100% found this document useful (1 vote)
430 views51 pagesC6713 Lab Manual
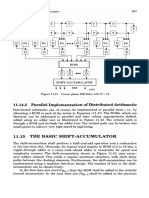
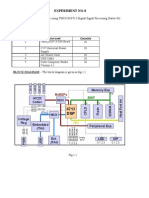
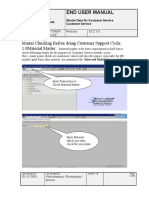
The document is a lab manual containing instructions and code examples for experiments using the TMS320C6713 DSP Starter Kit (DSK). It includes examples for linear and circular convolution, an N-point DFT, impulse response of systems, tone generation, square wave generation, audio loopback, voice scrambling, FIR and IIR filtering. The manual provides step-by-step instructions for setting up Code Composer Studio, creating projects, adding files and libraries. It also presents the code for each example and expected output.
Uploaded by
smganorkarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
430 views51 pagesC6713 Lab Manual
The document is a lab manual containing instructions and code examples for experiments using the TMS320C6713 DSP Starter Kit (DSK). It includes examples for linear and circular convolution, an N-point DFT, impulse response of systems, tone generation, square wave generation, audio loopback, voice scrambling, FIR and IIR filtering. The manual provides step-by-step instructions for setting up Code Composer Studio, creating projects, adding files and libraries. It also presents the code for each example and expected output.
Uploaded by
smganorkarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 51