0% found this document useful (0 votes)
107 views14 pagesClockwise Counterclockwise 180 60
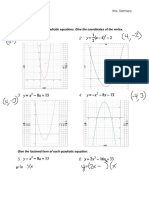
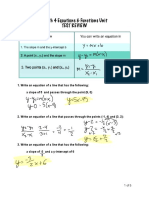
The document introduces the Cartesian plane and angles within it. It defines the Cartesian plane as being named after René Descartes and having four quadrants defined by the x and y axes, with quadrant angles at 0, 90, 180, and 270 degrees. Examples show how to identify the quadrant for given angle measures and perform angle operations like adding or subtracting to end at a given degree measure in a different quadrant.
Uploaded by
api-444439435Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
107 views14 pagesClockwise Counterclockwise 180 60
The document introduces the Cartesian plane and angles within it. It defines the Cartesian plane as being named after René Descartes and having four quadrants defined by the x and y axes, with quadrant angles at 0, 90, 180, and 270 degrees. Examples show how to identify the quadrant for given angle measures and perform angle operations like adding or subtracting to end at a given degree measure in a different quadrant.
Uploaded by
api-444439435Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 14