0% found this document useful (0 votes)
335 views2 pagess3 Lab Manual PDF
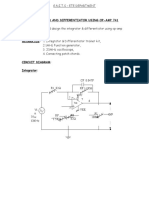
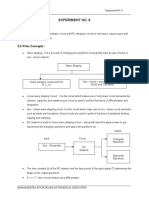
This document describes an electronics lab experiment to study and plot the frequency responses of passive differentiator and integrator circuits. The experiment involves using a function generator to supply sine, square, and triangular waveforms to differentiator and integrator circuits with varying RC time constants. The output waveforms will then be observed and plotted to analyze the frequency response characteristics of the differentiator and integrator.
Uploaded by
sruthyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
335 views2 pagess3 Lab Manual PDF
This document describes an electronics lab experiment to study and plot the frequency responses of passive differentiator and integrator circuits. The experiment involves using a function generator to supply sine, square, and triangular waveforms to differentiator and integrator circuits with varying RC time constants. The output waveforms will then be observed and plotted to analyze the frequency response characteristics of the differentiator and integrator.
Uploaded by
sruthyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2