0% found this document useful (0 votes)
365 views1 pageCrypto Map Version 1.0
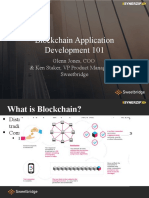
This document provides an overview of the domain of cryptography including hashing algorithms, symmetric and asymmetric encryption, digital signatures, public key infrastructure (PKI), and common cryptographic concepts, operations, and applications. It outlines the SHA family of hashing algorithms, symmetric encryption algorithms like AES and common key sizes, asymmetric or public key cryptography including the use of digital certificates, and hybrid cryptosystems that combine both symmetric and asymmetric techniques. The document was created by Henry Jiang, CISO and CISSP at Oppenheimer & Co., Inc. to map out the key components and concepts within cryptography.
Uploaded by
SylasMendesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
365 views1 pageCrypto Map Version 1.0
This document provides an overview of the domain of cryptography including hashing algorithms, symmetric and asymmetric encryption, digital signatures, public key infrastructure (PKI), and common cryptographic concepts, operations, and applications. It outlines the SHA family of hashing algorithms, symmetric encryption algorithms like AES and common key sizes, asymmetric or public key cryptography including the use of digital certificates, and hybrid cryptosystems that combine both symmetric and asymmetric techniques. The document was created by Henry Jiang, CISO and CISSP at Oppenheimer & Co., Inc. to map out the key components and concepts within cryptography.
Uploaded by
SylasMendesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 1