
severity of the
problem and its exact
location
32
�02-12-14
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
33
33
�02-12-14
Exception Report
34
�02-12-14
5. Diagnose Nature and Severity of Faults
Every Mechanical, Electrical or
Structural fault has a distinct vibration
behavior
Any changes in the vibration signature
indicate changes in the dynamic
condition of the machine
A single vibration measurement
provides information the machine and
its surrounding structure and other
machinery
35
�02-12-14
Plant
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
36
36
�02-12-14
Machine
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
37
37
�02-12-14
Machine
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
38
38
�02-12-14
Component
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
39
39
�02-12-14
Bearing
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
40
40
�02-12-14
Measurement Location
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
41
41
�02-12-14
Pattern Recognition
42
�02-12-14
Training Courses
Advanced
Training
(> 3 years)
Intermediate
Training (1-2 years)
Basic
Training (4-6 months)
43
�02-12-14
Fault Frequencies
Special calculations are used to indicate where specific
problems can be found on the spectrum called Fault
Frequencies
44
�02-12-14
Advanced Analysis
Orbit - Orbit Example - Side
7/26/2007 2:05:43 PM
Filter: 1X .. 4X
Revolution: 1
0.6
0.4
mils (Vertical)
0.2
-0.2
-0.4
-0.6
-0.8
7/26/2007 2:05:43 PM
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0
mils (Horizontal)
0.2
0.4
0.6
3600 RPM
45
�02-12-14
Steps of a Vibration Program
1. Gather machine information
2. Create database
3. Collect data
4. Detect problems
5. Analyze the nature and the severity of
problems
6. Generate reports on equipment status
7. Follow up on findings
46
�02-12-14
Generating Machine Diagnostic Report
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
47
47
�02-12-14
Title or Job Number | XX Month 201X
48
48
�02-12-14
Steps of a Vibration Program
1. Gather machine information
2. Create database
3. Collect data
4. Detect problems
5. Analyze the nature and the severity of
problems
6. Generate reports on equipment status
7. Follow up on findings
49
�02-12-14
Key Points in a Successful Vibration Program
Trained and committed expertise
Intuitive Software and hardware
Committed management
Clear work process
50
�02-12-14
Some of our customers
51
�02-12-14
QUESTIONS???
52