0% found this document useful (0 votes)
345 views4 pagesModule 6: Performance Management and Rewards Learning Outcomes
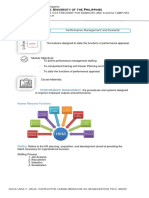
This document provides an overview of performance management and rewards. It defines performance management as procedures to improve outputs through incentive systems. It also describes the key aspects of performance management such as staffing, training, career development, performance appraisal, and rewards. Performance appraisal involves establishing standards, measuring actual performance, and providing feedback to help employees improve. There are various methods of appraisal and potential errors to avoid. Rewards can be intrinsic, extrinsic, financial, non-financial, or membership-based.
Uploaded by
Ella MontefalcoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
345 views4 pagesModule 6: Performance Management and Rewards Learning Outcomes
This document provides an overview of performance management and rewards. It defines performance management as procedures to improve outputs through incentive systems. It also describes the key aspects of performance management such as staffing, training, career development, performance appraisal, and rewards. Performance appraisal involves establishing standards, measuring actual performance, and providing feedback to help employees improve. There are various methods of appraisal and potential errors to avoid. Rewards can be intrinsic, extrinsic, financial, non-financial, or membership-based.
Uploaded by
Ella MontefalcoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4