0% found this document useful (0 votes)
424 views43 pagesLargest of Two Numbers Using Nested Function
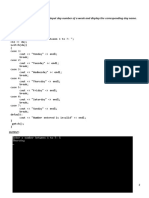
The document contains code snippets demonstrating various object-oriented programming concepts in C++, including:
1) Defining classes with methods and using objects of those classes.
2) Passing class objects to functions and accessing object properties.
3) More advanced concepts like inheritance, polymorphism, operator overloading, templates and exception handling.
The document serves as a reference of different OOP features in C++ with short code examples for each.
Uploaded by
Paras GoyalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
424 views43 pagesLargest of Two Numbers Using Nested Function
The document contains code snippets demonstrating various object-oriented programming concepts in C++, including:
1) Defining classes with methods and using objects of those classes.
2) Passing class objects to functions and accessing object properties.
3) More advanced concepts like inheritance, polymorphism, operator overloading, templates and exception handling.
The document serves as a reference of different OOP features in C++ with short code examples for each.
Uploaded by
Paras GoyalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 43