0% found this document useful (0 votes)
199 views6 pagesEmbryonic Period (3-8 Weeks AOG)
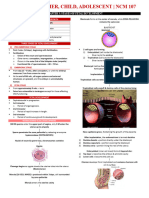
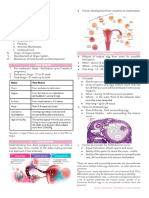
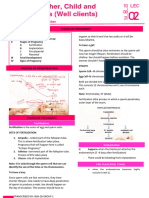
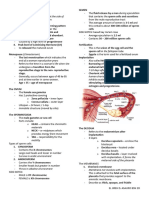
The document describes three phases of intrauterine life: pre-embryonic, embryonic, and fetal periods. It provides details about key developmental stages and structures that form during each period. These include cleavage of cells, formation of the blastocyst and implantation, development of the three germ layers and organ systems, growth and development of the fetus, and development of the placenta and umbilical cord. A variety of anatomical and physiological changes that occur throughout gestation are also outlined.
Uploaded by
clide11Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
199 views6 pagesEmbryonic Period (3-8 Weeks AOG)
The document describes three phases of intrauterine life: pre-embryonic, embryonic, and fetal periods. It provides details about key developmental stages and structures that form during each period. These include cleavage of cells, formation of the blastocyst and implantation, development of the three germ layers and organ systems, growth and development of the fetus, and development of the placenta and umbilical cord. A variety of anatomical and physiological changes that occur throughout gestation are also outlined.
Uploaded by
clide11Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6