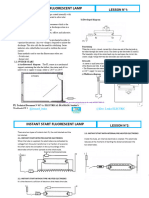
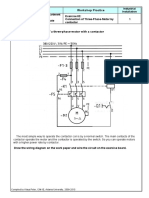
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
740 views17 pagesEarthing: Safety and Protection Guide
Here are the steps to solve this problem:
1) Calculate the rating current of the motor:
Ir = Power / Voltage
= 20 kW / 240 V
= 83.33 A
2) The fuse factor is given as 100 A / 83.33 A = 1.2
3) From regulation D22, the maximum fault current for a fuse with factor ≤ 1.5 is:
2.4 x Rating current
= 2.4 x 83.33 A
= 200 A
4) The given fault current is 200 A. Since this is less than or equal to the maximum allowed by D22, the fuse will rupture.
5) Heat produced at metal box = I
Uploaded by
Aidi RedzaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
740 views17 pagesEarthing: Safety and Protection Guide
Here are the steps to solve this problem:
1) Calculate the rating current of the motor:
Ir = Power / Voltage
= 20 kW / 240 V
= 83.33 A
2) The fuse factor is given as 100 A / 83.33 A = 1.2
3) From regulation D22, the maximum fault current for a fuse with factor ≤ 1.5 is:
2.4 x Rating current
= 2.4 x 83.33 A
= 200 A
4) The given fault current is 200 A. Since this is less than or equal to the maximum allowed by D22, the fuse will rupture.
5) Heat produced at metal box = I
Uploaded by
Aidi RedzaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 17