0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views1 pageGothic Architecture
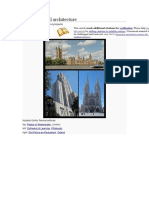
Gothic architecture flourished in Europe during the High and Late Middle Ages, evolving from Romanesque architecture and characterized by pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses. Most familiar as the architecture of Europe's great cathedrals and churches, Gothic architecture expressed powerful emotions through its designs and many ecclesiastical buildings remain as architecturally distinctive works of art. A Gothic revival began in the 18th century and continued into the 20th century, largely for churches and universities.
Uploaded by
LuxAeternaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views1 pageGothic Architecture
Gothic architecture flourished in Europe during the High and Late Middle Ages, evolving from Romanesque architecture and characterized by pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses. Most familiar as the architecture of Europe's great cathedrals and churches, Gothic architecture expressed powerful emotions through its designs and many ecclesiastical buildings remain as architecturally distinctive works of art. A Gothic revival began in the 18th century and continued into the 20th century, largely for churches and universities.
Uploaded by
LuxAeternaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 1