100% found this document useful (1 vote)
177 views23 pagesAutomotive Alternators: Team 9 Tyler Borysiak, Myles Moore, Alex Sklar, Joshua Lamb, Stephen Dunn
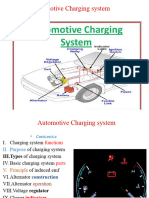
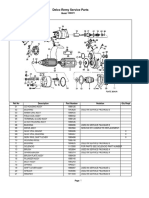
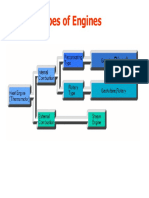
This document provides an overview of automotive alternators. It discusses the history of alternating current versus direct current, and how AC led to the development of generators. The key parts of a wye-connected alternator are described, including the rotor, stator, diode rectifier, and voltage regulator. Electromagnetic induction and the power generation process in an alternator are explained. Different types of alternators are classified by their excitation method, number of phases, rotating components, and applications. The importance of alternators in converting mechanical energy to electrical energy to power vehicles is highlighted.
Uploaded by
Mohan PreethCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
177 views23 pagesAutomotive Alternators: Team 9 Tyler Borysiak, Myles Moore, Alex Sklar, Joshua Lamb, Stephen Dunn
This document provides an overview of automotive alternators. It discusses the history of alternating current versus direct current, and how AC led to the development of generators. The key parts of a wye-connected alternator are described, including the rotor, stator, diode rectifier, and voltage regulator. Electromagnetic induction and the power generation process in an alternator are explained. Different types of alternators are classified by their excitation method, number of phases, rotating components, and applications. The importance of alternators in converting mechanical energy to electrical energy to power vehicles is highlighted.
Uploaded by
Mohan PreethCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 23