0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views15 pagesChapter 7
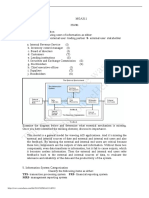
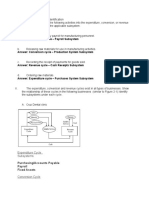
This document contains a chapter about the conversion cycle from a textbook. It includes 29 multiple choice questions about topics like world-class manufacturing, the production system, inventory control, just-in-time manufacturing, and internal controls. The questions cover terms and concepts related to the conversion cycle, production planning, cost accounting, and quality management.
Uploaded by
YnaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views15 pagesChapter 7
This document contains a chapter about the conversion cycle from a textbook. It includes 29 multiple choice questions about topics like world-class manufacturing, the production system, inventory control, just-in-time manufacturing, and internal controls. The questions cover terms and concepts related to the conversion cycle, production planning, cost accounting, and quality management.
Uploaded by
YnaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 15