0% found this document useful (0 votes)
190 views4 pagesME401 Engine Basics
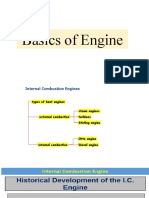
This document discusses different types of internal combustion engines. It describes spark ignition engines (SIE) which use a spark to ignite the fuel-air mixture, and compression ignition engines (CIE) which rely on high compression to ignite the fuel. It also discusses four-stroke and two-stroke engines, with two-stroke engines completing the combustion process in one revolution. Additionally, it examines the Otto, Diesel, and Dual cycles which model the thermodynamic processes in reciprocating engines.
Uploaded by
Adnan Shahariar AnikCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
190 views4 pagesME401 Engine Basics
This document discusses different types of internal combustion engines. It describes spark ignition engines (SIE) which use a spark to ignite the fuel-air mixture, and compression ignition engines (CIE) which rely on high compression to ignite the fuel. It also discusses four-stroke and two-stroke engines, with two-stroke engines completing the combustion process in one revolution. Additionally, it examines the Otto, Diesel, and Dual cycles which model the thermodynamic processes in reciprocating engines.
Uploaded by
Adnan Shahariar AnikCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4