0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views54 pagesOopsla - Introduction
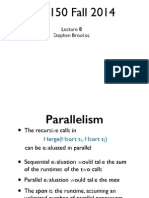
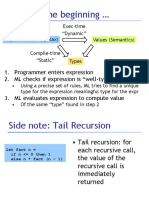
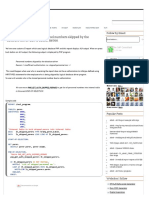
This document summarizes four parts of an article about the evolution of programming languages and type systems:
Part I discusses the origins of typed deduction in the work of Gerhard Gentzen and Alonzo Church, who developed natural deduction and the simply typed lambda calculus.
Part II covers Haskell's type classes and how they allow defining types like Ord that can be instantiated for different types like Int and Char.
Part III compares how generics were added to Java between versions 4.0 and 5.0, allowing the definition of lists with specific element types like List<Integer>.
Part IV discusses how Links aims to reconcile static and dynamic typing through its type system that allows both static verification and dynamic updates.
Uploaded by
sivaram vishnukumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views54 pagesOopsla - Introduction
This document summarizes four parts of an article about the evolution of programming languages and type systems:
Part I discusses the origins of typed deduction in the work of Gerhard Gentzen and Alonzo Church, who developed natural deduction and the simply typed lambda calculus.
Part II covers Haskell's type classes and how they allow defining types like Ord that can be instantiated for different types like Int and Char.
Part III compares how generics were added to Java between versions 4.0 and 5.0, allowing the definition of lists with specific element types like List<Integer>.
Part IV discusses how Links aims to reconcile static and dynamic typing through its type system that allows both static verification and dynamic updates.
Uploaded by
sivaram vishnukumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 54