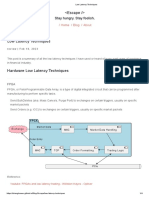
PC Assembly &
Hardware Maintenance
Information Technology Center
University of Peradeniya
�How a Computer System Works
Input
Processing
Output
Storage
�What is a Computer System
Computer System
Hardware
Software
Input H/W
Application S/W
Output H/W
System S/W
Live Ware
Storage H/W
Processing H/W
3
�What is Computer Hardware
All tangible physical components (inside or
outside) of a computer system
Examples :
Keyboard,
Mouse, Scanner
Printer, Monitor, Plotter
CD drive, Floppy drive, Hard disk, RAM
NIC, CPU, Motherboard, etc
4
�Identify Hardware Components
1.
2.
Physical identification
Just by looking at (observing) the
components
Using Software
Use a software application to identify the
hardware components & configuration
�Common Hardware
Motherboard
Keyboard, Mouse, Touchpad, Light pen
Scanner
Speakers
Monitor
Printer
Laser
printer
Ink jet, bubble jet
Line printer, Dot-matrix printer
�Common Hardware Cntd
How to connect
Why a driver is needed
�Computer Monitor
CRT (Cathode Ray Tube)
LCD (Liquid Crystals Display)
Aspect Ratio - ratio of the width of the
display screen to the height (Ex:- 4:3,
Wide Screen 16:9)
Screen size - measured in inches from
one corner to the corner diagonally across
from it (Ex:- 15. 17, 19, 21)
�Computer Monitor cntd.
Refresh rate Number of times that the
image on the screen is drawn in each
second
Resolution Total Number of pixels in the
screen
Written as (number of pixels in to Width X
number of pixels in to height)
Ex: 640X480, 800X600, 1024X768,
1600X1200, etc
�Computer Monitor cntd.
Colour bit depth number of bits used
to describe a pixel
Bit-Depth
Number of Colors
2 (monochrome)
4 (CGA)
16 (EGA)
256 (VGA)
16
65,536 (High Color, XGA)
24
16,777,216 (True Color,
SVGA)
32
16,777,216 (True Color +
Alpha Channel)
10
�How a CRT Monitor works
A CRT monitor contains millions of tiny
red, green, and blue phosphor dots that
glow when struck by an electron beam
Use three independent electron guns
11
�How a CRT Monitor works cntd..
12
�How a LCD Monitor works
There are some substances that can exist
in an odd state that is sort of like a liquid
and sort of like a solid
Liquid Crystals are neither a solid nor a
liquid
How to recover stuck pixels in LCD
13
�Inside the System Unit
Processor
Mother board
RAM
Cache
Hard disk
Optical disk drives
Floppy disk drives
VGA
Network Card, Sound Card, Modem
14
�The CPU (Central Processing
Unit)
Abbreviation for Central Processing Unit
The CPU is the brain of the computer
On personal computers and small
workstations, the CPU is housed in a
single chip called a microprocessor
CPUs are small and square and contain
multiple metallic connectors or pins on the
underside
15
�CPU
16
�A Dual CPU computer
17
�CPU
The CPU is inserted directly into a CPU
socket, pin side down, on the motherboard
Each motherboard will support only a
specific type or range of CPU
There are two typical components of a
CPU
arithmetic logic unit (ALU) -Performs
arithmetic and logical operations
control unit (CU) - which extracts instructions
from memory and decodes and executes
18
�Microprocessor
A silicon chip that contains a CPU or a
computer processor on a microchip
The terms microprocessor and CPU are
used interchangeably
Microprocessors also control the logic of
almost all digital devices, from clock radios
to fuel-injection systems for automobiles
19
�Characteristics of Microprocessors
Instruction set: The set of instructions that the
microprocessor can execute
bandwidth : The number of bits processed in a
single instruction
clock speed : Given in megahertz (MHz), the
clock speed determines how many instructions
per second the processor can execute.
The higher the value, more powerful the CPU
20
�Some Processor Models
Intel
Intel
Core i7 Processor
Intel Core2 Extreme processor
Intel Core2 Quad Processor
Intel Core 2 Duo
AMD
AMD
Athlon 64 X2 Dual-Core
AMD Athlon X2 Dual-Core
21
�Some Processor Models Cntd..
CYRIX
CYRIX
5x86
CYRIX 486
IBM
IBM
PPC750GX/GL
Comparisson on Intel Processors from
www.intel.com web site
22
�Characteristics of Microprocessors
Example : a 32-bit microprocessor that
runs at 50MHz is more powerful than a 16bit microprocessor that runs at 25MHz
23
�Motherboard
Central circuit board connecting all
components together
Form Factor
Sockets
Chipset
Bus
Slots
Other features
24
�Form Factor
Shape & layout of a motherboard
Determines what kind of PC case the
motherboard can fit into
Determines what types of components it
can hook up
Ex: ATX, mini ATX
ATX- Advanced Technology Extended
25
�Sockets
Place where the CPU is hooked up on the
motherboard
Determines what kind of CPU it can use
Earliest socket type is socket 7
Socket
PGA 478, PGA 423 - for older Pentium
and Celeron processors
Socket LGA 775 - for Pentium Dualcore &
pentium4
26
�Sockets cnt.
Socket
PGA 754 - for AMD Sempron and
some AMD Athlon processors
Socket PGA 939 - for newer and faster AMD
Athlon processors
PGA Pin Grid Array
LGA Land Grid Array (pins are part of
the socket)
27
�Picture of a Sockets
�Chipset
Chipset is usually made up of the
Northbridge and the Southbridge
29
�Chipset cnt
Northbridge and the Southbridge connect
the processor to other parts of the
computer
Chipset can not be upgraded or replaced
30
�CPU
31
�Northbridge
Connect directly to CPU via the front side
bus (FSB)
Connects to the AGP or PCI Express bus
and the memory to itself
A memory controller is located on the
Northbridge, which gives the CPU fast
access to the memory.
32
�Southbridge
Slower than the Northbridge
information from the CPU has to go
through the Northbridge before reaching
the Southbridge
Other busses connect the Southbridge to
the PCI bus, the USB ports and the IDE or
SATA hard disk connections.
33
�Bus
A circuit (path) that connects one part of
the motherboard to another
If the bus can handle more data at a time it
can transfer data fast
Speed measured in megahertz (MHz)
Bus speed usually refers to the speed of
the front side bus (FSB)
FSB - connects the CPU to the
Northbridge
34
�Bus cntd.
The back side bus connects the CPU with
the level 2 (L2) cache (secondary or
external cache)
The faster a computer's bus speed, the
faster it will operate
35
�Slots in Motherboard
PCI - Peripheral Component Interconnect
Used
to connect Network cards, Sound cards,
etc
ISA - Industry Standard Architecture
Used
to connect older VGA
AGP - Accelerated Graphics Port
targeted
at 3D graphical display applications
Several versions
36
�37
�AGP versions
AGP 1.0
1x
(266Mbps) (8 bytes per two clock cycles)
2x (533Mbps) (8 bytes per clock cycle)
AGP 2.0
1x
(266Mbps) (8 bytes per two clock cycles)
2x (533Mbps) (8 bytes per clock cycle)
4x (1.07Gbps) (16 bytes per clock cycle)
38
�AGP versions Cntd
AGP Pro
1x
(266Mbps) (8 bytes per two clock cycles)
2x (533Mbps) (8 bytes per clock cycle)
4x (1.07Gbps) (16 bytes per clock cycle)
AGP 3.0
1x
(266Mbps) (8 bytes per two clock cycles)
2x (533Mbps) (8 bytes per clock cycle)
4x (1.07Gbps) (16 bytes per clock cycle)
8x (2.1Gbps) (32 bytes per clock cycle)
39
�Other Features in Motherboard
Onboard VGA
Onboard Network
Onboard Sound
40
�Main memory (RAM)
Physical memory that is internal to the
computer
Another term for main memory is RAM
RAM - Random Access memory
The CPU can manipulate only data that is
in main memory
Every program you execute and every file
you access must be copied from a storage
device into main memory
41
�Main memory
The amount of main memory on a
computer is crucial
Computers often have too little main
memory
There are two different types of RAM
DRAM
(Dynamic Random Access Memory)
SRAM (Static Random Access Memory)
42
�DRAM Vs SRAM
Differ in the technology they use to hold
data
DRAM being the more common type
In terms of speed, SRAM is faster
DRAM needs to be refreshed thousands of
times per second while SRAM does not
need to be refreshed
SRAM is faster than DRAM
43
�DRAM Vs SRAM
Despite SRAM being faster, it's not as
commonly used as DRAM because it's so
much more expensive
Both types of RAM are volatile
44
�SDRAM
Synchronous DRAM
Synchronous Dynamic Random Access
Memory
SDRAM can run at 133 Mhz
45
�DDR RAM
DDR RAM - Double-Data-Rate RAM
DDR RAM is based on the same
architecture as SDRAM
Very fast computer memory
46
�DDR1 vs DDR2
DDR1 Memory
DDR2 Memory
Module package
184-pin DIMM/ 200-pin
SODIMM
240-pin DIMM/ 200-pin
SODIMM
Speeds (in
MHz)
200, 266, 333, 400
400, 533, 667
Voltage
2.5 volt
1.8 volt
Chip package
TSOP/BGA
FBGA
Module
Bandwidth
E
Up to 6.4GB/second
Up to 10.6GB/second
Chip densities
Up to 1Gb
Up to 4Gb
CAS Latency
2/2.5
3/4
47
�Cache Memory
A special high-speed storage mechanism
It can be either a reserved section of main
memory or an independent high-speed
storage device
Two types of caching
memory
caching
disk caching
48
�Cache Memory
Also called a cache store or RAM cache
is a portion of memory made of highspeed Static RAM (SRAM) instead of the
slower and cheaper Dynamic RAM
(DRAM) used for main memory
Memory caching is effective because most
programs access the same data or
instructions over and over
49
�Cache Memory
By keeping as much of this information as
possible in SRAM, the computer avoids
accessing the slower DRAM
Some memory caches are built into the
architecture of microprocessors
Example : The Intel 80486
microprocessor, contains an 8Kb memory
cache and the Pentium has a 16Kb cache
50
�Cache Memory
Such internal caches are often called
Level 1 (L1) caches
Most modern PCs also come with external
cache memory, called Level 2 (L2) caches
51
�L2 cache
Short for Level 2 cache
Cache memory that is external to the
microprocessor
Also called the secondary cache
Resides on a separate chip from the
microprocessor chip
52
�Disk caching
Works under the same principle as
memory caching
Instead of using high-speed SRAM, a disk
cache uses conventional main memory
(RAM)
The most recently accessed data from the
disk (as well as adjacent sectors) is stored
in a memory buffer
53
�Disk caching
When a program needs to access data
from the disk, first checks the disk cache
to see if the data is there
Disk caching can dramatically improve the
performance of applications
because accessing a byte of data in RAM
can be thousands of times faster than
accessing a byte on a hard disk
54
�Cache hit
When data is found in the cache, it is
called a cache hit
Effectiveness of a cache is judged by its
cache hit rate
55
�Hard disk
Non Volatile
Less Expensive
Slower than RAM
How Hard disk Works
56
�ATA, SATA and SATA II
ATA - Advanced Technology Attachment
ATA hard drives also known as IDE or
'Integrated Drive Electronics'
SATA - Serial Advanced Technology
Attachment
Electronic method of transferring information
(data) backwards and forwards between the
hard drive and the rest of the computer
57
�ATA
ATA standard has moved through seven
recognized phases, (ATA-1, 2, 3, etc)
These could make data transfer rates of
up to133 MB/sec
ATA, PATA and IDE similar
ATA is based on a 16 bit parallel interface
ATA hard drive uses a ribbon cable with
40 channels
58
�SATA
in the year 2000, hard drive technology
came up with a new hard drive standard
called Serial ATA
SATA cable which only has 7 wires
SATA hard drives operate cooler and on
higher bandwidths which equates to faster
data transfer
150 MB/second
59
�SATA
as of 2004 the new SATA II standard
allows for transfer rates of 300 MB/second
60
�Software tools to detect Hardware
DirectX :run
dxdiag
System Information :
Accessories
System tools
BIOS setup utility
Available other software tools (CPUID,
AIDA32, etc)
61
�Identify Hardware using Software
Processor
Speed
Type
Main memory (RAM)
Size
Speed
Bus Speed
Cache
62
Lab Sheet 1
�Preparing Specifications
64