PROCEDURE FOR INSTALLATION OF CATHODIC PROTECTION SYSTEM
All material received at site shall be inspected, handled and stored upon receipt in accordance
with Project
Procedure for “Field Material Control”.
Installation inspections shall be conducted by the Electrical Supervisors and witnessed by QC
Electrical Inspector.
The cathodic protection system shall be installed in accordance with the project specification,
manufacturer’s
instruction and reference standard installation detail.
Preparation of required tools and materials necessary for the installation work.
Installation of Cathodic Protection Equipment
Equipment shall be installed accurately with respect to their position, arrangement and
directions.
Lifting shall be carried out using properly tested and approved slings.
After completion of installation the following points shall be checked and corrected if necessary.
Check the level and alignment with the adjacent equipment are correct.
Check if the doors can be open and close normally.
Check if there is any damage to the paint coating.
Check the anchor bolts and set bolts have been tightened.
Test Box Installation
1. Test box shall be installed in accordance to the approved detail drawings.
2. Test box foundation shall be check in conformance to the drawings prior to equipment
installation. Concrete foundation shall be cured for a sufficient period of time. The concrete
shall extend 150mm minimum above ground.
3. Steel support shall be hot dipped galvanized. It is set in concrete which shall completely cover the
buried steel.
4. After installation of equipment; adjust their alignment and level.
Cathodic Cable Installation
1. 1 Check the actual cable length. Cables shall be cut from the drums to which they
allocated in accordance with the cable schedule and drum allocation sheet.
2. In cable drum haulage, cables shall be rotated in the direction of the arrow.
3. Cable laying shall be performed by individual cable being placed in orderly arrangement and/or
bundle.
�4. Both ends of each cable shall be firmly sealed with insulating tape and/or other sealing materials
to prevent dust & moisture.
5. Sufficient length shall be provided for both ends of each cable in the measurement of cable
lengths.
6. Sand filling, protection cover, and backfilling work shall be conducted as early and promptly as
possible.
7. Cathodic protection cables shall be properly identified before backfilling for later connection to
the test points. Connection method must be referred to vendor drawings.
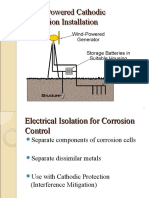
MMO Ribbon Anode & Reference Electrode Installation
1. Check above ground tank foundation level. Refer to Typical Installation Detail for Tank.
2. Perform welding machine adjustment and test. Anode to Anode conductor bar to conductor bar
anode to conductor bar. Ribbon to conductor, about 1 to 3 sec but to be changed depending on
fixed condition. Power feeder continuity check. Electrical resistance between both ends of power
feeder before installation.
3. Cut ribbon anode from reel to specified length that is shown on the relevant drawings.
4. Cut specified length of conductor bar. Required length is shown on the relevant drawings.
5. Laying of conductor bar. Verify material, spacing interval, overlap and installation. Spacing
intervals vary depending on each tank to be protected.
6. Laying anode ribbon on conductor bar.
7. Spot welding at all cross points of anode and conductor bar. Verify spot welding, one spot weld
at cross point between anode and conductor.
8. Install power feeder on Titanium conductor bar. Verify materials, installation and connection as
per Vendor Drawings.
9. Connect power feeder cables outside of tank through 2”dia. PVC conduit. Secure wiring without
tension and cable end with tag.
10. Power feeder continuity check before and after backfilling. Resistance between two power feeder
shall have a value of 5 ohms or less.
11. The reference electrode are to be installed at the location specified on the approved construction
drawing.
12. Soak pre-packed reference electrode into potable fresh water for 12 hours just
before installation. Verify material.
13. Install reference electrode lead cable and power feeder. Verify material, size, location and level.
14. Installed pre-packed reference electrode. Verify installation and soil covering around reference
electrode.
� 15. Connect reference electrode lead cable outside of tank through 2” dia. PVC conduit. Check wiring
without tension and cable end with tag.
16. Potential difference after installation shall be checked. Verify material specification and potential
difference using portable reference electrode.
17. Cable end treatment during civil work until wiring to junction box or test box.
Inspection of Cathodic Protection Installation
1. During working period, inspection shall be carried out on insulation testing by suitable instrument
on insulating joints before and after welding or fitting.
2. Soil and sand resistivity measurements of anodes and ground bed location.
3. Visual inspection of cathodic protection anodes and cables.
4. Visual inspection of transformer-rectifiers, test boxes and stations prior to installation.
5. Potential readings of permanent reference electrodes with respect to a calibrated one in the
same electrolyte conditions prior to laying.
6. All cathodic protection removable links inside the accessible equipment shall be left open and no
impressed current stations shall be energized without COMPANY’s approval.
7. Checking of all accessible cathodic protection equipment; their wiring, correct polarity (+/-),
terminations and cable tagging.
Testing and Records
1. All monitoring and measuring devices used shall be calibrated and have valid calibration
certificate during the time of inspection as per Control of Monitoring and Measuring Equipment
Procedure.
2. Quality records shall be prepared as per Inspection and Test Plan (ITP), inspect and signed by
authorized Electrical Inspector for the completion of Mechanical Completion prior
for Commissioning Phase.
3. All testing & inspection forms shall be developed as pre-requisite to ITP.
SOME DEFINITIONS
Aboveground storage tank: A stationary container, of greater than 500-barrel capacity usually
cylindrical in shapes, consisting of metallic roof, shell, bottom, and support structure where more
than 90 percent of the tank volume is above surface grade.
Anode: Refer to MMO ribbon anode. The electrode of an electrochemical cell at which
oxidation or corrosion occurs.
Backfill: Material placed in a hole to fill the space around the anode, vent pipe and buried
components of a cathodic protection system.
� Cathode: Refer to structure / pipe. The electrode of an electrochemical cell at which a
reduction reaction occurs.
Cathodic protection: A technique to reduce corrosion of a metal surface by making the entire
surface the cathode of ban electrochemical cell.
Electrochemical cell: An electrochemical system consisting of an anode and a cathode
immersed in an electrolyte so as to create an electrical circuit. The anode and cathode may be
separate metals or dissimilar areas on the same metal. The cell includes the external circuit which
permits the flow of electrons from the anode toward the cathode.
Electrode potential: The potential of an electrode as measured against a reference electrode.
Electrolyte: A chemical substance containing ions that migrate in an electric field. Electrolyte
refers to the soil or liquid adjacent to and in contact with the bottom of an aboveground storage
tank, including the moisture and other chemicals contained therein.
Impressed current: An electric current supplied by a device employing a power source that is
external to the electrode system.
Membrane: A thin, continuous sheet of nonconductive synthetic material used to contain
and/or separate two different environments.
Rectifier: A device for converting alternating current to direct current. Usually includes a step-
down AC transformer, a silicon or selenium stack (rectifying elements), meters, and other
accessories when used for cathodic protection purposes.
Reference electrode: An electrode whose open circuit potential is constant under similar
conditions of measurement.
Structure-to-electrolyte voltage: (also structure-to-soil potential or pipe-to-soil potential): The
voltage difference between a metallic structure and the electrolyte which is measured with a
reference electrode in contact with the electrolyte.
Test station:
A small enclosed box –like housing and the usual termination point of one or more test leads.
�cathodic protection, impressed current cathodic protection, sacrificial anode, cathodic protection system,
cathodic protection testing, cathodic, pipeline cathodic protection, cathodic protection rectifier, cathodic
protection companies, sacrificial anode cathodic protection, cathodic protection test station, pipeline
cathodic protection explained, cathodic protection for underground piping, anodic protectionism system,
cathodic protection anodes, impressed current, sacrificial anodic protection, galvanic anode, galvanic
protection, cathodic protection pdf, what is cathodic protection, cp design, cathodic protection ppt, cp
system, corrosion protection ,pipeline corrosion, sacrificial protection, how does cathodic protection
work, cathodic definition, cathodic disbandment, cathodic protection definition, cp test, cathodic
meaning