Họ tên: Nguyễn Đức Hoàng
Lớp: EBDB1
Mã sv: 11192077
Group assignment presentation 7.2
Exercise 1: The following data is for a firm which operates in a perfectly competitive
market:
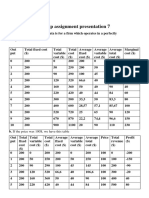
a. Complete the table.
Output Total Total Total Average Average Average Marginal
fixed variable cost fixed variable total cost ($)
cost($) cost ($) ($) cost ($) cost ($) cost ($)
0 200 0 200 - - - -
1 200 50 250 200 50 250 50
2 200 90 290 100 45 145 40
3 200 120 320 66.67 40 106.76 30
4 200 160 360 50 40 90 40
5 200 220 420 40 44 84 60
6 200 300 500 33.33 50 83.33 80
7 200 400 600 28.57 57.14 85.71 100
8 200 520 720 25 65 90 120
9 200 670 870 22.22 74.44 96.66 150
10 200 900 1100 20 90 110 230
b. If the price was 100$, what output would the firm produce and what type of profit (or
loss) would the firm make?
If the price was 100$ the firm would produce 7 units of output because that's
where the price equals MC is and the firm would make a profit maximizing firm in a
perfectly ompetitive market because:
� + For a firm in a perfectly competitive market P=MR=AR (true in perfectly
competitive market)
+ Condition for profit maximization is MR=MC (true in any type of market)
For a profit maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market when it choose
the output where price is equal to marginal cost P=MC.
c. Does the profitable situation in the question b exist in the long – run? Why?
The profitable in the question b won’t exist in the long-run becauese in the long-
run because the entry of new firms in the industry, the price of the product will go down
as a result of the increase in supply of output and also the cost will go up as a result of
more competition for factors of production. The firms will continue entering the industry
until the price is equal to average cost
Exercise 2: A perfect competition firm has selling price of P=21 $ and the relationship
between its output and total cost as below:
1. What are TR, MC, FC, VC, AVC, AFC, ATC ?
Output Total Total Total Average Average Average Marginal Output
fixed cost variable cost fixed variable total cost ($)
($) cost ($) ($) cost ($) cost ($) cost ($)
0 50 0 50 0 - - -
1 50 5 55 21 50 5 55 5
2 50 12 62 42 25 6 31 7
3 50 25 75 63 16,67 8,33 25 13
4 50 46 96 84 12,5 11,5 24 21
5 50 75 125 105 10 15 25 29
6 50 112 162 126 8,33 18,67 27 37
7 50 153 203 147 7,14 21,86 29 41
8 50 198 248 168 6,25 24,75 31 45
�2. Identify optimal output level (Q *) that gives the firm profit maximization? What is the
maximum profit ?
_ Q* = 4 that gives the firm profit maximization because:
+ For a firm in a perfectly competitive market P=MR=AR ( true in perfectly
competitive market)
+ Condition for profit maximization is MR=MC (true in any type of market)
For a profit maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market when it choose
the output where price is equal to marginal cost P=MC
_ Maximum profit = TR – TC = 84 – 96 = - 12
3. With the above profit (in the question 2), should the firm continue the production?
Why?
The firm should stop producing. Because MR would be less than MC, that is, the firm
would loss profit by producing additional units
This is the profit maximizing output level.
Exercise 3: A perfect competition firm has a demand equaltion of P=8 ($) and total cost
equation of TC= Q2 + 2Q + 4 ($)
1. Identify TR and MR equation?
TR = PQ = 8Q
MR = TR’ = 8
2. Identify MC, VC, AVC, AFC, ATC equation?
MC = TC’(Q) = 2Q + 2
� VC=Q 2 +2 Q
We have: TC = Q2 + 2Q + 4 = VC + FC { FC =4
TC 4
ATC = =Q + 2 +
Q Q
FC 4
AFC = =
Q Q
VC
AVC = = Q + 2
Q
3. What is optimal output level (Q*) that gives the firm profit maximization? What is the
maximum profit ?
We have: π = TR - TC = - Q2 + 6Q - 4 ( Q > 0 )
π' =-2Q + 6 π' =0 Q = 3
Q 0 3 +∞
π' + 0 -
π 5
-4 -∞
πmax =5 ($) Q = 3
4. What is break even price and break even quantity?
The firm meets break even price if P = MC 8 = 2Q + 2 Q = 3
FC 4 4
Break even quantity = =
P - AVC 8 - Q - 2
= 3
5. If market price decrease to P= 4$, should the firm continue the production? Why
When maximum profit MC = 2 x 3 + 2 = 8
If P = MR = 4 < MC = 8 The firm should lower it’s production because they are
producing too much.