0% found this document useful (0 votes)
146 views4 pagesSteps Ofvvector Estimating Error Correction Model
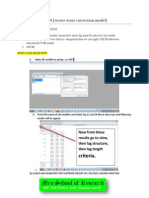
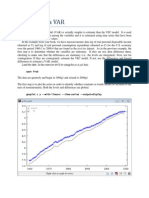
This document outlines the steps for vector error correction model estimation including: 1) specifying the model and preparing data for time series analysis, 2) testing for stationarity and determining the optimal lag length, 3) performing cointegration tests to determine whether to use a VAR or VECM model, and 4) diagnostic testing and corrections for issues like autocorrelation, heteroskedasticity, and model specification.
Uploaded by
Namdev UpadhyayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
146 views4 pagesSteps Ofvvector Estimating Error Correction Model
This document outlines the steps for vector error correction model estimation including: 1) specifying the model and preparing data for time series analysis, 2) testing for stationarity and determining the optimal lag length, 3) performing cointegration tests to determine whether to use a VAR or VECM model, and 4) diagnostic testing and corrections for issues like autocorrelation, heteroskedasticity, and model specification.
Uploaded by
Namdev UpadhyayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4