0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views21 pagesExampleproblemsandsolutionsogata Root Locus
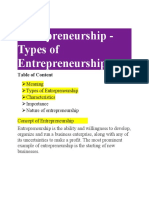
There are six main types of enterprises: high growth or venture-backed startups, lifestyle businesses, small organic growth businesses, businesses acquired through purchase, social ventures, and corporate intrapreneurship initiatives. Each type has different implications for business expectations and the founder's lifestyle in terms of financial requirements, growth expectations, and exit options. Understanding the different types helps entrepreneurs align their business ambitions with their desired lifestyle.
Uploaded by
Aamir MansoorCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views21 pagesExampleproblemsandsolutionsogata Root Locus
There are six main types of enterprises: high growth or venture-backed startups, lifestyle businesses, small organic growth businesses, businesses acquired through purchase, social ventures, and corporate intrapreneurship initiatives. Each type has different implications for business expectations and the founder's lifestyle in terms of financial requirements, growth expectations, and exit options. Understanding the different types helps entrepreneurs align their business ambitions with their desired lifestyle.
Uploaded by
Aamir MansoorCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 21