0% found this document useful (0 votes)
369 views10 pagesC Practical File
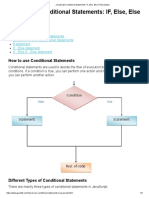
The document discusses various topics in C programming including arrays, pointers, strings, and dynamic memory allocation. Arrays allow storing of homogeneous data and are used to store lists of items. Pointers store the address of another variable and are used for dynamic memory allocation. Strings in C are arrays of characters terminated by a null character. Dynamic memory allocation functions like malloc(), calloc(), and realloc() allow allocating and resizing memory blocks at runtime.
Uploaded by
Nikhil SrivastavaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
369 views10 pagesC Practical File
The document discusses various topics in C programming including arrays, pointers, strings, and dynamic memory allocation. Arrays allow storing of homogeneous data and are used to store lists of items. Pointers store the address of another variable and are used for dynamic memory allocation. Strings in C are arrays of characters terminated by a null character. Dynamic memory allocation functions like malloc(), calloc(), and realloc() allow allocating and resizing memory blocks at runtime.
Uploaded by
Nikhil SrivastavaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10