0% found this document useful (0 votes)
173 views16 pagesIoT Lecture Unit II RFID
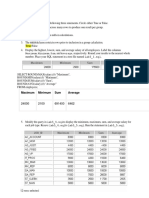
The document discusses Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology. It describes RFID as using radio waves to transfer data between a reader and a tagged item to identify and track it. The key components of an RFID system are the transceiver (reader), transponder (tag), and antenna. RFID tags can be attached to items and assets. They contain a microchip and antenna that broadcasts a unique identifier. RFID readers can remotely power tags and communicate with backend servers to inventory tags.
Uploaded by
Rajeshree JadhavCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
173 views16 pagesIoT Lecture Unit II RFID
The document discusses Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology. It describes RFID as using radio waves to transfer data between a reader and a tagged item to identify and track it. The key components of an RFID system are the transceiver (reader), transponder (tag), and antenna. RFID tags can be attached to items and assets. They contain a microchip and antenna that broadcasts a unique identifier. RFID readers can remotely power tags and communicate with backend servers to inventory tags.
Uploaded by
Rajeshree JadhavCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16