0% found this document useful (0 votes)
140 views3 pagesProgram Mod 5 PDF
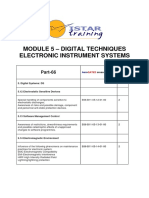
This document outlines the modules covered in a course on digital techniques and electronic instrument systems. Module 5 covers topics such as:
1) Electronic instrument systems and typical cockpit layouts.
2) Numbering systems including binary, octal, and hexadecimal, and conversions between numbering systems.
3) Data conversion including analog to digital and digital to analog.
4) Data buses and aircraft network systems.
5) Logic circuits including gates, tables, and diagrams.
Uploaded by
valerio freyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
140 views3 pagesProgram Mod 5 PDF
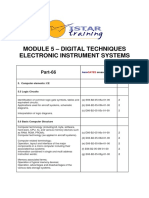
This document outlines the modules covered in a course on digital techniques and electronic instrument systems. Module 5 covers topics such as:
1) Electronic instrument systems and typical cockpit layouts.
2) Numbering systems including binary, octal, and hexadecimal, and conversions between numbering systems.
3) Data conversion including analog to digital and digital to analog.
4) Data buses and aircraft network systems.
5) Logic circuits including gates, tables, and diagrams.
Uploaded by
valerio freyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3