0% found this document useful (0 votes)
600 views2 pagesEASA Module 4 Syllabus
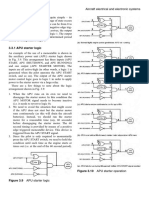
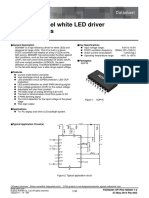
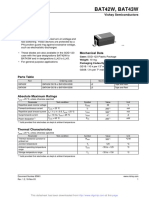
This document provides an overview of electronic fundamentals including semiconductors, diodes, transistors, integrated circuits, printed circuit boards, and servomechanisms. It describes the basic characteristics and operations of diodes, transistors, logic and linear circuits. It also discusses integrated circuit applications, printed circuit boards, open and closed loop systems, and components of synchro systems including resolvers, differentials, transmitters and their uses in servomechanisms.
Uploaded by
Prabuddha ChakrabortyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
600 views2 pagesEASA Module 4 Syllabus
This document provides an overview of electronic fundamentals including semiconductors, diodes, transistors, integrated circuits, printed circuit boards, and servomechanisms. It describes the basic characteristics and operations of diodes, transistors, logic and linear circuits. It also discusses integrated circuit applications, printed circuit boards, open and closed loop systems, and components of synchro systems including resolvers, differentials, transmitters and their uses in servomechanisms.
Uploaded by
Prabuddha ChakrabortyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2