Modbus Training
What is Modbus ?
An open data communication protocol
Published by Modicon
http://www.modicon.com
Open structure
Flexible
Widely known
Supplied by many SCADA and HMI software
2 serial transmission modes:
ASCII 10 bits
RTU (Binary) 11 bits
Communication interface
RS-232/485
Ethernet (TCP/IP)
Modbus Organization (http://www.modbus.org/default.htm)
P.2
�Types of Modbus:
A leading industrial open control protocol.
Several different types, depending upon the transported media
Modbus RTU - Original Modbus used over RS-232 and RS-485
Modbus ASCII - Similar to Modbus RTU, data is in ASCII instead
of raw binary. This version is mainly used over radio links.
Modbus/TCP - Used over Ethernet - similar to Modbus RTU, but
uses the Ethernet check-sum rather than the RTU check sum.
Modbus over Ethernet - This is a vague term used by some vendors,
but is not an officially recognised name. It is often used to refer to
tunnelling Modbus RTU over Ethernet between two points using
special hardware. Not part of the Modbus standard
Modbus/UDP - similar to Modbus/TCP but uses UDP Ethernet
sockets instead of TCP sockets. not part of the Modbus standard.
Modbus+ - This is a proprietary protocol doesn't follow the Modbus
communications standard. This P.3is rarely encountered.
�Modbus Types of communication
Modbus serial
1) Modbus on RS232(EIA/TIA-232)
2) Modbus on RS422
3) Modbus on RS485(EIA/TIA-485)
4) Transfer method : RTU/ASCII
RTU(Remote Terminal Unit)
ASCII
(American Standard Code For Information
Interchange)
Modbus plus
Modbus TCP/IP
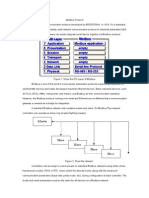
�Modbus Communication Stack
�Modbus network Architecture
�Modbus protocol &
system application
Modbus serial
�Modbus Serial Features I
1. Master-Slave Protocol
-Master: At the same time, only one can be connected only
-Slave : Up to 247 can be connected to
2. Master Request 2 modes
-Unicast mode
Master: request(Query)
Slave : reply(Response)
Address: 1 ~ 247
-Broadcast mode
Master sends a Request to all Slaves
Address: 0
3. Address : 248 ~ 256(reserved)
�Modbus Serial Features II
4. Communication speed
1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200 bps, 56Kbps, 115.2kbps
5. Max communication distance: 1000 m
6. Termination: 150 Ohms / 0.5W
7.1979 years developed by Modicon
8. Token passing by way communication
�General communication frame
(header) : in front of the data field
flag, address, control field
(trailer) : located behind data field
FCS and Flag
(frame check sequence : FCS)
header
Flag
Address Control
trailer
Data
FCS
Flag
�Modbus Serial
Modbus Frame
- PDU : Protocol Data Unit
- Address Field : Slaves Address
-
Function Code : Indicating the command code is performed
- CRC/LRC : Frame Error Check
�Modbus Serial
RTU(Remote Terminal Unit) Mode
�Modbus Serial
ASCII Mode(Frame inside the characters that apply)
FRAME ERROR CHECKING
1. CRC (Cyclical Redundancy Checking) => RTU
2. LRC (Longitudinal Redundancy Checking)=>ASCII
�Modbus protocol frame element
�Function code Definition
�Modbus Frame
(0x02) Read Discrete inputs
�Modbus Frame
(0x03) Read Holding Registers
�Master Query
�Slave Response
�Modbus transaction(exception response)
�Modbus Master AutoSense Feature
Slave
XMIT
Not Enabled
Master
Query
Response
�Modbus Master AutoSense Feature
Master
Query
Response
XMIT
Active
Query
Complete
Response
Slave
�Modbus Plus Frame
HDLC LEVEL
PREAMBL
E
OPENIN
G FLAG
BDCST
ADDRES
S
SOURCE
ADDRES
S
MAC
FUNCTIO
N
MAC / LLC FIELD
CRC
CLOSIN
G FLAG
MAC LEVEL
DEST
ADDRES
S
BYTE
COUNT
LLC
FIELD
LLC LEVEL
OUTPUT
PATH
ROUTER
COUNTE
R
TRANS
SEQUENC
E
ROUTING PATH
MODBUS
FRAME(MODIFIED)
MODBUS MESSAGE
SLAVE
ADDRES
S
FUNCTION
CODE
STARTING
ADDRESS HI
STARTING
ADDRESS
LO
NUMBER OF
REGISTER
HI
NUMBER OF
REGISTER
LO
�The flexibility of Modbus Plus
1. Data Communications
- Modbus Application solution to enhance more
- High-speed connectivity of the host, and improved
operator system
- Event handling of peer to peer communication
-Controller for distributed control interlock between
the easy and reliable
- Bridges and repeaters can be configured in a
flexible
- Schneider's products and products with a variety
of connectivity
2. Programming
Program to upload, download and can be Verify.
- The network connection is available in the eight
programmer productivity was increased.
�Modbus Plus System
Single network with dual cabling, all network traffic is carried
over both cables simultaneously
Available on
Standard on Quantum CPU controller
Quantum and NOM modules
Quantum DIO adapters
AT and VME bus adapters
Cable A
Some PanelMates
Cable B
Bridge Multiplexer and Bridge Plus
Bridge
Excellent for process and safety
Plus
critical applications
Dual cable
Modbus Plus
Network
Single cable
Modbus Plus
Network
�Modbus protocol &
system application
Modbus TCP/IP
�Modbus TCP/IP ADU
- ADU : Application Data Unit
- PDU : Protocol Data Unit
- MBAP : Modbus Application Protocol
- Function Code :What kind of a code indicating the
command is performed
�MBAP Header
�SERVER/CRIENT MODEL
SERVER
INDICATION
RESPONSE
MODBUS TCP/IP
TCP/IP TO MODBUS PLUS
REQUEST
REQUEST
CONFIRMATION
CONFIRMATION
CLIENT1
CLIENT3
CLIENT2
�Communication on and off
Communication Settings
- Modbus message, the program performs a new
communications link for exchanging data with other
devices in order to Port no 502 should provide a listening
socket.
- The local port must be greater than 1024 and each one
client to another are Different.
- Connecting the client and the server exceeds the number of
allowable features
Has not been used for a long time, it is the most closed.
Two. Communications closing (Closing)
- The communication between the client and the server, the
client ends
Was used to initiate the connection to close the connection.
�Communication on and off
�Modbus TCP/IP Features
1. Slave address field of a Modbus Serial line on the MBAP
Header Located in the unit identifier is replaced by a single
byte.
2. Unit identifier is to support multiple independent Modbus unit
Using the IP address of one of the bridges, routers, and devices
such as gateways are used to communicate.
3. Modbus requests and responses are all recipients of the
message Ended been designed so that they can be confirmed.
4. To be performed on Modbus TCP when the length of the
accompanying information Recipient of the message is
unknown, so the range is performed at MBAP.
5. CRC-32 error check code is used.
6. All Modbus / TCP ADU are a registed port 502 over TCP
Sent.
�Modbus TCP/IP mFeatures
Web
server
e-m@il
HTTP
SMTP
I/O
TCP Message Scanner
open
Modbus
Transmission Control Protocol - TCP
Modbus TCP
Read and write data
Update I / O
Benefit: Modbus Device connectivity with the
other is easy. Host computers and OPC servers
directly, without the PLC to communicate with
other devices can send and receive. .
Transparent link to Modbus Serial Devices
Results: The cost is reduced. (Special
equipment is not needed).
Simply build a communication system.
�Modbus TCP/IP Features
Modbus Accepted as Chinese
Standard
Modbus TCP Accepted as
IEC
Publicly Available
Specification
ARC Advisory Study
Places
Modbus TCP in the Lead
MODBUS is the world's most
widely used industrial protocol.
Modbus Ethernet (Modbus TCP) is
the best of the Industrial Ethernet.
By Modbus-IDA is a free, open
protocols.
Communication system, which is
easy to use, simply
Independent media; Ethernet, RS232/485 serial links, wireless, fiber
optic, radio, cellular, etc.
There are hundreds of MODBUS
device.
Modbus is a industrial protocol (IP)
standard to comply with. (Port 502)
�Modbus protocol &
system application
SYSTEM APPLICATION
�Modbus Plus network
�Quantum Hot Standby, the ultimate in high
availability
TCP/IP
Ethernet
TCP/IP Ethernet
To Modbus Plus
Bridge
Redundant cabling
Modbus Plus
Remote I/O
Redundant power
supplies
Primary and standby
controllers
Remote I/O drops
Cable B
Redundant
CPUs140cpu671 60
Remote I/O
processors
Hot standby
processors
Cable A
Fiber optic CHS
processor link
Dual cable
Modbus Plus
Network
Fiber
Optic
CHS
Link
Cable A
Cable B
Dual cable
Remote
I/O
Network
�Electrical Utility Infrastructure
Complete Substation Data Hub
Multi - vendor communications support
Protocol Gateway (Loadable)
Local or remote access
L&G 8979 Gateway to all Substation IEDS
and /or Internet/Intranet
DNP 3.0 Gateway
Modem
Modicon NW BM85D002 BRIDGE MUX
Modicon NW BM85D002 BRIDGE MUX
CURRENT INPUTS
HI
IA
IB
.....
....
IC
LO
Doble
PowerPlex
Bitronics, Inc.
Lehigh Valley, Pa
Made in USA
POWER STATUS
Digital transducer
STATUS
SYSTEM RESETN
VOLTAGE INPUTS
DPU
TARGETS
NORMAL
A
FAIL
B
PICKUP
RECLOSER OUTC
TIME
INSTANTANEOUS 2000R
FREQUENCY
NEGATIVE SEQUENCE
Network
Partner
V1.0
C
E
TARGET RESET
Modbus
POWER POWER
I1
133
I1
A
133
I1
Direct MB+
Devices
9
A
133
DNP 3.0
Gateway
ABB or Schweitzer
Cooper
Gateway
�System Communication
�Modbus TCP/IP
Ethernet TCP/IP and Web technologies
Modbus, industrial & Internet standard
Openness and partnership
Electrical Distribution
Reducing energy costs
Increasing energy availability
and quality
Optimizing electrical equipment
utilization
Automation & Control
Ingenuity of collaboration
Openness of Ethernet TCP/IP
universal network
Simple HMI, with Web
technologies
�Third party connectivity
�Application Structure (general)
Modbus Client (Master)
SCADA
HMI
Internet
RS-232/485
Modbus Device (Slave)
Modbus Device (Slave)
P.42
�Query-Response Cycle
Query
Station Number
Function Code
Data Bytes
(Flexible)
Station Number
Function Code
Data Bytes
(Flexible)
Error Check
Error Check
Response
P.43
�Communication
Client/Server or Master/Slave:
Modbus uses a client/server type protocol. Sometimes referred to as
master/slave. A "master" = "client", while a "slave" = a "server".
The master/slave terms originated in industry, while the
client/server terms originated in the computer industry. Typically,
the client is the PLC or controller, while the server is a field device
such as a valve bank or sensor block.
A "client" sends a request to a "server". The server decodes the
request and sends back a response with the requested data or an
acknowledgement.
Eg. when you use a web browser to view a web page on the
internet, your web browser sends a page request to the web server.
The web server decodes the request and sends back a web page as a
response. Your e-mail client program fetches your e-mail in the
same way from a mail server.
P.44
�Unit ID & Message ID
Unit ID:
A Modbus message includes the unit ID. A unit ID - from 0 and 255
used to identify the server (slave) address in RS-232 or RS-485 networks.
Each server (slave) is assigned a "slave ID" number and listens for
messages which contain this number in the unit ID field.
Modbus/TCP also has the unit ID in its messages, but the Ethernet TCP/IP
address is used to decide where to actually delivery the message. Many or
most server devices will ignore the unit ID. However, some will use the unit ID
to decide whether to forward the message out a built-in serial port. This
message forwarding allows older RS-485 devices to be used on newer
Ethernet networks. Support for this feature is only found in a few devices.
Message ID:
When a Modbus message sends a request, it includes a message ID number.
from 0 to 65,535. It is incremented by the client for each request (and
will roll over to 0 again when it overflows).
This message ID is echoed back by the server. The client can use this
message ID number to determine
if any messages are being lost or
P.45
delayed in transmission.
�Hardware Classification
Station Device: 0 ~ 255
Digital input module
1xxxx: 4 digits for hexadecimal address (0000 ~ FFFF)
1xxxxx: 5 digital for decimal address (0 ~ 65535)
Digital output module
0xxxx: 4 digits for hexadecimal address (0000 ~ FFFF)
0xxxxx: 5 digital for decimal address (0 ~ 65535)
Analog input module
3xxxx: 4 digits for hexadecimal address (0000 ~ FFFF)
3xxxxx: 5 digital for decimal address (0 ~ 65535)
Analog output module
4xxxx: 4 digits for hexadecimal address (0000 ~ FFFF)
4xxxxx: 5 digital for decimal address (0 ~ 65535)
Begining of Address
From 0: VLC
From 1: InduSoft, iFix
P.46
�Two Serial Transmission Modes
ASCII Mode
Data system
ASCII character, 0~9,A~F
Bits per data unit
1 Start Bit
7 Data Bits
1 Parity Bit (Even/Odd)
1 Start Bit
7 Data Bits
2 Stop Bit
1 Stop Bit
Error Check Field
Longitudinal Redundancy Check (LRC)
RTU Mode
Data system
8-bit Binary, 00~FF
Bits per data unit
1 Start Bit
8 Data Bits
1 Parity Bit (Even/Odd)
1 Start Bit
8 Data Bits
2 Stop Bit
Error Check Field
Cyclical Redundancy Check (CRC)
P.47
1 Stop Bit
�Modbus Message Packet
ASCII Mode
Start
1 Char
Station Number
2 Chars
Function Code
2 Chars
Data
n Chars
Error Check
2 Chars
LRC
End
2 Chars
CR,LF
Start
Station Number
Function Code
Data
Error Check
End
3.5 Char
Silence
1 Char
1 Char
n Chars
2 Chars
CRC
3.5 Chars
Silence
RTU Mode
Modbus Plus network
Prefixed Data
Station Number
Function Code
6 x 8Byte
Bits 0, 1: transaction ID usually 0
Byte 2, 3: protocol ID = 0
Byte 4, 5: number of bytes following
P.48
Data
�Modbus Function Code
01: read DOs (0xxxx)
02: read DIs (1xxxx)
03: read AOs (4xxxx)
04: read AIs (3xxxx)
05: write single DO (0xxxx)
06: write single AO (4xxxx)
15: wirte DOs (0xxxx)
16: write AOs (4xxxx)
P.49
�System Application
Multi Serial Clients (Masters)
Multi Modbus/TCP Clients (Masters)
command protocol depend on serial
devices
Internet
Modbus/TCP command protocol
VxComm Technique
Modbus/TCP Slave
RS-485
RS-232
P.50
�System Application
Multi Modbus/TCP Clients (Masters)
Modbus/TCP
Internet
Modbus/RTU
Modbus/RTU
P.51
�8000E MTCP Features
Supports Modbus/TCP communication protocol to access I/Os that plug on slots
Supports VxComm technique for every COM port of controllers
Auto scan I/O modules
Automatically range register address of I/O modules
Allows multi-client (or master) access simultaneously
Online configuration (using Modbus Utility via Ethernet)
Supports I-8000 and I-87000 series I/O modules
Firmware updateable and programmable
P.52
�Tools
MiniOS7 Utility (Download files and update OS
image)
PCDiag (Diagnostic tools)
NAP OPC Server (Check I/O action quickly)
MBTCP.exe (Check Modbus/TCP package details)
MBRTU.exe (Check Modbus/RTU package
details)
P.53
�8000E-MTCP Program Block
Modbus Client (Master)
Modbus protocol
SCADA
User-defined protocol
HMI
Modbus Embedded Controller
Check Modbus Request
Update I/O
RS-485
Run User Process
.. .
I-7000
I-7000
I-87K
RS-232
PLC
P.54
�8000E -MTCP SDK Features
2 communication protocols
User-defined: port 10000
Modbus/TCP: port 502
4 Internal register tables
(MTDemo50)
iMemory_DI
Points of DI module plug on slots
User-defined
iMemory_DO
Points of DO module plug on slots
User-defined
iMemory_AI
Points of AI module plug on slots
User-defined
Points of AO module plug on slots
User-defined
iMemory_AO
Access I/Os that plug on slots
Link I-7000 or I-87000 series modules via COM ports
(MTDemo51)
(MTDemo52)
Modbus/RTU master
(MTDemo53)
P.55
�P.56
�User-defined Internal Register
Modbus/TCP
Write
Modbus Kernel
Read
Slot
iMemory_DI
iMemory_DO
RS-232
User Process
iMemory_AI
iMemory_AO
RS-485
.. .
I-7000
P.57
I-7000
I-87K
�Be a Modbus/RTU Master
iMemory_DI
iMemory_DO
User Process
iMemory_AI
Modbus/RTU
iMemory_AO
Modbus/RTU
User-defined Input
Input
User-defined Output
Output
int ModbusMaster2Slave(int iPort,unsigned char cNetID, unsigned char cFunction,
int iControllerMemoryBaseAddress, int iDeviceMemoryBaseAddress,int iIOCount);
P.58
�Modify 8000E-MTCP Firmware
User.c
void UserInit(void)
{
int iRet;
iRet=InitModbus();
}
void UserLoopFun(void)
{
UpdateIOModule();
CheckModbusRequest(iModbusUpLinkPort); //Is any Modbus/RTU request from COM port ?
CheckLEDMenu();
}
int UserCmd(unsigned char *Cmd,unsigned char *Response)
{
int iRet;
if(Cmd[0]=='!')
iRet=Configuration(Cmd,Response);
return 1;
}
P.59
�Modify 8000E-MTCP Firmware
MBTCP_8E.h
//Memory base address of every slot
extern unsigned int iMemoryAddr_DI[8];
extern unsigned int iMemoryAddr_DO[8];
extern unsigned int iMemoryAddr_AI[8];
extern unsigned int iMemoryAddr_AO[8];
//I/O points of every slot
extern unsigned int iMemoryNum_DI[8];
extern unsigned int iMemoryNum_DO[8];
extern unsigned int iMemoryNum_AI[8];
extern unsigned int iMemoryNum_AO[8];
//The I/O values
extern unsigned char* iMemory_DI;
extern unsigned char* iMemory_DO;
extern int*
iMemory_AI;
extern int*
iMemory_AO;
//Total DI,DO,AI,AO points
extern int iDINum,iDONum,iAINum,iAONum;
P.60
�7188E-MTCP System Application
Multi Serial Master (Clients)
command protocol
depend on serial
devices
Multi Modbus/TCP Masters (Clients)
Internet
Modbus/TCP
command protocol
Modbus/RTU command
protocol
VxComm Technique
RS-232/485
Modbus/RTU
RS-485
RS-232
P.61
Single Modbus/RTU Masters (Clients)
�7188E-MTCP COM Port Enable Mode
VxComm (Virtaul COM)
Modbus/RTU Links to Modbus/RTU slave
devices
Programming Links to RS-232/485/422
devices (controlled by users program)
UpLink Links to a Modbus/RTU master
device
Debug Prints out communication messages
P.62
�7188E-MTCP Internal Block
Modbus Client (Master)
Modbus protocol
SCADA
User-defined protocol
HMI
Modbus Embedded Controller
Expansion Bus
X board
Check Modbus Request
RS-485
Read/Write I/O
Run User Process
I-7000
RS-232
P.63
I-7000
Modbus/RTU
I-87K
�7188E-MTCP Features
Converts single Modbus/TCP to multi
Modbus/RTU (Modbus/TCP slave port)
Converts single Modbus/RTU to multi
Modbus/RTU (Modbus/RTU slave port)
Supports VxComm technique for every COM
port of controllers
Allowed multi-client (or master) access
simultaneously
Firmware updateable and programmable
P.64
�7188E-MTCP SDK Features
Modbus/TCP to Modbus/RTU converter
4 Internal register tables
(Default function)
(MTDemo00)
User-defined
iMemory_DI
User-defined
iMemory_DO
User-defined
iMemory_AI
User-defined
iMemory_AO
Link I-7000 or I-87000 series modules via COM
ports
Access X-board
Modbus/RTU master
(MTDemo01)
(MTDemo02)
(MTDemo03)
P.65
�User-defined Internal Register (7188XB,7188E)
Modbus/TCP
Write
Modbus Kernel
Read
Expansion Bus
X board
iMemory_DI
iMemory_DO
RS-232
User Process
iMemory_AI
iMemory_AO
RS-485
.. .
I-7000
P.66
I-7000
I-87K
�Modbus/RTU master (7188XB,7188E)
iMemory_DI
iMemory_DO
User Process
iMemory_AI
Modbus/RTU
iMemory_AO
Modbus/RTU
User-defined Input
Input
User-defined Output
Output
int ModbusMaster2Slave(int iPort,unsigned char cNetID, unsigned char cFunction,
int iControllerMemoryBaseAddress, int iDeviceMemoryBaseAddress,int iIOCount);
P.67
�Modbus Gateway Application 1
Original system: one PC connect to a
HoneyWell PLC
Requirement: allow two extra PCs to
connect to the same PLC
Problem: the communication interface of
the PLC is RS-232.
RS-232 is point to point interface, it
cannot links 4 devices (3 PCs + 1 PLC)
HoneyWell
Modbus/RTU device
iFix (A)
RS-232 @ 38400 bps
iFix (B)
iFix (C)
P.68
�Thinking 1 (RS-485 method)
Thinking: RS-485 is a broadcast interface.
Change to RS-485 interface can allow all PCs
communicate with the PLC.
Problem: The PLC will broadcast its response
to every PC.
The two PCs will feel confuse.
iFix (A)
Final: Doesnt work
2
Response
iFix (B)
2
Request
iFix (C)
P.69
�Thinking 2 (Ethernet to RS-232 converter)
Thinking: the converter allow the 3 PCs share
one COM port
Problem: The communication band width is
shared by the 3 PCs.
Thus the communication efficiency
becomes 1/3.
iFix (A)
Ethernet/RS-232
converter
Hub
iFix (A)
COM1 @ 38400 bps
11 7
3
Modbus/RTU
8 Response
Final: Works but not efficient.
Modbus/RTU
Request
iFix (A)
Modbus/RTU
Response
Modbus/RTU
Request
12
9
P.70
10
HoneyWell
Modbus/RTU device
�Thinking 3 (Modbus/TCP Gateway)
Thinking: Doesnt need to install extra VxComm driver on the PC
Problem: The communication band width is shared by the 3 PCs.
Thus the communication efficiency becomes 1/3.
Final: Works but inefficient.
iFix (A)
7188E-MTCP
4
Hub
1
iFix (B)
Modbus/RTU
Response
11 7
3
Modbus/TCP
Response
Modbus/TCP
Request
iFix (C)
COM1 @ 38400 bps
Modbus/RTU
Request
12
9
P.71
10
HoneyWell
Modbus/RTU device
�Thinking 3 (Modbus/TCP Gateway)
Thinking: 7188E polls PLCs memory to its share
memory
The 3 PCs get PLCs data from the share
memory
Goods: Ethernet communication is much faster
than RS-232, 2
The 31 PCs can get PLC data in very short
B
time (less than 1 second)
iFix (A)
7188E-MTCP
Hub
COM1 @ 38400 bps
iFix (B)
Share
Memory
Modbus/TCP
4 Response
Modbus/TCP
Request
Final: Works and efficient
iFix (C)
6
5
P.72
Modbus/RTU
Request
Modbus/RTU
Response
HoneyWell
Modbus/RTU device
�Modbus Gateway Application 2
Original system: one ABB DCS connect to one
AB PLC
Requirement: The system needs to include
two AB PLC more.
AB PLC #1
RS-232 @ 9600 bps
AB PLC #2
Problem: The communication interface of the
DCS and PLC is RS-232
AB PLC #3
P.73
�Solution
Hardware: 7188XB + X505 = 4* RS-232 port +
1* RS-485
7188XB
ABB DCS
AB PLC #1
Software: 7188XB polls 3 AB PLCs data to its
share memory
ABB DCS access the 7188XB to get all
data of the 3 AB PLCs
Share
Memory
RS-232 @ 9600 bps
Analog Output
AB PLC #2
Analog Input
DI
DO
AI
AO
AB PLC #3
Analog Input
P.74
�Multi PC access PLCs on the same RS-485
Polling PLCs backgroundly
7188E-MTCP
2
Hub
Share
Memory
Modbus/TCP
Response
Modbus/TCP
Request
Modbus/RTU
Response
RS-485
B
A
Modbus/RTU
Request
PLC#1
6
5
P.75
PLC#2
PLC#3