Process Control Function
Process Control methods are roughly classified in to two
categories.
Loop Control and
Sequential Control
Loop control handles analog measured values (including
Feedback control and Feed forward control)
Sequential Control handles operating sequences and
process status signals.
�Process Control Methodologies
Feedback control is a control in which the controller
continuously checks the deviation between the input and
the set point and always corrects the input to match the
set point.
Feed forward Control is a control in which corrective
action is taken by measuring the disturbance and directly
driving the final control element before it affects the
process.
Sequential Control is a control which successively
advances each control step in accordance with a
predefined sequence.
�Basic Loop
Transmitter
4-20 mA
I/P
Convertor
SV
PV
MV
Controller
4-20 mA
I/P
Pneumatic Signal
(0.2 to 1 Kg/cm2 or 3 to 15 psi)
Final Control Element
�Process Control Systems
A process control system comprises of multiple simple and complex control
loops.
Process control systems are primarily classified into
Analog Control Systems
Analog control system uses Operational amplifiers to do the control
function.
Digital Control Systems
Digital Control system uses microprocessors to do the
control function. Digital control systems are preferred over
analog control systems since it is easy to interface with
Computers for data analysis.
�Analog Control System
Analog Control System
Operational Amplifier
Transmitter
Signal
Conversion
1 to 5V DC
4-20 mA DC
I/P
Set Point
Final Control Element
�Digital Control System
Digital Control System
Memory
Unit
Signal Conversion
&A / D
4-20 mA DC
D/A
I/P
Digital
Control
Unit
Input
Unit
Output
Unit
Processor
Arithmetic
Unit
Set
Point
�Digital Control System
Digital Control Systems are further classified
into
Centralized Control Systems (CCS)
Distributed Control Systems (DCS)
Let us understand the basics of CCS and DCS, their merits and
demerits.
�Centralized Control System
Centralized Control System
Centralized Control , Centralized Monitoring
PV1
Input
Signals
from
Field
PV2
PV3
MV1
Centralized
Processing
MV2
MV3
Unit
PVn
MVn
CPU
SV1 SV2 SV3
Set Points
SVn
Output
Signals
to
Field
�Distributed Control System
Distributed Control System
Distributed Control
PV1
Input
Signals
from
Field
Centralized Monitoring
MV1
FCS
PV8
MV8
SV8
SV1
PV9
MV9
Output
Signals
to Field
FCS
PV16
OPS
OPS
MV16
SV16
SV9
PV17
MV17
FCS
PVn
MVn
SV17
SVn
Set Points
Communication
Bus
�� Advantages of DCS for steam turbine
DCS for steam turbine has two partitions :Control & Protection
Supervisory systems :
Turbine stress evaluator : keeps acceleration less than limits increased
availability
Automatic turbine Run-UP system
Performance calculations
Heat Rate
Historians
Report generators
Automatic speed control
Automatic load control
Common co-ordinated Boiler Turbine control operation
�ProControl DCS at NTPC
�ProControl DCS at NTPC
Introduction
The PROCONTROL P is fast with total loop response times selectable
20ms/40ms from signal input to control signal output making it ideal for the
exacting demands of turbine governor control and protection.
Data transfer with in the control system is cyclic without interrupts. The
response time for each signal is thus deterministic, selectable during the
engineering stage and there is no possibility of communication channels
being overloaded during a plant upset.
�Introduction
The programmable control and monitoring system PROCONTROL P consists of:
PROCONTROL P Station (Signal conversion and signal processing)
PROCONTROL P Intra Plant Bus (Signal transport)
Both bus systems are based on the same data transmission principles and are fast,
true cyclic working bus systems, which transmit real time data with a very high
information bit rate.
�Procontrol P Station
The Procontrol station is fitted with
1. RBC - Remote Bus Coupler
2. LBTD - Local Bus Traffic Director
3. PRM - Universal Processing Module
4. IP
- Process Input Module
5. OP
- Process Output Module
6. IDM - Individual Drive Control Module
7. SIF
- Serial Interface Module
�DATA TRANSMISSION
THE DATA TRANSMISSION OF PROCONTROL P13 IS PERFORMED
WITH TWO LEVEL SERIAL BUS
SYSTEMS
LOCAL BUS
INTRAPLANT BUS ( IPB )
�Local Bus
The local bus is the heart of every station and connects all modules within the station.
The local bus itself is a printed circuit board, which is permanently fitted to the rear of the subracks.
�Local Bus
LOCAL BUS PCB (70BL01) HAS SEVEN LINES
AD :
DN :
DI :
CK :
US :
ZD :
Z :
ADDRESS
DATA OR INFORMATION
INVERTED DATA OR INFORMATION
CLOCK SIGNAL
24V DC POWER SUPPLY
REFERENCE CONDUCTOR FOR BUS SIGNAL
FOR REFERENCE CONDUCTOR
�Local Bus
The data exchange within the station is made via the local bus and is controlled by the local bus
traffic director 70BV01/05 which transmits address words serially and cyclically via the address line
of the local bus
Each input/output or processing module in the station compares the address on the local bus for
coincidence with its own address set with code switches / IL. If identical, the modules send /
receive information under the following address to the data lines of the local bus.
�Local Bus
A clock signal transmitted by the local bus traffic director 70BV01/05 over the clock
line of the local bus synchronizes the operation of all individual modules.
Based on the cycle time selected in BV it transmits address in address bus cyclically.
5 msec allows the transmission of 64 addresses, 00 to 3F
10 msec allows the transmission of 128 addresses, 00 to 7F and 2 service add
20 msec allows the transmission of 256 addresses, 00 to FF and 4 service add
40 msec allows the transmission of 256 normal & 256 service/special address (70BV05),
00 to FF and S00 to SFF
�Local Bus
The local bus 70BL01 can be extended beyond a Single subrack by fitting
prefabricated elements.
Local bus within a subrack
Local bus linking two subracks
Local bus linking more than two subracks in
the same cubicle
70BV01/70BV05 : local bus traffic director 70BL01
70BA01 : Bus end module
: Bus circuit board
70BL02: Bus cable between subracks
�Local Bus
70BV01/BV05: local bus traffic director
70BL01
: Bus circuit board
70BL02
: Bus cable between subracks
70BL03
: Bus cable between cubicles
70BT01
: Bus isolating amplifier
70BA01
: Bus end module
70BA02
: Bus access module
�Local Bus: System Data
1.CONFIGURATION
2. DATA
TRANSMISSION
A) LENGTH OF LOCAL BUS LINE
B) WITH ADITIONAL MODULE
C) NO OF MODULES PER LOCAL
BUS
D) DISTANCE B/N IPB BUS ACCESS
COUPLER AND LOCAL BUS/IPB
COUPLER
MAX. 3 MTR
MAX. 30 MTR
MAX. 64
A) SERVICE ADDRESS
B) USEFUL ADDRESSES PER CYCLE
(CYCLE TIME 40 ms)
2 EVERY 10 ms
256
F) TRANSMISSION MEANS
WITHIN SUBRACK
B/N TWO SUBRACK
B/N TWO CUBICLES
MAX. 3 MTR
P.C.B 70BL01
ROUND CABLE 70BL02
ROUND CABLE 70BL03
�PROCONTROL P Intra Plant Bus
The intra plant bus links all stations with local buses of one channel, the process computer
and the diagnostic station.
�PROCONTROL P Intra Plant Bus
The intra plant bus consists of a coaxial cable which is connected to the intra plant bus
access couplers of the stations in a line configuration.
�Intra Plant Bus: Modules
FV Interface
IPB #1
Line A
IPB
XV
IPB
TRAFFIC
DIRECTOR
IPB
TRAFFIC
DIRECTOR
XV
XV
XV
IPB
TRAFFIC
DIRECTOR
XV
FV: Intraplant bus traffic director 70FV01
XV: Intraplant bus coupler XV 7713
IPB # 1
Line B
�Intra Plant Bus: Modules - XV
Intraplant bus power supply module XV 7715
The power supply module XV 7715 serves to supply the intra plant bus. It is
plugged into the intra plant bus coupling module XV 7713.
Intraplant bus coupling module XV 7717
XV 7717 serves to transmit data and address signals from the intra plant bus to
the connected local bus & to transmit data signals from the local bus to the
connected intra plant bus. It is plugged into the intra plant bus coupling
module XV 7713.
Intraplant bus input module XV 7718 for addresses
The module XV 7718 transmits the address signals from the intra plant bus traffic
director to the coaxial cable of the intra plant bus. The module is plugged into
the intra plant bus coupler XV 7713.
�Intra Plant Bus: Modules XV7713
�FA, FK, BK interface &
DATA EXCHANGE B/N LOCAL BUS AND IPB
IPB
L
O
C
A
L
B
U
S
LOCAL/IPB
BUS
COUPLER(BK02)
XV
XV
70 FV01
70 FA01
L
O
C
A
L
B
U
S
LOCAL/IPB
BUS
COUPLER(BK02)
70 FK01
70 FK01
LINE#A
LINE#B
�FA, FK, BK interface
�LOCAL / INTRA-PLANT BUS
XV1
STATION -1
BUS
LOCAL/ IPB
COUPLER
PROCESSOR
70FV01
I/O
MODULE
TRAFFIC
DIRECTOR
LOCAL BUS
INTRA PLANT BUS
BUS
70FA01
LOCAL/ IPB
COUPLER
PROCESSOR
DRIVE
CONTROL
I/O
MODULE
TRAFFIC
DIRECTOR
LOCAL BUS
BUS
70FA01
LOCAL/ IPB
COUPLER
PROCESSOR
DRIVE
CONTROL
I/O
MODULE
TRAFFIC
DIRECTOR
STATION -2
�Intra Plant Bus: Data sheet
1.CONFIGURATION
2. DATA
TRANSMISSION
A) NO. OF INTRA-PLANT BUS LINES
B) LENTH FROM ADDRESS
TRANSMITTER
C) NUMBER OF STATIONS PER
INTRAPLANT BUS LINE
D) NUMBER OF STATIONS PER
ENTIRE CONTROL SYSTEM
A) NUMBER OF ADDRESS FOR
MAXIMUM OF 64 STATIONS
B) TIME REQUIRED TO TRANSMIT 1
TELEGRAM
C) INFORMATION RATE
D) SIGNAL CODE
E) AMPLITUDE
F) DATA SECURITY
F) TRANSMISSION MEANS
COXIAL CABLE,TYPE
CHARACTERISTICS IMPEDANCE
MAX. 16
MAX. 1400 MTR
MAX. 64
1024
256 X NO. OF STATIONS
60 MICRO SECONDS
204. 8 KBAUD
DPDM
+- 10V
PARITY BIT
RG 213 U
50 Ohm
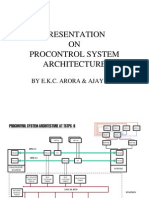
�PROCONTROL P-13 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE AT TSTPS -II
OWS 1
STATION
IPB TRAFFIC DIRECTOR
HUB 1
IPB TRAFFIC DIRECTOR
70FV01
70FV05
70FV01
OWS 2
OWS 3
OWS 4
HUB 2
70FV01
70FV01
70FV01
70FV01
SERVER 1
XV
SERVER 2
XV
IPB # 1A
DIAGNOSTIC
IPB # 1B
IPB # 2A
STATION
WSPOSE
PANEL
IPB # 2B
70FA01
BUS TRAFFIC
DIRECTOR
70BV05
70FA01
BUS
COUPLER
70BK02
BUS
COUPLER
70BK02
LOCAL BUS
BUS END
MODULE
70BA01
INDIVIDUAL
CONTROL
MCC
STATION
ANALOG
INPUT
ANALOG
OUTPUT
E
P
PROCESSOR
70PR05
BINARY
INPUT
BINARY
OUTPUT
�PROCONTROL MODULES
PROCESS CONTROL MODULES
INPUT / OUTPUT MODULES
DRIVE CONTROL MODULE
LOCAL BUS MODULE
IPB MODULE
�PROCESS CONTROL MODULES
PROCONTROL HAVE TWO BASIC TYPES OF
CONTROL MODULES
INDIVIDUAL CONTROL MODULES
UNIVERSAL PROCESSING MODULES
THESE MODULES ARE CONNECTED TO LOCAL BUS,ONE
OR SEVERAL OF THEM CAN BE CONNECTED TO THE SAME
BUS OR TO VARIOUS ONES
�PROCESS CONTROL MODULES
INDIVIDUAL CONTROL MODULES/
DRIVE CONTROL MODULE
Optional hardware
connection to
control room
Interface
I/o
Microprocessor
I/o
Signal from/to process,
final control element
(Valves,pumps,on/off,modulating)
�PROCESS CONTROL MODULES
DRIVE CONTROL MODULE
TYPE
APPLICATION
BRIEF DESCRIPTION
70AS04
DRIVE CONTROL MODULE
TO PROCESS CONTROL TASK
PROGRAMMABLE IN
PROCONTROL P10 LANGUAGE
6 BINARY INPUTS, 9 CONTACT INPUTS,
2 COMMAND OUTPUTS AND 5 LAMP
OUTUTS ARE PROVIDED
ANNUNCIATION AVAILABLE FOR
ELECTRONIC SYSTEM AND DRIVE
SYSTEM
EPROM(2732) AVAILABLE FOR
PROGRAMMNG
IMPLEMENT SOFTWARE TYPE 70 AS
45/46/47
�PROCESS CONTROL MODULES
DRIVE CONTROL MODULE
TYPE
APPLICATION
BRIEF DESCRIPTION
70AS06
(70AS65/67)
DRIVE CONTROL MODULE
TO PROCESS CONTROL TASK
PROGRAMMABLE IN
PROCONTROL P10 LANGUAGE
6 BINARY INPUTS, 10 CONTACT
INPUTS, 2 COMMAND OUTPUTS, 5
LAMP OUTUTS, 1 ANALOG INPUT, 3
ANALOG OUTPUT ARE PROVIDED
ANNUNCIATION AVAILABLE FOR
ELECTRONIC SYSTEM AND DRIVE
SYSTEM
EPROM(2732) AVAILABLE FOR
PROGRAMMNG
�PROCESS CONTROL MODULES
PROCESSOR MODULE
SUPERVISION
POWER
SUPPLY
LOCAL
BUS
INTERFACE
DATA BUS
SIMULATION
MEMORY
ADDRESS BUS
I/O
REGISTER
PROCESING
UNIT
DATA
MEMORY
CONTROL
UNIT
ADDRESS BUS
TEST
MEMORY
INSTRUCTION
LIST
MULTI
FUNCTION LIST
CODE BUS
SIM
�PROCESS CONTROL MODULES
PROGRAMMABLE PROCESSOR
TYPE
APPLICATION
BRIEF DESCRIPTION
70PR05
PROCESSING OF BINARY AND
ANALOG SIGNAL FOR LOGIC
CONTROL ,MODULATING
CONTROL AND COMPUTING
FUNCTION ACCORDING TO
INSTRUCTION LIST
PARAMETER CAN BE CHANGED
ON LINE WITHOUT PROGRAM
MODIFICATION
2 SOCKET FOR OPERATION WITH
SIMULATION AND PROGRAMMING
UNIT
1CODE SWITCH FOR SETTING
MODULE ADDRESS
EPROMS AVAILABLE FOR BASIC
FUNCTIONS/INSTRUCTION
LINE/MULTIFUNCTION
RAM FOR STARAGE OF PARAMETER
VALUE IN THE EVENT OF POWER
FAILURE
SIMULATION CAN BE POSSIBLE FOR
LOCAL BUS DATA
�PROCESS CONTROL MODULES
PROGRAMMABLE PROCESSOR:PR05
�Input / Output Modules
70AA01 Output Module for Voltages
70AA02 Output Module for Currents
70AB01 Output Module for Binary Signals
70AB02 Output Module for Binary Signals (potentially isolated)
70EA01 Input Module for Voltages and Currents
70EA02 Input Module for 2-Wire Transducers
70EA05 Input Module for Thermocouples or RTDs
70EB01 Input Module for Binary Signals
70EB02 Input Module for Contacts
70EB03 Input Module for Supervised Contacts
70EB10 Input Module for Event Recording
70EI05 Input Medule for Rotational Speed
�Input / Output Modules
70AA01 Output Module for Voltages
The module serves for the output of analog signals from the PROCONTROL P13
local bus. Each of the 4 output channels supplies a voltage signal in the range
of:
-10 V to +10 V (corresponding to -100 % to +100 %)
70AA02 Output Module for Currents
The module serves for the output of analog signals from the PROCONTROL P13
local bus. The 4 output channels may be configured to supply the following
current signals:
0 mA to +20 mA (corresponding to 0 % to +100 %)
+4 mA to +20 mA (corresponding to 0 % to +100 %)
�Input / Output Modules
70AB01 Output Module for Binary Signals
The module serves for the output of binary signals from the PROCONTROL P13
local bus. Each of the 16 output channels may be loaded as follows:
Max. 50 Normal loads (Electronic inputs with a load of 15 k)
Resistive load with a nominal current of max. 100 mA at 24 V nominal voltage
Inductive load with a nominal current of max. 100 mA at 24 V nominal voltage
70AB02 Output Module for Binary Signals (potentially isolated)
The module serves for the output of binary signals from the PROCONTROL P13
local bus. The modules serves the purpose of controlling electronic modules
in-outs,relays & lamps by means of potential free contacts.module having 16
output channels.
�Input / Output Modules
70EA01 Input Module for Voltages and Currents
The module serves as input device for analog signals to the PROCONTROL P13
local bus. Three different versions are available:
R 1: With 4 input channels to be configured for:
-20 mA to +20 mA (corresponding to -100 % to +100 %) or
-10 V to +10 V (corresponding to -100 % to +100 %)
R2: With 4 input channels configured for:
-10 V to +10 V ( 5 V corresponds to 100 %)
R3: With 4 input channels to be configured for:
0 mA to +20 mA (corresponding to -199.988 to 0 %) or
0 V to +10 V (corresponding to -199.988 to 0 %)
�Input / Output Modules
70EA02 Input Module for 2-Wire Transducers
The module serves as input device for analog signals to the PROCONTROL P13
local bus. Each of the 4 input channels may be configured to accept one of
the following signals:
4 mA to +20 mA from 2-wire transducers (power supply by the input module)
0 mA to +20 mA from 4-wire transducers (external power supply)
�Input / Output Modules
70EB01 Input Module for Binary Signals
The module serves as input device for contacts to the PROCONTROL P13 local bus. The
16 input channels with an interrogation voltage of 24 V may be used for the
connection of:
16 standard binary signals
16 single pole contacts
8 double throw contacts
70EB02 Input Module for Contacts
The module serves as input device for contacts to the PROCONTROL P13 local bus. The
16 input channels with an interrogation voltage of 48 V may be used for the
connection of the following contacts:
16 single pole contacts
8 double throw contacts
�Input / Output Modules
70EB03 Input Module for Supervised Contacts
The module serves as input device for supervised contacts to the PROCONTROL
P13 local bus. The 5 input channels with an interrogation voltage of 48 V may
be used for the connection of the following contacts:
5 single pole contacts or
5 double throw contacts
70EI05 Input Module for Rotational Speed
The module converts input pulse signals from speed transmitters into frequency
proportional local bus and current signals.
The module may be configured to the following ranges:
Nominal frequency
Nominal number of teeth
Over speed protection Limit value fortrip
Over speed protection Trip limit bias
244 Hz to 20 kHz
1 to 255
100 to 120 %
0 to 10 %
�Local bus Modules
TYPE
APPLICATION
BRIEF DESCRIPTION
70BA01
BUS END MODULE
USED AT THE END OF THE
LOCAL BUS FOR MATCHING
INE IMPEDANCE
ADDITIONAL SUPPLY TO THE BUS LINE
70BA02
BUS ACCES MODULE FOR
CONNECTING BUS CABLE
WHEN THE LOCAL BUS
CONNECTED FORM CUBICAL
TO CUBICAL
SOCKET ON THE FRONT FOR BUS
CABLE
70BL01
BUS CIRCUIT BOARD
BUS PCB WITH CONNECTOR
BUS LINE
SOCKET FOR BUS CABLE
POSSIBILITY FOR FITTING SEVERAL
BUS SOCKET
70BL02
BUS CABLE SUBTRACK
/SUBTRACK
LINK THE BUS PCB OF TWO
SUBRACK
CABLE UP TO 3M LONG
�Local bus Modules
TYPE
APPLICATION
BRIEF DESCRIPTION
70BL03
BUS CABLE CUBICAL/CUBICAL
LINK THE BUS PCB OF TWO
CUBICALS
CABLE UP TO 30M LONG
70BT01
BUS ISOLATION AMPLIFIER
SOCKET ON THE FRONT FOR BUS
CABLE
70BV01
BUS TRAFFIC DIRECTOR
CONTROL EXCHANGE B/N
MODULE CONNECTED TO
LOCAL BUS
PLUG IN JUMPER SETTING FOR CYCLE
PERIOD
JACK FOR FORCE INTERRUPT OR
ADDRESS TRANSMISSION
LED FOR INDICATION OF
OPERATION
�IPB Modules
TYPE
APPLICATION
BRIEF DESCRIPTION
70FA01
IPB ACCESS COUPLER
CONNECT NORMAL LOCAL BUS
STATION WITH INTRA PLANT
BUS
COUPLING BY THE WAY OF
MULTICORE INTERCONNECTING
CABLE
SERVE FOR TRANSFER DATA SIGNAL
IN TO INTRAPLANT BUS CABLE
FOR TRANSFER OF ADDRES AND
DATA FROM INTRAPLANT BUS CABLE
TO LOCAL BUS CABLE
70FK01
IPB COUPLER USE TO CONNECT
LOCAL BUS STATION NOT CONTAINING
THE IPB TRAFFIC DIRECTOR
USE TO TRANSMISSION AND
RECEPTION OF ADDRESS AND
DATA SIGNAL TO FROM IPB CABLE
70FV01
IPB TRAFFIC DIRECTOR
MANAGE THE SIGNAL
TRANSMISSION SEQUENCE
OPERATE IN SINGAL AND
REDUNDANT MODE
FITTED IN TO LOCAL BUS SUBRACK
GENERATE MAXIMUM 4000 ADDRESS
WORD TRANSMITTED CYCLIC IN 8
DIFFERENT SEQUENCE
�Problems observed
DATA RELATED TO ONE/FEW CARDS IS BAD
DATA RELATED TO ONE LOCAL BUS IS BAD
IN 70BK02 LINE CHANGE-OVER (A TO B OR VICE-VERSA) NOT TAKING PLACE.
LINE A FAULT / LINE-B FAULT IS BEING ANNUNCIATED BY ALL THE BK02 OF AN IPB
AND LINE-A / LINE-B TOGGLING.
PROCESSOR CHANGEOVER PROBLEM.
IN THE PROCESSOR (70PR05), SIGNALS GETTING SIMULATED ON THEIR OWN.
�DATA RELATED TO ONE/FEW CARD IS BAD
S.N
PROBABLE REASON
ACTION TO BE TAKEN
CARD IS NOT FLOATING DATA ON LOCAL BUS.
IDENTIFY & REMOVE THE CARD,REPLACE
BY SPARE.
CARD IS FLOATING DATA ON AN ADDRESS OTHER
THAN SET ON IT.
IDENTIFY & REMOVE THE CARD,REPLACE
BY SPARE.
IF SIGNAL IS GOOD AT LB THEN ADDRESS
CONFIGURATION IN MMI IS WRONG.
CORRECT THE MMI ADDRESS
CONFIGURATION .
�DATA RELATED TO ONE LOCAL BUS (STATION) IS BAD
S.N
PROBABLE REASON
ACTION TO BE TAKEN
IF IN ONE WSPOSE PANEL LINE-A & IN OTHER LINE-B IS
ACTIVE & BOTH THE MMI SERVERS ARE SHOWING DATA
OF A PARTICULAR STN AS BAD, WHEREAS DATA IN LB IS
GOOD, BK02 CARD GOT DEFECTIVE
REMOVE THE CARD & REPLACE BY SPARE
WITH SAME CONDITION AS ABOVE, ONE SERVER IS
SHOWING DATA AS BAD BUT OTHER IS SHOWING AS
GOOD, BK02 IS PARTLY DEFECTIVE.
REMOVE BK02 & REPLACE BY SPARE
IF PROBLEM STILL THERE,FK01 IS DEFECTIVE
MAKE THE HEALTHY LINE ACTIVE IN ALL THE
BK02 & BOTH WSPOSE OF THAT IPB. REPLACE
THE FK01.
IF ALL THE DATA IS BAD IN THE LB, A DEFECTIVE CARD
(AS04, AS06, PR05 OR BK02) IS TRYING TO FLOAT DATA
FOR ALL THE ADDRESSES.
IDENTIFY (BY PULLING ONE BY ONE) THE CARD
AND REPLACE BY SPARE
�BK02 LINE CHANGE-OVER (A TO B OR VICE-VERSA) NOT TAKING PLACE IN AN IPB.
S.N
PROBABLE REASON
ACTION TO BE TAKEN
ONE OF THE BK02 IS DEFECTIVE
IDENTIFY & REPLACE THE DEFECTIVE BK02. TO
IDENTIFY THE DEFECTIVE BK02, ONE BY ONE ALL
THE BK02 HAVE TO BE RACKED OUT TILL LINE
C/O STARTS TAKING PLACE.
ONE OF THE FK01 IS DEFECTIVE
IDENTIFY & REPLACE THE DEFECTIVE FK01. TO
IDENTIFY THE DEFECTIVE FK01, ONE BY ONE ALL
THE BK02 HAVE TO BE RACKED OUT TILL LINE
C/O STARTS TAKING PLACE.
IPB TERMINATIONS IN THE FA01 MODULES ARE LOOSE
SOMEWHERE
INSPECT & TIGHTEN THE LOOSE TERMINATION
IPB END TERMINATION RESISTORS / CAPACITOR ARE DRY
SOLDERED / DEFECTIVE
INSPECT THE END TERMINATIONS AND RECTIFY
THE FAULT
NOTE: THIS PROBLEM PREFERABLY SHALL BE ATTENDED
DURING AN OPPORTUNITY UNIT S/D. TILL THEN ENSURE
THAT THE HEALTHY LINE IS ACTIVE IN ALL THE BK02 &
BOTH WSPOSE OF THAT IPB.)
�LINE-A FAULT / LINE-B FAULT IS BEING ANNUNCIATED BY ALL THE BK02
OF AN IPB AND LINE-A / LINE-B TOGGLING.
S.N
PROBABLE REASON
ACTION TO BE TAKEN
IF ANNUNCIATIONS ARE COMING FROM ALL BUT
ONE BK02, THAT ONE IS DEFECTIVE
REMOVE BK02 & REPLACE BY SPARE.
SAME STATION ADDRESS HAS BEEN SET TO TWO
BK02
INSPECT ADDRESS SWITCHES SETTINGS
FOR CORRECTNESS & RECTIFY THE ERROR
ONE BK02 IS DEFECTIVE
TO IDENTIFY THE DEFECTIVE BK02, ONE
BY ONE ALL THE BK02 HAVE TO BE
RACKED OUT TILL TOGGLING STOPS.
REPLACE IT.
�ACTIVE PROCESSOR (70PR05), WITH ODD NO. ADDRESS, NOT GOING TO
STAND-BY MODE WHILE TRYING CHANGE-OVER. OR STANDBY
PROCESSOR (70PR05), WITH EVEN NO. ADDRESS, NOT BECOMING ACTIVE
WHILE TRYING CHANGE-OVER.
S.N
PROBABLE REASON
ACTION TO BE TAKEN
PROGRAM IN BOTH THE PR05 ARE NOT
IDENTICAL
COPY PROGRAM OF PR#1 IN PR#2
PROBLEM STILL PERSISTING
REPLACE THE MODULE.
�IN THE PROCESSOR (70PR05), SIGNALS GETTING SIMULATED ON THEIR
OWN.
S.N
PROBABLE REASON
ACTION TO BE TAKEN
IF PROBLEM IS OCCURRING ONLY WHEN
CONNECTING THE SK06 KIT, PROCESSORS FRONT
CONNECTORS CENTRAL GROUNDING PIN GOT
DISCONNECTED FROM PCB OR GOT FLARED TOO
MUCH.
REMOVE THE CARD & REPLACE BY SPARE.
IF PROBLEM IS OCCURRING ON ITS OWN, THE
PR05 CARD IS DEFECTIVE
REMOVE THE CARD & REPLACE BY SPARE.