100% found this document useful (1 vote)
91 views6 pagesBachelor of Computer Applications
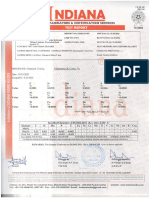
This document provides information on the first semester examination for a Bachelor of Computer Applications degree program. It lists the courses, course codes, credit hours, and examination instructions for 6 courses: Mathematics I, Business Communication, Programming with C, Fundamentals of Information Technology, Basics of Physics, and Practical I. The total credits for the semester are 27 spread across 17 lecture hours and 16 tutorial/practical hours. Examination instructions are provided for Mathematics I, including topics covered in each of 4 units and textbook references. Similar course outlines are then provided for the Business Communication and Programming with C courses.
Uploaded by
bansiiboyCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
91 views6 pagesBachelor of Computer Applications
This document provides information on the first semester examination for a Bachelor of Computer Applications degree program. It lists the courses, course codes, credit hours, and examination instructions for 6 courses: Mathematics I, Business Communication, Programming with C, Fundamentals of Information Technology, Basics of Physics, and Practical I. The total credits for the semester are 27 spread across 17 lecture hours and 16 tutorial/practical hours. Examination instructions are provided for Mathematics I, including topics covered in each of 4 units and textbook references. Similar course outlines are then provided for the Business Communication and Programming with C courses.
Uploaded by
bansiiboyCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6