0% found this document useful (0 votes)
460 views1 pageFluid Statics Tutorial Guide
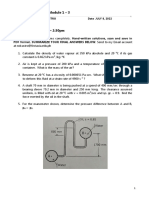
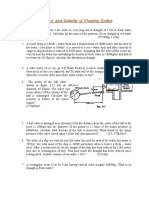
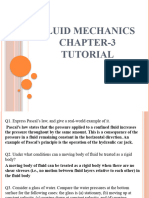
This document provides 6 problems from the fluid statics chapter in the textbook to work through. The problems cover: [1] defining hydrostatic force and center of pressure; [2] calculating total and horizontal forces on a reservoir wall; [3] calculating force and line of action on a circular dam; [4] calculating minimum spring force to close a circular gate; [5] explaining if buoyant forces are the same on identical submerged spheres at different depths; and [6] calculating percent change in cable tension when pressure in an attached air balloon increases. Numerical answers are provided for direct verification of problem solutions.
Uploaded by
Paula HoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
460 views1 pageFluid Statics Tutorial Guide
This document provides 6 problems from the fluid statics chapter in the textbook to work through. The problems cover: [1] defining hydrostatic force and center of pressure; [2] calculating total and horizontal forces on a reservoir wall; [3] calculating force and line of action on a circular dam; [4] calculating minimum spring force to close a circular gate; [5] explaining if buoyant forces are the same on identical submerged spheres at different depths; and [6] calculating percent change in cable tension when pressure in an attached air balloon increases. Numerical answers are provided for direct verification of problem solutions.
Uploaded by
Paula HoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 1