100% found this document useful (1 vote)
385 views19 pagesC Programming Quirks
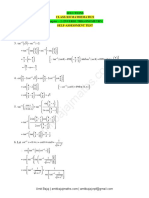
The document contains code snippets and output related to C programming concepts like operators, data types, control flow, functions etc. Some key things demonstrated include:
1. Pointer dereferencing and address manipulation.
2. Pre and post increment operators.
3. Bitwise operators.
4. String concatenation and printing.
5. Structures and bit fields.
6. Control flow using loops and conditional statements.
Uploaded by
Deepan KishoreCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
385 views19 pagesC Programming Quirks
The document contains code snippets and output related to C programming concepts like operators, data types, control flow, functions etc. Some key things demonstrated include:
1. Pointer dereferencing and address manipulation.
2. Pre and post increment operators.
3. Bitwise operators.
4. String concatenation and printing.
5. Structures and bit fields.
6. Control flow using loops and conditional statements.
Uploaded by
Deepan KishoreCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 19