0% found this document useful (0 votes)
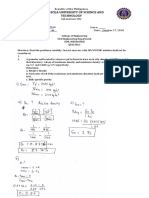
199 views4 pagesABEF For This Plate - Two ABCD Is A Shorter Route,: Solution. The Critical Section Could Possibly Be ABCD, ABCEF, or ABEF
The document provides three examples of calculating the critical net area of steel plates with bolt holes.
In the first example, it determines the critical net area is 2617.2 mm^2 for a plate with multiple bolt holes by calculating the gross area and subtracting the total area of holes.
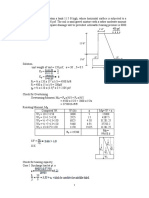
The second example calculates the required pitch between two lines of bolt holes as 64.81mm to achieve a net area equal to the gross area minus one bolt hole.
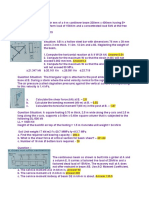
The third example calculates the net areas of different sections of a plate with various bolt hole configurations, finding the largest net area is 2663.6 mm^2.
Uploaded by
عبدالرحمن الشرعبيCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
199 views4 pagesABEF For This Plate - Two ABCD Is A Shorter Route,: Solution. The Critical Section Could Possibly Be ABCD, ABCEF, or ABEF
The document provides three examples of calculating the critical net area of steel plates with bolt holes.
In the first example, it determines the critical net area is 2617.2 mm^2 for a plate with multiple bolt holes by calculating the gross area and subtracting the total area of holes.
The second example calculates the required pitch between two lines of bolt holes as 64.81mm to achieve a net area equal to the gross area minus one bolt hole.
The third example calculates the net areas of different sections of a plate with various bolt hole configurations, finding the largest net area is 2663.6 mm^2.
Uploaded by
عبدالرحمن الشرعبيCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4