0% found this document useful (0 votes)
317 views1 pageVLSI Fabrication Assignment Guide
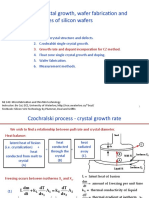
1. A Czochralski crystal is pulled from a melt containing boron and phosphorus. As the crystal is pulled, more phosphorus builds up in the melt due to segregation. The crystal will transition from P-type to N-type when the phosphorus concentration exceeds the boron concentration. The question calculates the distance along the crystal where this transition occurs.
2. A Czochralski crystal is grown with an initial antimony concentration in the melt. More pure silicon is added to the melt to return it to its original volume after 80% of the melt is used. The question calculates the new antimony concentration in the crystal after 50% of the new melt
Uploaded by
Avinash GuptaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
317 views1 pageVLSI Fabrication Assignment Guide
1. A Czochralski crystal is pulled from a melt containing boron and phosphorus. As the crystal is pulled, more phosphorus builds up in the melt due to segregation. The crystal will transition from P-type to N-type when the phosphorus concentration exceeds the boron concentration. The question calculates the distance along the crystal where this transition occurs.
2. A Czochralski crystal is grown with an initial antimony concentration in the melt. More pure silicon is added to the melt to return it to its original volume after 80% of the melt is used. The question calculates the new antimony concentration in the crystal after 50% of the new melt
Uploaded by
Avinash GuptaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 1