A small program that calculates and prints terms of the Fibonacci series
; fibo.asm
; assemble using nasm:
; nasm -o fibo.com -f bin fibo.asm
;
;****************************************************************************
; Alterable Constant
;****************************************************************************
; You can adjust this upward but the upper limit is around 150000 terms.
; the limitation is due to the fact that we can only address 64K of memory
; in a DOS com file, and the program is about 211 bytes long and the
; address space starts at 100h. So that leaves roughly 65000 bytes to
; be shared by the two terms (num1 and num2 at the end of this file). Since
; they're of equal size, that's about 32500 bytes each, and the 150000th
; term of the Fibonacci sequence is 31349 digits long.
;
maxTerms
equ 15000
; number of terms of the series to calculate
;****************************************************************************
; Number digits to use. This is based on a little bit of tricky math.
; One way to calculate F(n) (i.e. the nth term of the Fibonacci seeries)
; is to use the equation int(phi^n/sqrt(5)) where ^ means exponentiation
; and phi = (1 + sqrt(5))/2, the "golden number" which is a constant about
; equal to 1.618. To get the number of decimal digits, we just take the
; base ten log of this number. We can very easily see how to get the
; base phi log of F(n) -- it's just n*lp(phi)+lp(sqrt(5)), where lp means
; a base phi log. To get the base ten log of this we just divide by the
; base ten log of phi. If we work through all that math, we get:
;
; digits = terms * log(phi) + log(sqrt(5))/log(phi)
;
�; the constants below are slightly high to assure that we always have
; enough room. As mentioned above the 150000th term has 31349 digits,
; but this formula gives 31351. Not too much waste there, but I'd be
; a little concerned about the stack!
;
digits
equ (maxTerms*209+1673)/1000
; this is just the number of digits for the term counter
cntDigits equ 6
org
100h
; number of digits for counter
; this is a DOS com file
;****************************************************************************
;****************************************************************************
main:
; initializes the two numbers and the counter. Note that this assumes
; that the counter and num1 and num2 areas are contiguous!
;
mov
ax,'00'
; initialize to all ASCII zeroes
mov
di,counter
; including the counter
mov
cx,digits+cntDigits/2
cld
; two bytes at a time
; initialize from low to high memory
rep
stosw
; write the data
inc
ax
; make sure ASCII zero is in al
mov
[num1 + digits - 1],al ; last digit is one
mov
[num2 + digits - 1],al ;
mov
[counter + cntDigits - 1],al
jmp
.bottom
.top
; add num1 to num2
mov
di,num1+digits-1
; done with initialization, so begin
�mov
si,num2+digits-1
mov
cx,digits
call
AddNumbers; num2 += num1
mov
bp,num2
call
PrintLine
dec
dword [term]
jz
.done
;
;
; decrement loop counter
; add num2 to num1
mov
di,num2+digits-1
mov
si,num1+digits-1
mov
cx,digits
call
AddNumbers; num1 += num2
.bottom
mov
bp,num1
call
PrintLine
dec
dword [term]
jnz
.top
call
CRLF
; finish off with CRLF
mov
ax,4c00h
; terminate
int
21h
;
; decrement loop counter
.done
;****************************************************************************
;
; PrintLine
; prints a single line of output containing one term of the
; Fibonacci sequence. The first few lines look like this:
;
; Fibonacci(1): 1
; Fibonacci(2): 1
�; Fibonacci(3): 2
; Fibonacci(4): 3
;
; INPUT:
; OUTPUT:
ds:bp ==> number string, cx = max string length
CF set on error, AX = error code if carry set
; DESTROYED: ax, bx, cx, dx, di
;
;****************************************************************************
PrintLine:
mov
dx,eol
; print combined CRLF and msg1
mov
cx,msg1len+eollen ;
call
PrintString
mov
di,counter
; print counter
mov
cx,cntDigits ;
call
PrintNumericString
call
IncrementCount
; also increment the counter
mov
dx,msg2
; print msg2
mov
cx,msg2len ;
call
PrintString
mov
di,bp
; recall address of number
mov
cx,digits
; deliberately fall through to PrintNumericString
;****************************************************************************
;
; PrintNumericString
; prints the numeric string at DS:DI, suppressing leading zeroes
; max length is CX
�;
; INPUT:
ds:di ==> number string, cx = max string length
; OUTPUT:
CF set on error, AX = error code if carry set
; DESTROYED: ax, bx, cx, dx, di
;
;****************************************************************************
PrintNumericString:
; first scan for the first non-zero byte
mov
al,'0'
cld
; look for ASCII zero
; scan from MSD to LSD
repe
scasb
mov
dx,di
; points to one byte after
dec
dx
; back up one character
inc
cx
; deliberately fall through to PrintString
;****************************************************************************
;
; PrintString
; prints the string at DS:DX with length CX to stdout
;
; INPUT:
ds:dx ==> string, cx = string length
; OUTPUT:
CF set on error, AX = error code if carry set
; DESTROYED: ax, bx
;
;****************************************************************************
PrintString:
mov
mov
int
ret
bx, 1
; write to stdout
ah, 040h
21h
; write to file handle
; ignore return value
;
�;****************************************************************************
;
; AddNumbers
; add number 2 at ds:si to number 1 at es:di of width cx
;
;
; INPUT:
es:di ==> number1, ds:si ==> number2, cx= max width
; OUTPUT:
CF set on overflow
; DESTROYED: ax, si, di
;
;****************************************************************************
AddNumbers:
std
; go from LSB to MSB
clc
pushf
; save carry flag
.top
mov
ax,0f0fh
; convert from ASCII BCD to BCD
and
al,[si]
; get next digit of number2 in al
and
ah,[di]
; get next digit of number1 in ah
popf
adc
; recall carry flag
al,ah
; add these digits
aaa
; convert to BCD
pushf
add
al,'0'
stosb
; convert back to ASCII BCD digit
; save it and increment both counters
dec
si
loop
.top
; keep going until we've got them all
popf
; recall carry flag
ret
;****************************************************************************
;
�; IncrementCount
; increments a multidigit term counter by one
;
; INPUT:
none
; OUTPUT:
CF set on overflow
; DESTROYED: ax, cx, di
;
;****************************************************************************
IncrementCount:
mov
cx,cntDigits ;
mov
di,counter+cntDigits-1
std
; go from LSB to MSB
stc
; this is our increment
pushf
; save carry flag
.top
mov
ax,000fh
; convert from ASCII BCD to BCD
and
al,[di]
; get next digit of counter in al
popf
adc
; recall carry flag
al,ah
; add these digits
aaa
; convert to BCD
pushf
add
al,'0'
stosb
loop
; convert back to ASCII BCD digit
; save and increment counter
.top
popf
; recall carry flag
ret
;****************************************************************************
;
; CRLF
; prints carriage return, line feed pair to stdout
;
�; INPUT:
none
; OUTPUT:
CF set on error, AX = error code if carry set
; DESTROYED: ax, bx, cx, dx
;
;****************************************************************************
CRLF: mov
dx,eol
mov
cx,eollen
jmp
PrintString
;****************************************************************************
; static data
;****************************************************************************
eol
db 13,10
; DOS-style end of line
eollen equ $ - eol
msg1 db 'Fibonacci('
msg1len
equ $ - msg1
msg2 db '): '
msg2len
equ $ - msg2
;****************************************************************************
; initialized data
;****************************************************************************
term dd maxTerms
;****************************************************************************
; unallocated data
;
; A better way to do this would be to actually ask for a memory
; allocation and use that memory space, but this is a DOS COM file
; and so we are given the entire 64K of space. Technically, this
; could fail since we *might* be running on a machine which doesn't
; have 64K free. If you're running on such a memory poor machine,
�; my advice would be to not run this program.
;
;****************************************************************************
; static data
counter:
num1 equ counter+cntDigits
num2 equ num1+digits
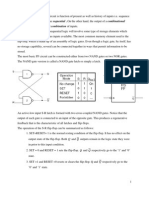
Alarm
cseg segment para public 'code'
org
100h
alarm proc far
; Memory-resident program to intercept the timer interrupt and display the
; system time in the upper right-hand corner of the display.
; This program is run as 'ALARM hh:mm x', where hh:mm is the alarm time and
; x is '-' to turn the display off. Any other value of x or no value will
; turn the clock on
intaddr equ 1ch*4
; interrupt address
segaddr equ 62h*4
; segment address of first copy
mfactor equ 17478
; minute conversion factor * 16
whozat
equ 1234h
color equ 14h
; signature
; color attribute
assume cs:cseg,ds:cseg,ss:nothing,es:nothing
jmp p150
; start-up code
jumpval dd 0
; address of prior interrupt
signature dw whozat
; program signature
state db 0
; '-' = off, all else = on
�wait
dw 18
; wait time - 1 second or 18 ticks
hour dw 0
; hour of the day
atime dw 0ffffh
; minutes past midnite for alarm
acount
dw 0
atone db 5
; alarm beep counter - number of seconds (5)
; alarm tone - may be from 1 to 255 - the
; higher the number, the lower the frequency
aleng dw 8080h
dhours
dw 0
; alarm length (loop count) may be from 1-FFFF
; display hours
db ':'
dmins dw 0
; display minutes
db ':'
dsecs dw 0
; display seconds
db '-'
ampmdb 0
; 'A' or 'P' for am or pm
db 'm'
tstack db 16 dup('stack ') ; temporary stack
estack
db 0
; end of stack
holdsp
dw 0
; original sp
holdssdw 0
; original ss
p000:
; interrupt code
push ax
; save registers
push ds
pushf
push cs
pop ds
mov ax,wait
dec ax
jz p010
; make ds=cs
; check wait time
; zero?
; yes - 1 second has elapsed
�mov wait,ax
; not this time
jmp p080
; return
p010: cli
mov ax,ss
; disable interrupts
; save stack
mov holdss,ax
mov holdsp,sp
mov ax,ds
mov ss,ax
; point to internal stack
mov sp,offset estack
sti
; allow interrupts
push bx
; save other registers
push cx
push dx
push es
push si
push di
push bp
mov ax,18
; reset wait time
mov wait,ax
mov al,state
; are we disabled?
cmp al,'-'
jnz p015
; no
jmp p070
p015: mov ah,0
; read time
int 1ah
; get time of day
mov ax,dx
; low part
mov dx,cx
; high part
�mov cl,4
shl dx,cl
; multiply by 16
mov bx,ax
mov cl,12
shr bx,cl
; isolate top 4 bits of ax
add dx,bx
; now in upper
mov cl,4
shl ax,cl
; multiply by 16
mov bx,mfactor
div bx
; compute minutes
; minutes in ax, remainder in dx
cmp ax,atime
; time to sound the alarm?
jnz p020
; no
call p100
; yes - beep the speaker twice
push ax
mov ax,acount
; get beep count
dec ax
; down by 1
mov acount,ax
; save beep count
cmp ax,0
; is it zero?
jnz p018
; no - keep alarm on
mov ax,0ffffh
; turn off alarm
mov atime,ax
p018: pop ax
p020: mov dsecs,dx
; save remainder
mov bx,60
; compute hours
xor dx,dx
; zero it
div bx
; hours in ax, minutes in dx
mov dmins,dx
; save minutes
cmp ax,0
; midnight?
jnz p030
; no
mov ax,12
; yes
�jmp p040a
p030: cmp ax,12
; set am
; before noon?
jb p040a
; yes - set am
jz p040p
; noon - set pm
sub ax,12
; convert the rest
p040p:
mov bl,'p'
jmp p040x
p040a:
mov bl,'a'
p040x:
mov ampm,bl
aam
; fix up hour
cmp ax,hour
; top of the hour?
jz p060
; no
mov hour,ax
call p120
p060: add ax,3030h
; beep the speaker once
; convert hours to ascii
xchg ah,al
mov dhours,ax
mov ax,dmins
; get minutes
aam
add ax,3030h
; convert to ascii
xchg ah,al
mov dmins,ax
mov ax,dsecs
xor dx,dx
mov bx,60
; get seconds (remainder)
�mul bx
mov bx,mfactor
div bx
; seconds in ax
aam
add ax,3030h
xchg ah,al
mov dsecs,ax
xor ax,ax
; check monitor type
mov es,ax
mov ax,es:[410h]
; get config byte
and al,30h
; isolate monitor type
cmp al,30h
; color?
mov ax,0b000h
jz p061
; assume mono
; its mono
mov ax,0b800h
; color screen address
p061: mov dx,es:[463h] ; point to 6845 base port
add dx,6
; point to status port
mov es,ax
; point to monitor
mov bh,color
; color in bh
mov si,offset dhours
; point to time
mov di,138
; row 1, col 69
cld
mov cx,11
; loop count
p062: mov bl,[si]
; get next character
p063: in al,dx
; get crt status
test al,1
; is it low?
�jnz p063
; no - wait
cli
; no interrupts
p064: in al,dx
; get crt status
test al,1
; is it high?
jz p064
; no - wait
mov ax,bx
; move color & character
stosw
; move color & character again
sti
; interrupts back on
inc si
; point to next character
loop p062
; done?
p070: pop bp
; restore registers
pop di
pop si
pop es
pop dx
pop cx
pop bx
cli
; no interrupts
mov ax,holdss
mov ss,ax
mov sp,holdsp
sti
; allow interrupts
p080: popf
pop ds
pop ax
jmp cs:[jumpval]
p100 proc near
; beep the speaker twice
�call p120
push cx
mov cx,20000
p105: loop p105
; wait around
pop cx
call p120
push cx
mov cx,20000
p106: loop p106
; wait around
pop cx
call p120
ret
p100 endp
p120 proc near
; beep the speaker once
push ax
push cx
mov al,182
out 43h,al
; setup for sound
mov al,0
out 42h,al
mov al,atone
out 42h,al
; low part
; get alarm tone
; high part
in al,61h
push ax
; save port value
or al,3
out 61h,al
mov cx,aleng
p125: loop p125
pop ax
out 61h,al
pop cx
; turn speaker on
; get loop count
; wait around
; restore original port value
; turn speaker off
�pop ax
ret
p120 endp
p150:
; start of transient code
mov dx,offset copyr
call p220
; print copyright
mov ax,0
mov es,ax
; segment 0
mov di,segaddr+2 ; this program's prior location
mov ax,es:[di]
mov es,ax
; get prior code segment
; point to prior program segment
mov di,offset signature
mov cx,es:[di]
; is it this program?
cmp cx,whozat
jnz p160
; no - install it
call p200
; set state & alarm
int 20h
; terminate
p160: mov di,segaddr+2 ; point to int 62h
mov ax,0
mov es,ax
; segment 0
mov ax,ds
; get current ds
mov es:[di],ax
; set int 62h
mov si,offset jumpval
mov di,intaddr
; point to timer interrupt
mov bx,es:[di]
; get timer ip
mov ax,es:[di+2]
; and cs
mov [si],bx
; save prior ip
mov [si+2],ax
mov bx,offset p000
mov ax,ds
; and cs
�cli
; clear interrupts
mov es:[di],bx
; set new timer interrupt
mov es:[di+2],ax
sti
; set interrupts
push ds
pop es
call p200
; set state & alarm
mov dx,offset p150; last byte of resident portion
inc dx
int 27h
p200 proc near
mov si,80h
; terminate
; set state & alarm
; point to command line
mov ax,0
mov di,0ffffh
; init hours
mov bh,0
mov ch,0
mov dh,0
; : counter
mov es:[state],bh ; turn clock on
mov cl,[si]
; get length
jcxz p210
; it's zero
p203: inc si
mov bl,[si]
cmp bl,'-'
; point to next char
; get it
; is it a minus?
jnz p204
; no
mov es:[state],bl
; turn clock off
push dx
mov dx,offset msg3
call p220
pop dx
jmp p206
; print msg
�p204: cmp dh,2
jz p206
; seen 2nd colon?
; yes - ignore seconds
cmp bl,':'
; colon?
jnz p205
; no
inc dh
cmp dh,2
; second colon?
jz p206
; yes - ignore seconds
push cx
push dx
mov cx,60
mul cx
; multiply current ax by 60
pop dx
pop cx
mov di,ax
; save hours
mov ax,0
jmp p206
p205: cmp bl,'0'
jb p206
; too low
cmp bl,'9'
ja p206
sub bl,'0'
; too high - can be a problem
; convert it to binary
push cx
push dx
mov cx,10
mul cx
add ax,bx
; multiply current value by 10
; and add latest digit
pop dx
pop cx
p206: loop p203
; done yet?
cmp di,0ffffh
; any time to set?
jz p210
; no
�add ax,di
; add hours
cmp ax,24*60
jb p209
; ok
mov dx,offset msg1
; print error message
call p220
jmp p210
p209: mov es:[atime],ax ; save minutes past midnight
mov ax,5
mov es:[acount],ax ; set alarm count
mov dx,offset msg2
; print set msg
call p220
p210: ret
p200 endp
p220 proc near
; print message
push ax
mov ah,9
int 21h
pop ax
ret
p220 endp
copyr db 'Alarm - Clock',10,13,'$'
msg1 db 'Invalid time - must be from 00:00 to 23:59',10,13,'$'
msg2 db 'Resetting alarm time',10,13,'$'
msg3 db 'Turning clock display off',10,13,'$'
alarm endp
cseg ends
end
alarm
�8086 microprocessor assembly language programs
Write a Program For Read a Character From The Keyboard
MOV
INT
ah,
1h
//keyboard
//
21h
//
MOV c, al
character
is
//copy character from alto c
input
character
subprogram
input
in
al
stored
Write a Program For Reading and Displaying a Character
MOV
ah,
1h
//
INT
MOV
21h
dl,
MOV
INT 21h
ah,
2h
// display character in dl
keyboard
//read
//copy
al
input
character
character
//character
subprogram
into
to
output
al
dl
subprogram
Write a Program Using General Purpose Registers
ORG
100h
MOV
LEA
AL, VAR1
BX,
VAR1
MOV
MOV
BYTE
PTR
AL, VAR1
//
check
value
//get
of
[BX],
44h
//
//check value
RET
VAR1
VAR1
address
modify
of VAR1
by
moving it
of
VAR1
the
contents
by moving it
to
the
in
AL.
BX.
of
VAR1.
to the AL.
DB
22h
END
Write a Program For Displaying The String Using Library Functions
include
ORG
emu8086.inc
//Macro
PRINT
GOTOXY
PUTC
PUTC
RET
END
declaration
100h
Hello
10,
65
//
65
//return
//directive to stop the compiler.
World!
5
is
to
an
ASCII
the
code
operating
for
A
B
system.
Arithmetic and Logic Instructions
The 8086 processes of arithmetic and logic unit has separated into three groups such as
addition, division, and increment operation. Most Arithmetic and Logic Instructions affect the
processor status register.
The assembly language programming 8086 mnemonics are in the form of op-code, such as
MOV, MUL, JMP, and so on, which are used to perform the operations. Assembly language
programming 8086 examples
�Addition
ORG0000h
MOV DX, #07H
// move the value 7 to the register AX//
MOV AX, #09H
Add AX, 00H
// move the value 9 to accumulator AX//
// add CX value with R0 value and stores the result in AX//
END
Multiplication
ORG0000h
MOV DX, #04H
// move the value 4 to the register DX//
MOV AX, #08H
MUL AX, 06H
// move the value 8 to accumulator AX//
// Multiplied result is stored in the Accumulator AX //
END
Subtraction
ORG 0000h
MOV DX, #02H
// move the value 2 to register DX//
MOV AX, #08H
SUBB AX, 09H
// move the value 8 to accumulator AX//
// Result value is stored in the Accumulator A X//
END
Division
ORG 0000h
MOV DX, #08H
// move the value 3 to register DX//
MOV AX, #19H // move the value 5 to accumulator AX//
DIV AX, 08H // final value is stored in the Accumulator AX //
END
Example programs
Character transmission using a time delay
A program shown below takes the character in 'A' register, transmits it, delays for transmission time, and returns to the calling
program. Timer-1 is used to set the baud rate, which is 1200 baud in this program
The delay for one character transmission (in Mode 1 i.e.10 bits) is
10/2400
Or, 8.33 milliseconds
0.00833
Hence
software
delay
of
10ms
Timer-1 generates a baud rate close to 1200. Using a 12MHz crystal, the reload value is
Or, 230 i.e. E6H
seconds
is
used.
�This
gives
rise
SMOD is programmed to be 0.
to
an
actual
baud
rate
of
1202.
Assembly language Program is as follows
; Code to wait for the transmission to complete
The subroutine TRMITTIME generates a delay of about 10ms. With a clock of 12MHz, one instruction cycle time is
The loop "MILSEC" generates a delay of about 1 x 10-3 sec. This gets executed 10 times for a total delay of 10 x 10-3 sec or 10ms
Interrupt driven character transmission
In 8051, when a character is transmitted, SBUF register becomes empty and this generates a serial port interrupt (TI). TI and RI
both point to the vector location 0023H in the program memory. An interrupt service routine can be written at 0023H to send the nex
�character.
A program is written here to transmit a character say 'A' continuously based on interrupt. The microcontroller uses a clock of 12MHz
with a baud rate of 1202. The program is executed following a hardware reset.
Assembly language program is as follows.
Interrupt driven data reception
When a character is received, if receive mode is enabled, RI flag is set. This leads to the interruption of the main program and the
processor goes to the interrupt vector location, i.e. 0023H for serial port. The interrupt service routine at 0023H gets executed to
read the character so that the next character can be received. The following program receives a character on interrupt basis and
outputs the character to port-1, possibly for a display.
The crystal frequency is12MHz and baud rate is set at 1202 baud.
Assembly language program is as follows