0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views14 pagesAlgebra Unit 3 Exponential Functions
The document covers several topics in mathematics including:
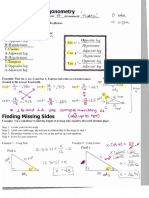
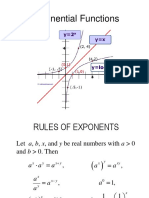
1) Properties of exponents such as expanding, compressing, products and powers of exponents, zero exponents, and negative exponents.
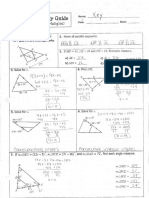
2) Arithmetic and geometric sequences including explicit and recursive formulas with examples of writing formulas for given sequences and finding terms.
3) Compound interest including the compound interest formula and examples of calculating balances with different compounding frequencies.
4) Growth and decay including the formulas and an example of calculating participants remaining after rounds of elimination.
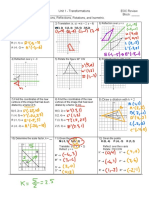
5) Graphing and characteristics of exponential functions including their domains, ranges, intercepts, intervals of increase/decrease, and end behaviors.
Uploaded by
api-287816312Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views14 pagesAlgebra Unit 3 Exponential Functions
The document covers several topics in mathematics including:
1) Properties of exponents such as expanding, compressing, products and powers of exponents, zero exponents, and negative exponents.
2) Arithmetic and geometric sequences including explicit and recursive formulas with examples of writing formulas for given sequences and finding terms.
3) Compound interest including the compound interest formula and examples of calculating balances with different compounding frequencies.
4) Growth and decay including the formulas and an example of calculating participants remaining after rounds of elimination.
5) Graphing and characteristics of exponential functions including their domains, ranges, intercepts, intervals of increase/decrease, and end behaviors.
Uploaded by
api-287816312Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 14