0% found this document useful (0 votes)
93 views6 pagesPivot Mapping in Informatica
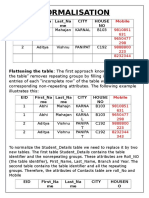
This document discusses several scenarios for pivoting records in Informatica mappings. It describes using an aggregator transformation to transpose rows into columns, aggregating multiple rows of attribute data for an entity into columns in a single row. It also provides examples of pivoting records to group employees by department, with the output combining employee names into pipe-delimited strings for each department. Another scenario shows pivoting column data into multiple rows using a normalizer transformation.
Uploaded by
Raghu NathCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
93 views6 pagesPivot Mapping in Informatica
This document discusses several scenarios for pivoting records in Informatica mappings. It describes using an aggregator transformation to transpose rows into columns, aggregating multiple rows of attribute data for an entity into columns in a single row. It also provides examples of pivoting records to group employees by department, with the output combining employee names into pipe-delimited strings for each department. Another scenario shows pivoting column data into multiple rows using a normalizer transformation.
Uploaded by
Raghu NathCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6