Graphics processing unit
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to: navigation, search
"GPU" redirects here. For other uses, see GPU (disambiguation).
This article is outdated. Please update this article to reflect recent events or newly
available information. Please see the talk page for more information. (November 2010)
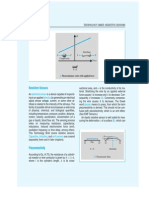
GeForce 6600GT (NV43) GPU
A graphics processing unit or GPU (also occasionally called visual processing unit or VPU) is
a specialized microprocessor that offloads and accelerates graphics rendering from the central
(micro-)processor. It is used in embedded systems, mobile phones, personal computers,
workstations, and game consoles. Modern GPUs are very efficient at manipulating computer
graphics, and their highly parallel structure makes them more effective than general-purpose
CPUs for a range of complex algorithms. In a personal computer, a GPU can be present on a
video card, or it can be on the motherboard, or as in certain Core Intel CPUs, on a CPU die.
More than 90% of new desktop and notebook computers have integrated GPUs, which are
usually far less powerful than those on a dedicated video card.[1]
The term was defined and popularized by Nvidia in 1999, who marketed the GeForce 256 as "the
world's first 'GPU', or Graphics Processing Unit, a single-chip processor with integrated
transform, lighting, triangle setup/clipping, and rendering engines that is capable of processing a
minimum of 10 million polygons per second." Rival ATI Technologies coined the term visual
processing unit or VPU with the release of the Radeon 9700 in 2002.
Contents
[hide]
1 History
o 1.1 Graphics accelerators
� 1.1.1 1970s
1.1.2 1980s
1.1.3 1990s
1.1.4 2000 to present
o 1.2 GPU companies
2 Computational functions
o 2.1 GPU accelerated video decoding
2.1.1 Video decoding processes that can be accelerated
3 GPU forms
o 3.1 Dedicated graphics cards
o 3.2 Integrated graphics solutions
o 3.3 Hybrid solutions
o 3.4 Stream Processing and General Purpose GPUs (GPGPU)
4 See also
5 References
6 External links
[edit] History
[edit] Graphics accelerators
A GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is a graphics coprocessor that offloads graphics tasks from
the CPU with the intention of performing them faster than the CPU can perfrom them. A
graphics accelerator incorporates one or more custom microchips which contain special
mathematical operations commonly used in graphics rendering. The efficiency and clock speed
of the microchips and the algorithms implemented therefore determines the effectiveness of the
graphics accelerator. They were once mainly used for playing 3D games or high-end 3D
rendering, but now take on more roles and therefore have grown more popular as a result. A GPU
implements a number of graphics primitive operations in a way that makes running them much
faster than drawing directly to the screen with the host CPU. The most common operations for
early 2D computer graphics include the BitBLT operation, combining several bitmap patterns
using a raster op, usually in special hardware called a "blitter", and operations for drawing
rectangles, triangles, circles, and arcs. Modern GPUs also have support for 3D computer
�graphics, and typically include digital videorelated functions. More recent GPUs now support
handling highly parallel tasks that CPUs would take a long time to perform.
[edit] 1970s
The ANTIC and CTIA chips provided for hardware control of mixed graphics and text modes,
sprite positioning and display (a form of hardware blitting), and other effects on Atari 8-bit
computers. The ANTIC chip was a special purpose processor for mapping (in a programmable
fashion) text and graphics data to the video output. The designer of the ANTIC chip, Jay Miner,
subsequently designed the graphics chip for the Commodore Amiga.