14-Sep-19
Lecture No.02
Data Structures and Algorithms
Implementing Lists
We have designed the interface for the List; we
now must consider how to implement that
interface.
1
� 14-Sep-19
Implementing Lists
We have designed the interface for the List; we
now must consider how to implement that
interface.
Implementing Lists using an array: for example,
the list of integers (2, 6, 8, 7, 1) could be
represented as:
current size
A 2 6 8 7 1
3 5
1 2 3 4 5
List Implementation
add(9); current position is 3. The new list would thus
be: (2, 6, 8, 9, 7, 1)
We will need to shift everything to the right of 8 one
place to the right to make place for the new element ‘9’.
current size
step 1: A 2 6 8 7 1
3 5
1 2 3 4 5 6
current size
step 2: A 2 6 8 9 7 1
4 6
1 2 3 4 5 6
notice: current points
to new element
2
� 14-Sep-19
Implementing Lists
next():
current size
A 2 6 8 9 7 1
4 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 5
Implementing Lists
There are special cases for positioning the
current pointer:
a. past the last array cell
b. before the first cell
3
� 14-Sep-19
Implementing Lists
There are special cases for positioning the
current pointer:
a. past the last array cell
b. before the first cell
We will have to worry about these when we
write the actual code.
Implementing Lists
remove(): removes the element at the current
index
Step 1: current size
A 2 6 8 9 1
5 6
1 2 3 4 5 6
5
current size
Step 2: A 2 6 8 9 1
5 5
1 2 3 4 5
4
� 14-Sep-19
Implementing Lists
remove(): removes the element at the current
index
Step 1: current size
A 2 6 8 9 1
5 6
1 2 3 4 5 6
5
current size
Step 2: A 2 6 8 9 1
5 5
1 2 3 4 5
We fill the blank spot left by the removal of 7 by
shifting the values to the right of position 5 over
to the left one space.
Implementing Lists
find(X): traverse the array until X is located.
int find(int X)
{
int j;
for(j=1; j < size+1; j++ )
if( A[j] == X ) break;
if( j < size+1 ) { // found X
current = j; // current points to where X found
return 1; // 1 for true
}
return 0; // 0 (false) indicates not found
}
5
� 14-Sep-19
Implementing Lists
Other operations:
get() return A[current];
update(X) A[current] = X;
length() return size;
back() current--;
start() current = 1;
end() current = size;
Analysis of Array Lists
add
we have to move every element to the right of
current to make space for the new element.
Worst-case is when we insert at the beginning; we
have to move every element right one place.
Average-case: on average we may have to move
half of the elements
6
� 14-Sep-19
Analysis of Array Lists
remove
Worst-case: remove at the beginning, must shift all
remaining elements to the left.
Average-case: expect to move half of the elements.
find
Worst-case: may have to search the entire array
Average-case: search at most half the array.
Other operations are one-step.
List Using Linked Memory
Various cells of memory are not allocated
consecutively in memory.
7
� 14-Sep-19
List Using Linked Memory
Various cells of memory are not allocated
consecutively in memory.
Not enough to store the elements of the list.
List Using Linked Memory
Various cells of memory are not allocated
consecutively in memory.
Not enough to store the elements of the list.
With arrays, the second element was right next
to the first element.
8
� 14-Sep-19
List Using Linked Memory
Various cells of memory are not allocated
consecutively in memory.
Not enough to store the elements of the list.
With arrays, the second element was right next
to the first element.
Now the first element must explicitly tell us
where to look for the second element.
List Using Linked Memory
Various cells of memory are not allocated
consecutively in memory.
Not enough to store the elements of the list.
With arrays, the second element was right next
to the first element.
Now the first element must explicitly tell us
where to look for the second element.
Do this by holding the memory address of the
second element
9
� 14-Sep-19
Linked List
Create a structure called a Node.
object next
The object field will hold the actual list element.
The next field in the structure will hold the
starting location of the next node.
Chain the nodes together to form a linked list.
Linked List
Picture of our list (2, 6, 7, 8, 1) stored as a
linked list:
head
2 6 8 7 1 size=5
current
10
� 14-Sep-19
Linked List
Note some features of the list:
Need a head to point to the first node of the list.
Otherwise we won’t know where the start of the
list is.
Linked List
Note some features of the list:
Need a head to point to the first node of the list.
Otherwise we won’t know where the start of the
list is.
The current here is a pointer, not an index.
11
� 14-Sep-19
Linked List
Note some features of the list:
Need a head to point to the first node of the list.
Otherwise we won’t know where the start of the
list is.
The current here is a pointer, not an index.
The next field in the last node points to nothing.
We will place the memory address NULL which
is guaranteed to be inaccessible.
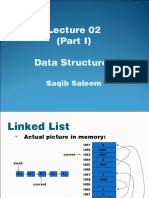
Linked List
Actual picture in memory:
1051 6
1052 1063
current 1053 1063
1054 2
head 1055 1051
1056
2 6 8 7 1 1057 7
1058 1060
current 1059
1060 1
1061 0
head 1062 1054
1063 8
1064 1057
1065
12
� 14-Sep-19
Linked List Operations
add(9): Create a new node in memory to hold ‘9’
Node* newNode = new Node(9);
newNod 9
e
Linked List Operations
add(9): Create a new node in memory to hold ‘9’
Node* newNode = new Node(9);
newNod 9
e
Link the new node into the list
head
2 6 8 7 1 size=5 6
current 2 1
3
9
newNod
e
13
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
The Node class
class Node {
public:
int get() { return object; };
void set(int object) { this->object = object; };
Node *getNext() { return nextNode; };
void setNext(Node *nextNode)
{ this->nextNode = nextNode; };
private:
int object;
Node *nextNode;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
The Node class
class Node {
public:
int get() { return object; };
void set(int object) { this->object = object; };
Node *getNext() { return nextNode; };
void setNext(Node *nextNode)
{ this->nextNode = nextNode; };
private:
int object;
Node *nextNode;
};
14
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
The Node class
class Node {
public:
int get() { return object; };
void set(int object) { this->object = object; };
Node *getNext() { return nextNode; };
void setNext(Node *nextNode)
{ this->nextNode = nextNode; };
private:
int object;
Node *nextNode;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
The Node class
class Node {
public:
int get() { return object; };
void set(int object) { this->object = object; };
Node *getNext() { return nextNode; };
void setNext(Node *nextNode)
{ this->nextNode = nextNode; };
private:
int object;
Node *nextNode;
};
15
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
The Node class
class Node {
public:
int get() { return object; };
void set(int object) { this->object = object; };
Node *getNext() { return nextNode; };
void setNext(Node *nextNode)
{ this->nextNode = nextNode; };
private:
int object;
Node *nextNode;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
The Node class
class Node {
public:
int get() { return object; };
void set(int object) { this->object = object; };
Node *getNext() { return nextNode; };
void setNext(Node *nextNode)
{ this->nextNode = nextNode; };
private:
int object;
Node *nextNode;
};
16
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
The Node class
class Node {
public:
int get() { return object; };
void set(int object) { this->object = object; };
Node *getNext() { return nextNode; };
void setNext(Node *nextNode)
{ this->nextNode = nextNode; };
private:
int object;
Node *nextNode;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
The Node class
class Node {
public:
int get() { return object; };
void set(int object) { this->object = object; };
Node *getNext() { return nextNode; };
void setNext(Node *nextNode)
{ this->nextNode = nextNode; };
private:
int object;
Node *nextNode;
};
17
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
The Node class
class Node {
public:
int get() { return object; };
void set(int object) { this->object = object; };
Node *getNext() { return nextNode; };
void setNext(Node *nextNode)
{ this->nextNode = nextNode; };
private:
int object;
Node *nextNode;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
The Node class
class Node {
public:
int get() { return object; };
void set(int object) { this->object = object; };
Node *getNext() { return nextNode; };
void setNext(Node *nextNode)
{ this->nextNode = nextNode; };
private:
int object;
Node *nextNode;
};
18
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Node.cpp"
class List {
public:
// Constructor
List() {
headNode = new Node();
headNode->setNext(NULL);
currentNode = NULL;
size = 0;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Node.cpp"
class List {
public:
// Constructor
List() {
headNode = new Node();
headNode->setNext(NULL);
currentNode = NULL;
size = 0;
};
19
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Node.cpp"
class List {
public:
// Constructor
List() {
headNode = new Node();
headNode->setNext(NULL);
currentNode = NULL;
size = 0;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Node.cpp"
class List {
public:
// Constructor
List() {
headNode = new Node();
headNode->setNext(NULL);
currentNode = NULL;
size = 0;
};
20
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Node.cpp"
class List {
public:
// Constructor
List() {
headNode = new Node();
headNode->setNext(NULL);
currentNode = NULL;
size = 0;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Node.cpp"
class List {
public:
// Constructor
List() {
headNode = new Node();
headNode->setNext(NULL);
currentNode = NULL;
size = 0;
};
21
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Node.cpp"
class List {
public:
// Constructor
List() {
headNode = new Node();
headNode->setNext(NULL);
currentNode = NULL;
size = 0;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Node.cpp"
class List {
public:
// Constructor
List() {
headNode = new Node();
headNode->setNext(NULL);
currentNode = NULL;
size = 0;
};
22
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Node.cpp"
class List {
public:
// Constructor
List() {
headNode = new Node();
headNode->setNext(NULL);
currentNode = NULL;
size = 0;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Node.cpp"
class List {
public:
// Constructor
List() {
headNode = new Node();
headNode->setNext(NULL);
currentNode = NULL;
size = 0;
};
23
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
24
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
25
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
26
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
27
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
28
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
29
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
30
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
C++ Code for Linked List
void add(int addObject) {
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->set(addObject);
if( currentNode != NULL ){
newNode->setNext(currentNode->getNext());
currentNode->setNext( newNode );
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->setNext(NULL);
headNode->setNext(newNode);
lastCurrentNode = headNode;
currentNode = newNode;
}
size++;
};
31
� 14-Sep-19
Building a Linked List
List list; headNode size=0
Building a Linked List
List list; headNode size=0
currentNode
list.add(2); headNode 2 size=1
lastcurrentNode
32
� 14-Sep-19
Building a Linked List
List list; headNode size=0
currentNode
list.add(2); headNode 2 size=1
lastcurrentNode
currentNode
list.add(6); headNode 2 6 size=2
lastcurrentNode
Building a Linked List
List.add(8); list.add(7); list.add(1);
currentNode
headNode 2 6 8 7 1 size=5
lastcurrentNode
33
� 14-Sep-19
C++ Code for Linked List
int get() {
if (currentNode != NULL)
return currentNode->get();
};
C++ Code for Linked List
bool next() {
if (currentNode == NULL) return false;
lastCurrentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode->getNext();
if (currentNode == NULL || size == 0)
return false;
else
return true;
};
34