0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views2 pagesPDC Lesson Plan - II-II
This document outlines the topics and schedule for a course on pulse and digital circuits. It includes 5 units: 1) linear wave shaping, 2) non-linear wave shaping, 3) switching characteristics of devices, 4) multivibrators, and 5) sampling gates and logic gate realization. Some of the key topics covered are RC and RLC circuits, diode and transistor clippers, comparators, clamping circuits, transistor and diode switching characteristics, multivibrators like astable and monostable, and logic gate implementation using diodes and transistors. The document lists the relevant textbooks and references for each topic.
Uploaded by
Srinivasu RajuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views2 pagesPDC Lesson Plan - II-II
This document outlines the topics and schedule for a course on pulse and digital circuits. It includes 5 units: 1) linear wave shaping, 2) non-linear wave shaping, 3) switching characteristics of devices, 4) multivibrators, and 5) sampling gates and logic gate realization. Some of the key topics covered are RC and RLC circuits, diode and transistor clippers, comparators, clamping circuits, transistor and diode switching characteristics, multivibrators like astable and monostable, and logic gate implementation using diodes and transistors. The document lists the relevant textbooks and references for each topic.
Uploaded by
Srinivasu RajuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2
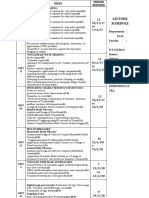
PULSE AND DIGITAL CIRCUITS
Branch: E.C.E DEPARTMENT: ECE
………………………………………………………………………………………………
TEXT BOOKS:
T1. Pulse, Digital and switching waveforms -- J.Milliman and H.Taub, McGraw-Hill,2008 .
T2. Solid State Pulse circuits -- David A.Bell, PHI, 4th Edn., 2002
REFERENCE BOOKS:
R1: Fundamentals of Pulse and Digital Circuits, Ronald J. Tocci, 3rd ed., 2008
R2. Pulse & Digital circuits -- A.Anand Kumar, PHI
R3:Pulse and Digital Circuits-Motheki S.Prakash Rao,2006,TMH
R4: Wave Generation and Shaping-L Strauss
S.No Topics to be covered No. of Referred date
c bo
l ok
a s
s
s
e
s
UNIT-1 LINEAR WAVE SHAPING
1 Introduction to PDC, Linear wave shaping: 1 T1,R2 28/12
2 High pass RC circuits, response for sinusoidal, step 1 T1,R2 29/12
3 pulse, square 1 T1,R2 4/1
4 ramp, exponential inputs 1 T1,R2 5/1
5 low pass RC circuits, response for sinusoidal, step 1 T1,R2 7/1
6 Pulse, square ramp inputs. 1 T1,R2 10/1
7 RC networks as differentiator and integrator 1 T1,R2 11/1
8 attenuators, 1 T1,R2 15/1
9 applications in CRO probe 1 T1,R2 18/1
10 RL, and their response for step input 1 T1,R2 21/1
11 RLC circuits and their response for step input 1 T1,R2 24/1
12 Ringing circuit 1 T1,R2 25/1
UNIT II: Non –Linear Wave Shaping
13 Non-Linear wave shaping: Diode clippers 1 T1,R2 28/1
14 clipping at two independent levels, transfer characteristics of 1 T1,R2 31/1
clippers
15 transistor clipper 1 T1,R2 ½
16 Emitter coupled clipper 1 T1,R2 2/2
17 comparators 1 T1,R2 4/2
18 applications of voltage comparators 1 T1,R2 7/2
19 clamping operation 1 T1,R2 8/2
20 clamping circuits using source and diode resistance 1 T1,R2 14/2
21 clamping circuit theorem 1 T1,R2 15/2
22 practical clamping circuits 1 T1,R2 16/2
23 effect of diode characteristics on clamping voltage, transfer 1 T1,R2 21/2
characteristics of clampers, synchronized clamping
UNIT III: SWITCHING CHARACTERSTICS OF DEVICES
24 Switching characteristics of devices: Diode as switch 1 T1,R2 22/2
25 piecewise linear diode characteristics, diode switching times 1 T1,R2 23/2
26 transistor as switch 1 T1,R2 25/2
27 Breakdown voltage consideration of transistor 1 T1,R2 28/2
28 saturation parameters of transistor and their variation with 1 T1,R2 1/3
temperature
29 Design of transistor switch, transistor switching times 1 T1,R2 1/3
30 Silicon controlled switch circuits 1 T1,R2 2/3
UNIT V: SAMPLING GATES REALIZATION OF LOGIC GATES USING DIODES & TRANSISTORS
31 Basic operating principles of sampling gates, unidirectional 1 T1,R2 7/3
sampling gates,
32 Reduction of pedestal in gate circuits, 1 T1,R2 8/3
33 bi-directional sampling gates, Reduction of pedestal in gate 1 T1,R2 11/3
circuits,
34 Four diode sampling gates. 1 T1,R2 14/3
35 AND , OR, NOT gates using Diodes and transistors 1 T1,R2 15/3
36 Resistor transistor logic ,DCTL 1 T1,R2 16/3
37 Diode Transistor logic, TTL ,CML 1 T1,R2 18/3
38 Logic families and its comparison 1 T1,R2 22/3
UNIT IV:MULTIVIBRATORS
40 Analysis of fixed bias and self bias bi-stable multi. 1 T1,R2 23/3
41 Analysis of Mono-stable 1 T1,R2 25/3
42 Analysis of Astable 1 T1,R2 28/3
43 Schmitt trigger using transistors, problems 1 T1,R2 29/3
44 Design of astable, mono stable, bi-stable and Schmitt trigger 2 T1,R2 30/3
45 Time base generator ,general features of time base signal 1 T1,R2 1-4
46 Methods of generating time base waveform 1 T1,R2 8/4
47 Miller and bootstrap 1 T1,R2 4/4
48 Time base signal, methods of generating time base waveform 1 T1,R2 11/4
49 UJT sweep generator 1 T1,R2 12/4
50 Miller and bootstrap time base generators-basic principles 1 T1,R2 13/4
51 transistor miller time base generator 1 T1,R2 15/4
52 transistor bootstrap time base generators 1 T1,R2 18/4
53 current time base generators 1 T1,R2 20/4
TOTAL 54