International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering
Available Online at www.ijecse.org
897
ISSN- 2277-1956
Analysis of xDSL Technologies
Dimple Saproo 1, Megha Goyal 2, Asha Bhagashra 3, A.N.Mahajan
1, 2, 3, 4
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
Dronacharya College of Engineering, Gurgaon, India
Email-1dimplesaproo@gmail.com,2meghagoyal2010@gmail.com,4aparnanmahajan@yahoo.co.in,
3
Shekhawati Engineering College, Dundlod, India
Email- 3 a_balara@rediffmail.com
1,2,4
Abstract- The Rapid development in the field of information technologies has led to the appearance of new services that
requires high speed data transmission technologies. For example VoIP, online education, online video gaming etc, uses
high speed internet access for efficient operation. This paper explores the information carrying capabilities of different
types of DSL technologies along with the limitations of various high speed data services like ISDN, Dial-up and Cable
modem.
Keywords ADSL, DSL, DSLAM, SDSL, VDSL
I. INTRODUCTION
Digital subscriber line (DSL, originally digital subscriber loop) is a family of technologies that provide internet
access by transmitting digital data over the wires of a local telephone network. Other technologies are ISDN, dialup, cable modem etc. In telecommunication marketing, term DSL is widely understood to mean asymmetric digital
subscriber line (ADSL), the most commonly installed DSL technology. The bit rate of consumer DSL services
typically ranges from 256Kbps to 40 Mbps in the direction to the customer, depending on line conditions, DSL
technology and service level implementation. Bandwidth in DSL is dedicated to all subscribers i.e. speed doesnt
drop when other users uses it at same time. The advances in electronics have largely made DSL a successful, faster
and cheaper while using new copper or fiber optical cables. There are several variations in DSL technology known
as xDSL where x is variable.
The main advantage of using DSL over other technologies is the cost, speed and bandwidth. DSL can be used on the
wires that are already installed into homes or businesses [1]. Whereas ISDN lines need to be installed and
connection charges vary depending upon the connection you choose. In case of dedicated or, "always on"
connections you will have to pay more as some ISDN packages are charged on per minute basis. Fig. 1 shows the
comparison of various high speed data services.
ISSN 2277-1956/V2N3-897-902
�IJECSE,Volume2,Number 3
IJECSE,Volume
Dimple Saproo et al.
Figure 1. Comparison of DSL over other technologies
II. PRINCIPLE OF DSL TECHNOLOGIES
DSL technology is a modern technology
technology that uses existing twisted pair, telephone lines to transport high bandwidth
data such as multimedia and video to service subscriber. DSL is dedicated to point to point communication. DSL
connections are provided by using the same telephones lines and network
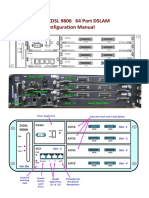
network element called DSLAM (Digital
subscriber line access multiplexer).It is installed at the central office / telephone exchange along with a modem
placed in a subscriber home or work place. The connection to the subscriber is given from DSLAM via copper
coppe lines.
The pair from the DSLAM is terminated into the main distribution frame from where connections are provided to
subscriberr through twisted copper wires. The twisted pair lines terminate at DP box placed near a subscriber
s
home
as shown in fig.2.DSL technology
echnology divides the frequency used in a single phone line into two primary bands. The
higher frequency band is used for data services and lower frequency band below 4 KHz is utilized for voice [2].
[
ISSN 2277-1956/V2N3-897-902
898
�899
Analysis of xDSL Technologies
Figure 2: XDSL setup
III. VARIOUS DSL TECHNOLOGIES
3.1 ADSL
ADSL is popular of all DSL types. It is called asymmetric because the download speed is greater than upload speed.
ADSL provides high speed transmission of information at high bandwidth over regular phone lines. Unlike dial up
phone, ADSL gives permanent internet connectivity .ADSL can contain both the analog and digital information on
the same telephone line. ADSL gives speed up to 8Mbps which translates into over 100 times faster the speed of
regular dial-up. Up-stream speed can be up to 800Kbps. ADSL uses dedicated bandwidth so multiple connection to
several home will not affect its performance or speed. Rather speed will depend on how far you are from DSL
provider. Homes and small business find ADSL easy to use [3].
3.2 SDSL
Symmetric DSL technology offers symmetric bandwidth of upstream and downstream. It supports data on a single
line. It can offer speed up to 2.3 Mbps. Its mainly used in teleconferencing and uploading of heavy data such as
multimedia to remote sensors.
3.3 HDSL
High rate DSL is symmetrical technology that provides the same amount of bandwidth for uploading and
downloading. Its speed is up to 2.048 Mbps over two copper pair wires with operating distance of 3.6 to 4.6 Km. Its
mainly used for connecting PBX system, digital local loops, internet servers and campus based networks.
3.4 HDSL-II
HDSL-II offers the performance of HDSL. It can transmit data up to speeds of 1.5 Megabits per second (Mbps)
across a single pair of copper wires and covers distances of up to 20,000 feet. . HDSL-II supports voice, data, video
using synchronous transfer mode (ATM), private-line T1 service and frame relay.
ISSN 2277-1956/V2N3-897-902
�IJECSE,Volume2,Number 3
Dimple Saproo et al.
3.5 IDSL
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), IDSL is slower than most other forms of DSL, operating at fixed rate
of 144 Kbps in both directions. The advantage for ISDN customers is that they can use their existing equipment, but
the actual speed gain is typically only 16 Kbps (ISDN runs at 128 Kbps).
3.6 SHDSL
Symmetric high-speed DSL (SHDSL) is another version of SDSL, which attempts to improve on both HDSL and
SDSL by only requiring a single line and by integrating low-level services of interest to small businesses. SHDSL
generates speeds of 2.3 Mbps upstream and downstream. SHDSL gives providers a platform to deliver improved
services at a much lower cost than traditional T1/E1. SHDSL offers the benefits of T1/E1 and can be used in the
same bundled cable loop as ADSL, without causing interference. SHDL also operates in a fixed rate mode at 784
kbps and 1.544Mbps [4].
3.7 VDSL
Very high bit rate digital subscriber line (VDSL) is one of the newest developments in DSL. VDSL delivers fast
data rates across short distances - the shorter the distance, the faster the connectivity. VDSL can produce speeds up
to 13 to 52 Megabits per second (Mbps) for downloading and 1.5 to 2.3 Mbps for uploading over a distance of 300
m to 1.4 Km. VDSL can deliver interactive video, video on demand and high definition TV [5].
Table 1 shows the comparative analysis of DSL technologies in terms of downstream, upstream, distance and phone
support.
Table 1. Comparison of various DSL technologies
DSL Type
Download Speed
Upload Speed
Distance in Feet
Phone Support
ADSL
8Mbps
800 Kbps
18000
Yes
SDSL
2.3 Mbps
2.3 Mbps
22000
No
HDSL
2.048 Mbps
2.048 Mbps
12000-15000
No
HDSL-II
1.5 Mbps
1.5 Mbps
20000
No
IDSL
144 Kbps
144 Kbps
35000
No
SHDSL
2.3 Mbps
2.3 Mbps
22000
No
VDSL
13 to 52 Mbps
1.5 to 2.3 Mbps
1000-4500
Yes
ISSN 2277-1956/V2N3-897-902
900
�901
Analysis of xDSL Technologies
Figure 3: Comparison of various DSL technologies in terms of downstream data rate
Figure 4: Comparison of various DSL technologies in terms of upstream data rate
ISSN 2277-1956/V2N3-897-902
�IJECSE,Volume2,Number 3
Dimple Saproo et al.
IV.CONCLUSION
DSL has the ability to deliver high speed data transmission over existing infrastructure with relatively small changes.
XDSL provides data and voice services on the cooper wires at the same time. Data services are provided on higher
frequency bands and regular voice services on lower frequency range. In India, ADSL is widely used. It is depicted
from the graph 2& 3 that VDSL is fastest technology amongst the all mentioned above.
REFERENCE
[1]
http://www.tech-faq.com/difference-between-isdn-and-dsl.html
[2]
xDSL configuration, Alcatel lucent university
[3]
http://computer.howstuffworks.com/vdsl3.htm
[4]
http://www.dsl-isp-info.com/type_dsl.htm
[5]
http://www.telebyteusa.com/dslprimer/dslch2.htm
ISSN 2277-1956/V2N3-897-902
902